“`html
Cloudflare 500 Internal Server Error: Your Ultimate Troubleshooting Guide
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- A **Cloudflare 500 Internal Server Error** is a generic error indicating a problem on the origin server, not typically Cloudflare itself.
- Understanding Cloudflare’s role as a reverse proxy is crucial, as it relays the origin server’s error.
- Common causes include database connection issues, origin server overload, application/code errors, server misconfigurations, and external service failures.
- Troubleshooting involves checking Cloudflare status, examining origin server logs, verifying database connectivity, and reviewing recent changes.
- Temporarily pausing Cloudflare can help isolate whether the issue lies with Cloudflare or the origin server.
- Detailed logs from your origin server are your most valuable tool for diagnosing the root cause.
- Always ensure proper backups and use staging environments for testing changes.
Table of contents
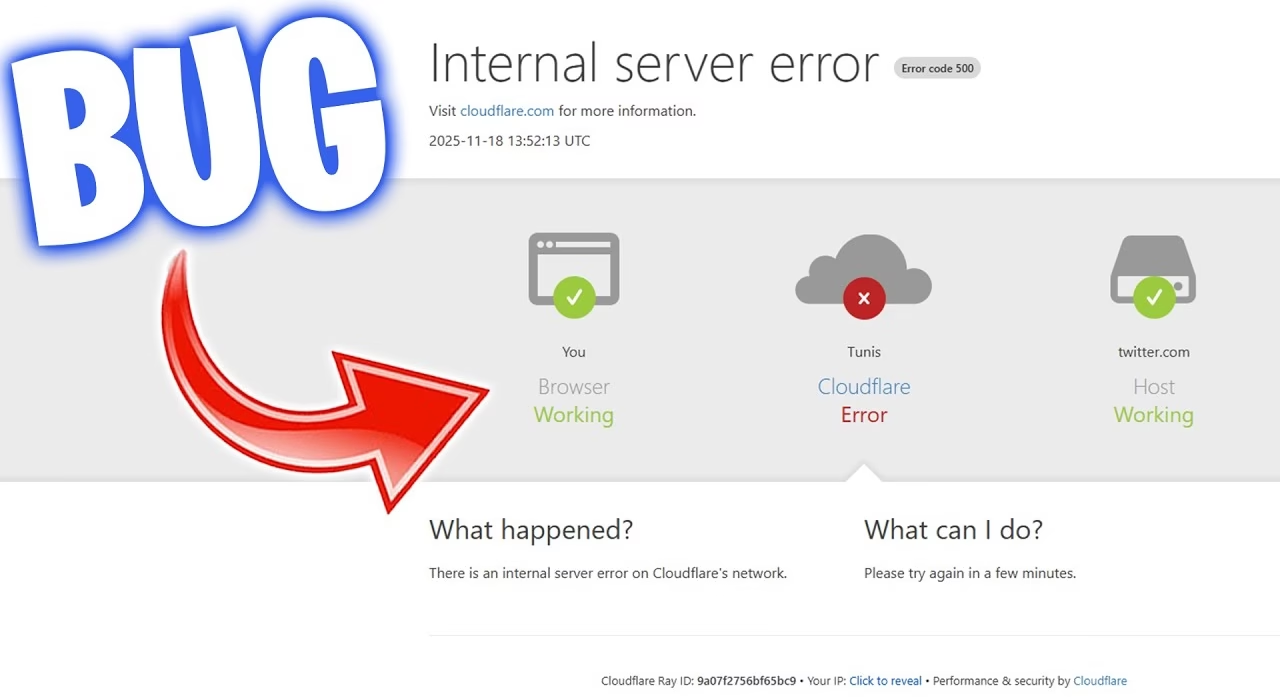
You’re in the middle of a crucial task, or perhaps just browsing your favorite site, when suddenly – BAM! A stark white page greets you with the ominous message: “500 Internal Server Error.” For users of Cloudflare, this can be particularly perplexing. Does it mean Cloudflare is down? Is there a problem with your website’s configuration?
This “something went wrong on the server, but the server cannot be more specific about the exact problem” message (Source: kinsta.com/blog/500-internal-server-error/) is a universal indicator of a server-side hiccup. When it appears alongside Cloudflare, it often leads to confusion. However, understanding the underlying mechanics can demystify the issue.
The primary goal of this post is to provide comprehensive guidance on **Cloudflare 500 internal server error troubleshooting**. We will delve into the **common Cloudflare 500 errors and solutions**, empowering you with the knowledge and actionable steps to diagnose and resolve these frustrating interruptions, ensuring your website stays accessible and functional.
Understanding the Cloudflare 500 Error
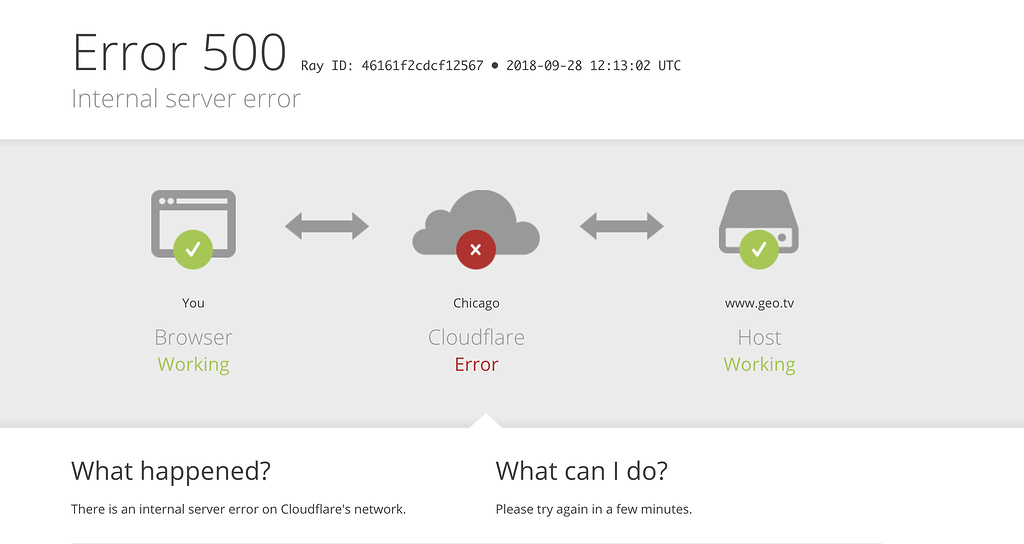
To effectively troubleshoot a Cloudflare 500 error, it’s essential to grasp Cloudflare’s role in your website’s architecture. Cloudflare acts as a reverse proxy, sitting between your visitors and your origin web server. This means that when a visitor requests a page on your site, the request first goes to Cloudflare’s network, and then Cloudflare forwards that request to your actual web server (the origin server). (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)

Crucially, Cloudflare itself is rarely the direct cause of a 500 Internal Server Error. Instead, a 500 error relayed by Cloudflare almost always signifies that your origin server encountered a problem while trying to process the request and couldn’t fulfill it. Cloudflare simply reports this failure back to the user. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)
The typical flow for a request involving Cloudflare goes like this:
- A user’s browser sends a request to your website.
- Cloudflare receives this request.
- Cloudflare forwards the request to your origin server.
- Your origin server attempts to process the request but fails due to an internal issue.
- The origin server sends a 500 status code back to Cloudflare.
- Cloudflare then relays this 500 status code to the user’s browser.
Therefore, when you encounter a Cloudflare 500 error, you should primarily focus your investigation on your origin server. This could be an issue with your website’s application code, its server configuration, or a dependent service such as your database. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)

While rare, there are edge cases where Cloudflare’s configuration or network could contribute to a 500 error. This might involve specific firewall rules, SSL issues, or misconfigurations within Cloudflare itself. For these specific scenarios, consulting Cloudflare’s extensive documentation is advisable. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)
Common Causes of Cloudflare 500 Errors
Understanding the common culprits behind a 500 error will significantly streamline your troubleshooting process.
Database Connection Issues
Perhaps one of the most frequent offenders is the inability of your website’s application to connect to its database. This can manifest in numerous ways, leading to that dreaded 500 error.
- Incorrect Credentials: Double-check your database hostname, username, password, and database name. A single typo can prevent a connection.
- Database Server Unreachable: The database server itself might be down, undergoing maintenance, or experiencing network issues, making it inaccessible from your web server.
- Firewall Restrictions: A firewall on either your web server or your database server could be blocking the connection attempt.
- Resource Exhaustion: The database server might be overloaded. This could be due to a high number of concurrent connections exceeding its limits, insufficient RAM, or high CPU usage.
- Database Corruption: In rarer cases, the database files themselves might become corrupted, preventing proper access.
Addressing these issues is critical, and a focus on the **cloudflare error establishing database connection fix** is paramount for many users. (Source: kinsta.com/blog/500-internal-server-error/)

Origin Server Overload / Resource Exhaustion
Your origin server is the engine powering your website. If that engine is running too hot or trying to do too much, it can stall, resulting in a 500 error.
- Traffic Spikes: A sudden surge in visitors can overwhelm your server’s capacity to handle requests.
- Resource-Intensive Tasks: Background processes, complex scripts, or poorly optimized code can consume excessive CPU, RAM, or I/O resources, leading to an overload.
- Shared Hosting Limitations: If you’re on a shared hosting plan, your server resources are divided among multiple websites. Exceeding your allocated limits, or another site on the server consuming disproportionate resources, can trigger errors.
(Source: kinsta.com/blog/500-internal-server-error/)
Application / Code Errors
The software that runs your website – your Content Management System (CMS), plugins, themes, or custom code – is a frequent source of internal server errors.
- Faulty Code: Syntax errors, logic flaws, or unhandled exceptions in your website’s code can cause the server to crash.
- Incompatible Plugins or Themes: Installing a new plugin or theme, or updating an existing one, can introduce conflicts or bugs that trigger a 500 error.
- Fatal PHP Errors: These are often the most direct indicators of code problems and are usually logged by the server.
- Recent Updates: Sometimes, updates to your CMS core, plugins, themes, or even server software can inadvertently break functionality.
(Source: kinsta.com/blog/500-internal-server-error/)
Server-Side Misconfiguration
The way your server is configured plays a vital role in how it handles requests. Misconfigurations can lead to unexpected behavior and errors.
- Corrupted `.htaccess` File: On Apache servers, the `.htaccess` file controls much of the server’s behavior, including redirects and access. A syntax error or corruption in this file is a very common cause of 500 errors.
- Incorrect File/Folder Permissions: If files or directories have the wrong permissions set, the web server might not have the necessary rights to read or execute them, leading to an error.
- Server Directives: Incorrectly configured directives in server configuration files (like `httpd.conf` or `nginx.conf`) can cause issues.
- PHP Configuration Issues: Problems with PHP settings, such as memory limits or execution time limits, can also result in 500 errors.
(Source: kinsta.com/blog/500-internal-server-error/)
External Service Dependencies
Modern websites often rely on external services – think payment gateways, APIs for social media feeds, or third-party data providers. If one of these services fails or becomes unresponsive, it can cause your origin server to falter.
- API Outages: If your site makes calls to an external API that is down or returning errors, your server might not be able to process the request, leading to a 500 error.
- Payment Gateway Failures: Issues with a payment processor during checkout can sometimes cascade into a server error if not handled gracefully.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide: How to Fix Cloudflare 500 Error
Now that we understand the common causes, let’s walk through a systematic approach to diagnose and resolve Cloudflare 500 errors.
Step 1: Verify the Issue Isn’t Cloudflare Itself
While Cloudflare rarely causes 500 errors, it’s good practice to rule it out first.
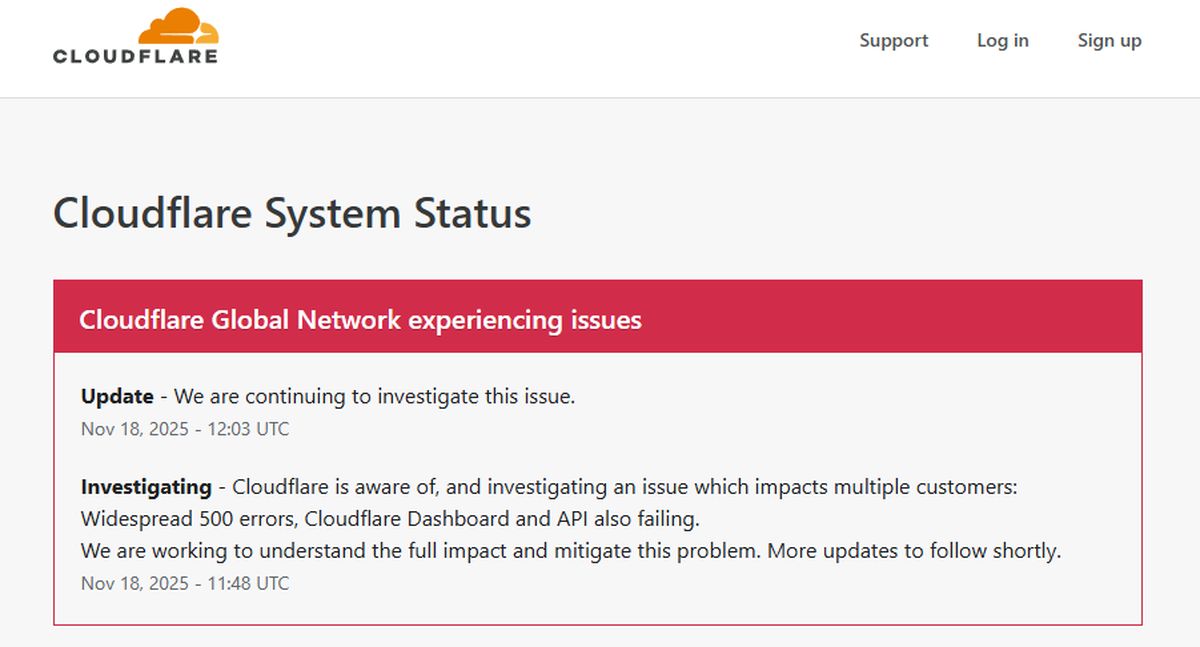
- Check Cloudflare Status: Visit the official Cloudflare Status page to see if there are any widespread incidents affecting their services.
- Inspect the Error Page: Carefully examine the HTML content of the 500 error page. If it contains specific mentions of “cloudflare” or “cloudflare-nginx,” Cloudflare’s documentation suggests this might indicate a problem on their end, and you should contact their support with details. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)
- Temporarily Pause Cloudflare: This is a critical diagnostic step. You can temporarily disable Cloudflare’s proxy for your domain by changing your DNS record from “Proxied” (orange cloud) to “DNS Only” (grey cloud) in your Cloudflare dashboard. This routes traffic directly to your origin server, bypassing Cloudflare. If the 500 error disappears when Cloudflare is paused, the problem likely lies within Cloudflare’s configuration or network. If the error persists, it almost certainly points to an issue on your origin server. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)
Remember to re-enable Cloudflare’s proxy (orange cloud) once you’ve completed your tests.

Step 2: Check Your Origin Server Logs
Your origin server’s logs are an invaluable resource for pinpointing the exact cause of a 500 error. They often contain specific error messages that provide clues. This is fundamental for **diagnosing Cloudflare 500 internal server error** problems. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)
Common log locations vary by hosting environment, but generally, you should look for:
- Web Server Error Logs:
- Apache: Typically found at `/var/log/apache2/error.log` or `/var/log/httpd/error_log`.
- Nginx: Often located at `/var/log/nginx/error.log`.
- Application-Specific Logs: Many Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress, or frameworks like Laravel or Symfony, have their own error logs. Check your CMS or framework’s documentation for their locations (e.g., `wp-content/debug.log` for WordPress, or a `storage/logs` directory for Laravel).
- Database Logs: If you suspect a database issue, check the error logs for your database system (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL).
Pay close attention to log entries that correspond to the exact time you experienced the 500 error. Look for specific error messages, file paths, line numbers, and descriptions that indicate what went wrong.
Step 3: Investigate Database Connectivity
Given how common database issues are, this step warrants detailed attention for a **Cloudflare error establishing database connection fix**.
- Test Connection from Server: Log in to your origin server via SSH and attempt to connect to your database directly using a command-line client. For MySQL/MariaDB, this would look like:
mysql -u your_db_user -p -h your_db_host your_db_nameIf this command fails, it confirms a connectivity problem from the server to the database.
- Verify Database Service Status: Ensure that your database service is actually running on its designated port.
- Check Firewall Rules: Confirm that no firewall on your web server or database server is blocking the necessary port (e.g., port 3306 for MySQL).
- Review Database Server Resources: Monitor the CPU, RAM, and active connections on your database server. If any of these are maxed out, it could be the cause.
- Managed Database Providers: If you’re using a managed database service (like Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, etc.), check their dashboard for any alerts or status issues.
If you’ve exhausted these checks and still can’t pinpoint the database issue, it’s often best to contact your hosting provider or database administrator with the specific error messages and troubleshooting steps you’ve already taken. They can offer more specialized assistance. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/error-500/)

Step 4: Review Recent Changes
It’s a common adage in IT: “If it was working yesterday and broken today, something changed.” This is especially true for 500 errors.
- Code Deployments: Did you recently push new code to production? Roll back to the previous stable version to see if the error resolves.
- Plugin/Theme Updates: Were any plugins, themes, or modules updated or installed just before the error started appearing? Try deactivating them one by one (if possible via a staging environment or by temporarily renaming plugin folders via FTP/SSH) to identify the culprit.
- Server Configuration Changes: Any modifications to server settings, virtual host configurations, or `.htaccess` files? Revert these changes to test.
- Version Control: If you use version control systems like Git, this is the perfect time to leverage your commit history to track down the exact change that introduced the error.
(Source: kinsta.com/blog/500-internal-server-error/)

Step 5: Server Resource Monitoring
If your server logs indicate resource exhaustion or you suspect overload, actively monitor your server’s performance.
- Tools: Use command-line tools like `top`, `htop`, `vmstat`, `iostat`, or your hosting provider’s control panel (cPanel, Plesk, etc.) or dedicated monitoring dashboards.
- Identify Bottlenecks: Look for consistently high CPU usage, memory leaks, excessive disk I/O, or a large number of running processes.
- Optimization: If resource usage is high, consider optimizing your application code, database queries, or implementing caching mechanisms.
- Scaling: If your traffic consistently demands more resources than your current plan provides, you may need to upgrade your hosting plan (vertical scaling) or distribute your load across multiple servers (horizontal scaling).

Step 6: Debugging Application Code
If logs point to a specific code error, you’ll need to debug it.
- Enable Error Reporting (Safely): In a development or staging environment (NEVER on a live production site unless absolutely necessary and with extreme caution), you can enable more verbose error reporting. For PHP, you might add these lines to your script’s entry point or `php.ini`:
ini_set('display_errors', 1); ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1); error_reporting(E_ALL); - Use Debugging Tools: Many frameworks have built-in debugging tools or allow integration with professional debuggers (like Xdebug for PHP).
- Log Stack Traces: Instead of displaying errors publicly, ensure your application logs detailed stack traces. This information is crucial for developers to understand the sequence of function calls that led to the error.
- Fix and Disable: Once you’ve identified and fixed the bug, remember to disable `display_errors` on your production server to prevent exposing sensitive information.

Step 7: `.htaccess` and Server Configuration
For Apache servers, `.htaccess` file issues are a prime suspect.
- Backup and Rename `.htaccess`:** Locate the `.htaccess` file in your website’s root directory. Back it up, then rename it to something like `.htaccess_old`. Try accessing your site again. If the 500 error is gone, you know `.htaccess` was the problem.
- Inspect and Restore: Examine the contents of your backed-up `.htaccess` file for syntax errors, incorrect directives, or problematic rewrite rules. You can either clean it up or regenerate a default `.htaccess` file (many CMS platforms provide instructions for this).
- Check Other Configurations: If `.htaccess` isn’t the cause, investigate other server configuration files. This might include your main Apache configuration (`httpd.conf` or `apache2.conf`), Nginx configuration files (`nginx.conf` and site-specific configs), or PHP configuration files (`php.ini`, `.user.ini`). Ensure directives are correctly formatted and don’t conflict.
(Source: kinsta.com/blog/500-internal-server-error/)

Advanced Troubleshooting & Best Practices
Beyond the core steps, here are some advanced considerations and best practices to enhance your troubleshooting and prevention efforts.
Utilizing Cloudflare Tools
Cloudflare offers tools and documentation that can be helpful.
- Cloudflare 5xx Errors Documentation: Familiarize yourself with Cloudflare’s detailed guides on their various 5xx error codes. Understanding the nuances can guide your troubleshooting. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)
- Log Explorer (Enterprise Plans): For users on higher-tier plans, Cloudflare’s Log Explorer can be powerful. It allows you to query logs for specific requests, using the unique **Ray ID** found in the response headers or error pages, to pinpoint issues within Cloudflare’s network or between Cloudflare and your origin. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/)
- Contacting Cloudflare Support: If, after thorough investigation, you suspect the issue lies with Cloudflare’s infrastructure or configuration, do not hesitate to contact their support. Be prepared to provide essential details like your domain name, the exact time of the error, the Ray ID, and the output of a `cdn-cgi/trace` request (e.g., `yourdomain.com/cdn-cgi/trace`). (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/error-500/)

Contacting Your Hosting Provider
Your hosting provider is your first line of defense for origin server issues, especially if you lack direct server access or expertise.
- When to Contact Them: Reach out if you’re unable to access server logs, don’t have root/SSH access, cannot resolve the issue independently, or suspect a problem with the hosting environment itself.
- Information to Provide: When contacting support, be prepared with:
- The specific URL(s) affected.
- The exact status code (500 Internal Server Error).
- Precise timestamps of when the errors occurred (including timezone).
- Any error messages or log snippets you’ve found.
- The troubleshooting steps you’ve already taken.
- Leverage Their Expertise: Hosting providers have deep knowledge of their infrastructure and can often diagnose and resolve server-level issues quickly. They are your best resource for problems originating from the server itself. (Source: developers.cloudflare.com/support/troubleshooting/http-status-codes/cloudflare-5xx-errors/error-500/)

Proactive Monitoring and Prevention
The best way to deal with errors is to prevent them from happening in the first place.
- Uptime and Error Monitoring: Implement external monitoring services that regularly check your website’s availability and performance. These tools can alert you to 500 errors (or other issues) before your visitors do.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM): For complex applications, APM tools can provide deep insights into performance bottlenecks, slow database queries, and code errors that might lead to 500s.
- Regular Log Review: Don’t just check logs when an error occurs. Periodically review them for unusual patterns or recurring warnings.
- Staging Environments: ALWAYS test updates (plugins, themes, core code, server configurations) on a staging or development server that mirrors your production environment before deploying them live. This helps catch errors like the **Cloudflare 500 internal server error** before they impact users.
- Keep Software Updated: While updates can sometimes cause issues, running outdated software (CMS, plugins, server software) often poses a greater security and stability risk. Ensure you have a strategy for applying security patches and updates promptly, ideally after testing.

Dealing with a **Cloudflare 500 internal server error** can be frustrating, but by adopting a systematic approach, understanding Cloudflare’s role, and diligently checking your origin server, you can effectively diagnose and resolve these issues. Remember, the error usually lies within your hosting environment, not Cloudflare itself.
For broader insights into website and technology trends that complement your technical knowledge, consider these resources:
- Curious about enhancing your mobile content creation? Explore how to improve your smartphone photography skills.
- Stay ahead with advancements in AI: learn about what is Apple Intelligence in iOS 18: AI.
- Simplify AI integrations by understanding what is model context protocol (mcp) explained: simplifying ai integrations.
- Grasp the future of the internet with insights on the explosive web3 revolution: decoding the future of the decentralized internet.
- If you’re encountering generic “try again later” messages, this guide on how to fix an error occurred please try again later and reclaim your online experience might be helpful.

“`