“`html
Diagnosing the “Requested URL Could Not Be Retrieved” Error
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Encountering the “requested URL could not be retrieved error” is a common and frustrating experience for many internet users.
- This error can manifest in various forms, such as “windows 10 requested url unavailable.”
- Understanding the underlying causes, which range from browser issues to network disruptions, is the first step to resolving it.
- Comprehensive troubleshooting involves checking browser settings, network configurations, and system-level network components.
- In some cases, the issue might be server-side, requiring patience or direct communication with the website administrator.
Table of contents
- Diagnosing the “Requested URL Could Not Be Retrieved” Error
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding the “Requested URL Could Not Be Retrieved” Error
- Troubleshooting Steps: Browser-Related Solutions
- Troubleshooting Steps: Network-Related Solutions
- Troubleshooting Steps: System-Related Solutions (Windows Focus)
- When the Issue Might Be Server-Side
- Concluding Thoughts and Next Steps
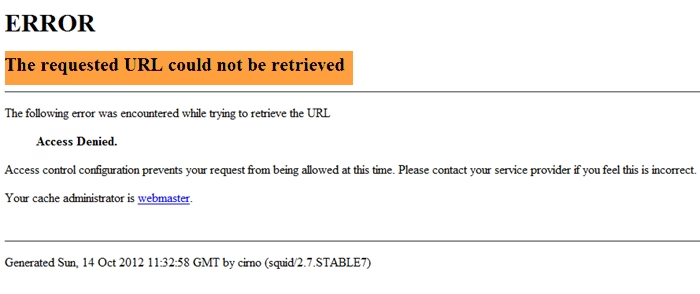
It’s a moment of digital dread: you click a link, type in a URL, and instead of the content you expect, you’re met with a stark message: “The requested URL could not be retrieved.” This common internet hiccup can be incredibly frustrating, leaving you wondering what went wrong and how to get back online. Many users encounter the “requested URL could not be retrieved” message while trying to load websites, often leading to confusion and frustration. This guide explains why the issue occurs and how to systematically troubleshoot and resolve it, focusing on solutions relevant for various operating systems and browsers, with a particular emphasis on the “windows 10 requested url unavailable” scenario. We’ll walk you through a series of actionable steps to help you fix this persistent error and regain access to the web.
Understanding the “Requested URL Could Not Be Retrieved” Error
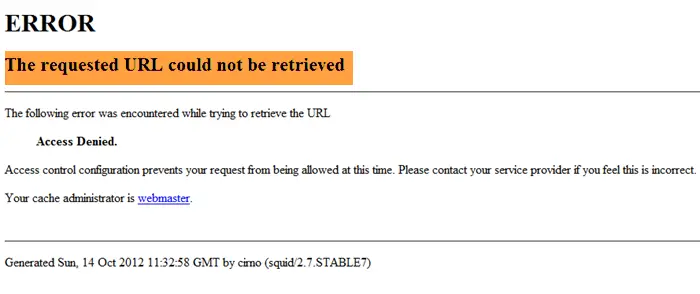
At its core, the “requested URL could not be retrieved” error means that your web browser attempted to fetch a specific web page (the URL you requested) from a server, but the connection failed or was interrupted before the page could be delivered. Think of it like trying to order a book from a library, but the librarian couldn’t find it, or the delivery truck broke down. Your request reached the system, but the item you asked for never arrived.
This error is a general indicator of a communication breakdown between your device and the web server. The underlying causes are diverse and can stem from several different points in the data’s journey:
- Browser Configuration Issues or Outdated Cache: Your browser stores temporary data (cache) and information about your browsing habits (cookies) to speed up loading times and personalize your experience. However, this data can become corrupted or outdated, leading to connection problems.
- Network Disruptions or DNS Problems: Your internet connection might be unstable, or there could be an issue with the Domain Name System (DNS) server, which acts like a phonebook for the internet, translating website names into IP addresses.
- Proxy Settings Misconfiguration: If you’re using a proxy server to access the internet, incorrect settings can block your requests from reaching their destination.
- Antivirus/Firewall or VPN Interference: Sometimes, your security software or a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can be overly aggressive and mistakenly block access to legitimate websites.
- Temporary Issues or Restrictions on the Web Server Itself: The website you are trying to access might be temporarily down for maintenance, experiencing a high volume of traffic, or have specific access restrictions in place.

This error often overlaps with “website access denied error solution” scenarios, where the web server or an intermediary proxy actively blocks access. It’s a signal that something is preventing your request from being successfully processed and fulfilled.
Troubleshooting Steps: Browser-Related Solutions
Often, the simplest solutions are the most effective. Many instances of the “requested URL could not be retrieved error” can be resolved by addressing issues within your web browser itself.
Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
This is a critical first step because accumulated cache or corrupted cookies can prevent loading the latest version of a webpage or contain incorrect routing information, directly leading to the “requested URL could not be retrieved error.” Outdated cached data can cause your browser to try and access old, non-existent versions of files or pages.
Here’s how to clear your cache and cookies for popular browsers:
- Chrome: Navigate to Chrome’s Settings → Privacy and Security → Clear browsing data. Instruct users to select “All Time” for cache and cookies, and then click “Clear data.”
- Firefox: Navigate to Firefox’s Settings → Privacy & Security → Cookies and Site Data and click “Clear Data.” Make sure to select both “Cookies and Site Data” and “Cached Web Content.”
- Edge: Navigate to Edge’s Settings → Privacy, search, and services → Clear browsing data. Choose a time range (e.g., “All time”) and ensure “Cookies and other site data” and “Cached images and files” are selected before clicking “Clear now.”

Reinforce that clearing this data helps remove outdated or conflicting information that might be causing the retrieval error. This is a fundamental step in trying to “clear cache to fix url retrieval error.”
Test in Incognito/Private Browsing Mode
Incognito or Private Browsing mode is a powerful diagnostic tool. It bypasses your browser’s existing cache and stored data, and typically disables most extensions. This allows you to see if the problem is with your stored browser data or an interfering extension. Instruct users to try accessing the problematic URL in this mode. If the website loads successfully in Incognito mode, it strongly suggests that the issue lies with your regular browser session’s cache, cookies, or extensions.
Disable Browser Extensions
Browser extensions, especially VPNs, ad-blockers, or security add-ons, can sometimes interfere with web requests and cause the “requested URL could not be retrieved error.” Some extensions might inadvertently block certain content or connections. Provide a method for users to disable extensions one by one. After disabling an extension, they should retest the website access. By doing this systematically, they can pinpoint the exact extension causing the problem. Once identified, they can either disable that extension permanently, reconfigure its settings, or look for an alternative.
Troubleshooting Steps: Network-Related Solutions
If browser-specific solutions don’t resolve the issue, it’s time to look at your network connection. Network glitches can be surprisingly common culprits for URL retrieval errors.
Restart Your Router and Modem

A simple “network glitch url not retrieved” can often be resolved by a full restart of your network equipment. This process refreshes your connection to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and can clear temporary issues like IP address conflicts or routing problems that might be preventing access. Provide clear instructions: unplug both your router and modem from their power sources. Wait for at least 30 seconds to allow them to fully discharge. Then, plug them back in, ensuring the modem is powered on and fully connected before plugging in the router. This is a foundational troubleshooting step that can fix many intermittent connectivity issues.
Verify Internet Connection
Before diving deeper, confirm that your general internet connection is stable. Advise users to test their overall internet connectivity by attempting to visit multiple other websites. They can also run an internet speed test using a reputable service. If only one specific site is inaccessible, the problem is likely not with their general internet connection but potentially with the website itself or a specific network path to that site. If multiple sites are also inaccessible, the problem is more likely with your modem, router, or ISP.
Flush DNS Cache
The Domain Name System (DNS) is essential for navigating the internet. It translates human-readable domain names (like google.com) into machine-readable IP addresses (like 172.217.160.142). Your computer and router cache this information to speed up future requests. However, a corrupted or outdated DNS cache can lead to incorrect routing and contribute to the “requested URL could not be retrieved error.”
For Windows users, flushing the DNS cache is straightforward:
- Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. You can do this by searching for “cmd” in the Windows search bar, right-clicking on “Command Prompt,” and selecting “Run as administrator.”
- Type the following command and press Enter:
ipconfig /flushdns - You should see a confirmation message stating that the DNS Resolver Cache was successfully flushed.

On macOS, you can open the Terminal and use commands like sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder. For Linux, the command varies depending on the distribution, but often involves restarting a service like systemd-resolved.
Troubleshooting Steps: System-Related Solutions (Windows Focus)
In certain cases, especially when dealing with a “windows 10 requested url unavailable” issue, system-level settings might be the culprit. These steps are particularly relevant for Windows users but may have parallels on other operating systems.
Check and Adjust Proxy Settings
Incorrect proxy settings are a common culprit, particularly in scenarios like “windows 10 requested url unavailable.” These can often be misconfigured unintentionally, especially after installing VPN software or connecting to different networks. It’s crucial to ensure your proxy settings are correct for your network environment.
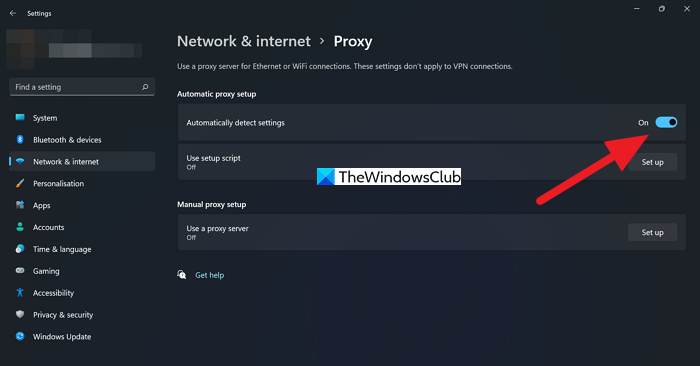
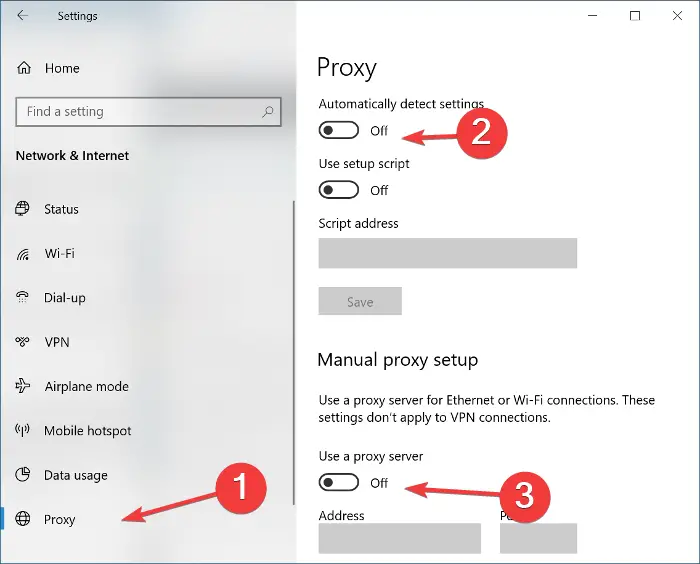
Here’s how to check and disable proxy settings in Windows:
- Navigate to Windows Settings → Network & Internet → Proxy.
- Under “Manual proxy setup,” ensure that “Use a proxy server” is toggled OFF.
- Also, under “Automatic proxy setup,” make sure “Automatically detect settings” is toggled ON, or if you have specific proxy configurations required by your network, ensure they are correctly entered.
- Additionally, it’s wise to check your browser’s specific network or connection settings. For instance, in Chrome, you can access this by going to Settings → System → Open your computer’s proxy settings. Ensure that “No proxy” is selected or that the settings align with your system’s network environment. Incorrect proxy settings can lead to the “requested URL could not be retrieved error,” as the browser attempts to route its traffic through a server that is unavailable or misconfigured.
Perform a Network Reset
If the above steps haven’t worked, a network reset can be a more comprehensive solution for Windows users. This action reinstalls network adapters and resets network components to their default configuration. It can resolve persistent connectivity issues that might be causing the “requested URL could not be retrieved error.”
To perform a network reset:
- Go to Settings → Network & Internet → Status.
- Scroll down and click on Network reset.
- Click “Reset now” and confirm. Your PC will restart after this process. Note that you may need to re-enter Wi-Fi passwords and reconfigure any VPN software after the reset.

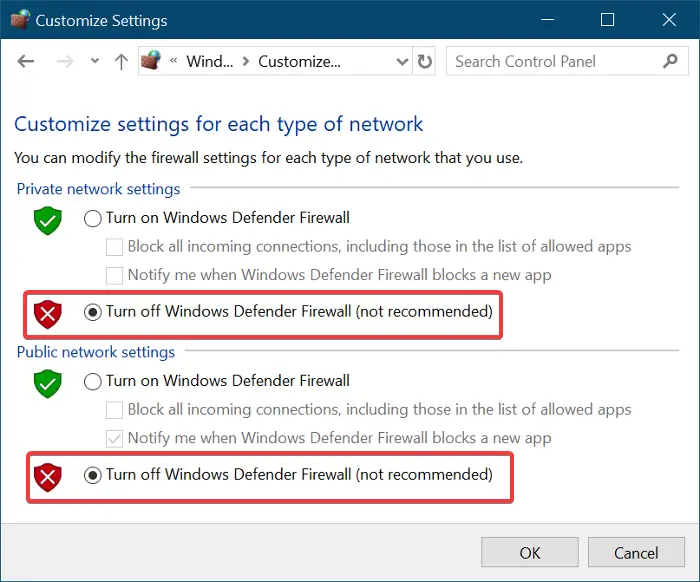
Temporarily Disable Antivirus/Firewall
Security software, while crucial for protection, can sometimes be overzealous. It might mistakenly flag legitimate website access as a threat, leading to the “requested URL could not be retrieved error.”
Crucial Caution: This step should be performed *only* for diagnostic purposes. It is vital to re-enable your antivirus and firewall protection immediately after testing to prevent security vulnerabilities. Leaving your system unprotected is a significant risk.

Instructions for temporarily disabling security software vary widely depending on the vendor. Users should consult the documentation for their specific antivirus or firewall program. After disabling, try accessing the problematic URL. If it works, you know your security software was the cause. You may then need to adjust its settings to allow access to that specific website or consider an alternative security solution.
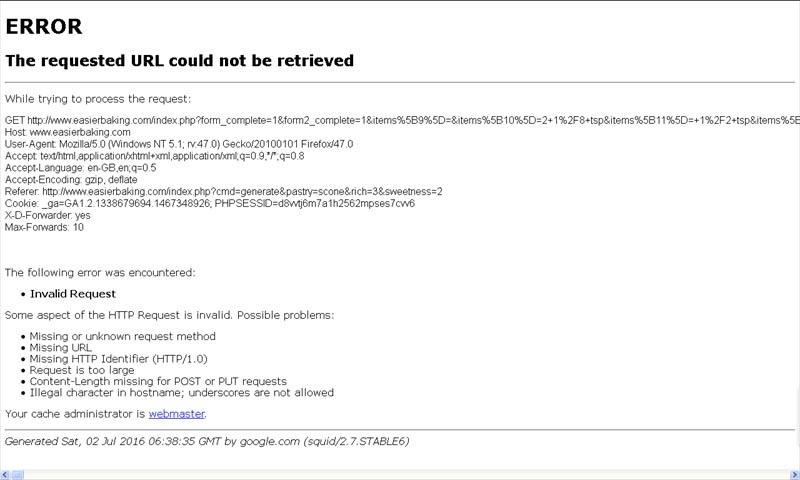
When the Issue Might Be Server-Side
If you’ve diligently followed all the troubleshooting steps above and are still encountering the “requested URL could not be retrieved error,” it’s possible that the problem doesn’t lie with your device or network, but with the website’s server itself. In this scenario, the “website access denied error solution” is typically out of your hands.
Potential server-side causes include:
- Server Outage: The website’s servers might be temporarily down due to hardware failure, maintenance, or an unexpected technical issue.
- Server Misconfiguration: The website’s server might have an incorrect configuration that is preventing requests from being processed.
- Network Filters: Your ISP or workplace network might have implemented filters that are blocking access to that specific website.
What can you do in this situation?
- Check if the Website is Down for Everyone: Use online tools like “Down For Everyone Or Just Me?” to see if other users are experiencing the same problem.
- Attempt Access from a Different Device or Network: Try loading the website on your smartphone using cellular data, or on a friend’s computer on a different internet connection. This helps isolate whether the issue is specific to your current network environment.
- Contact the Website Administrator: If the problem appears to be persistent and localized to the website, reach out to their support team or administrator. They may be aware of the issue and working on a fix, or they can provide specific guidance.
Concluding Thoughts and Next Steps

The “requested URL could not be retrieved error” can be a puzzling issue, but by taking a systematic approach, you can often resolve it. The most effective steps to fix the requested URL could not be retrieved error include clearing browser data, reviewing extension and proxy configurations, restarting network equipment, flushing DNS, and checking system security settings. Apply these steps systematically to pinpoint the cause. Network and browser issues are frequent sources of the problem, but persistent issues may require the intervention of the website administrator or your network provider. Remember that patience and methodical troubleshooting are key to overcoming this common web connectivity hurdle. If the problem persists after trying all these steps, it might be time to contact your ISP for further assistance or report the issue to the website owner.


“`