Here is the enriched blog post with 9 strategically placed, relevant images.
Mastering the Multi-Agent Orchestration AI Trends 2026: Your Strategic Blueprint
The landscape of artificial intelligence is rapidly shifting away from singular, monolithic models toward complex ecosystems. If you are planning for the next few years, understanding the core drivers of this change is non-negotiable. We are standing at the precipice of true autonomous workflow management, driven by the convergence of specialized AI agents collaborating via orchestration platforms to manage autonomous workflows, dynamic task allocation, and complex problem-solving (Source).

This evolution defines the critical multi-agent orchestration AI trends 2026. Gartner forecasts a monumental shift, predicting that 80% of customer-facing processes will be handled by multi-agent AI by 2028 (Source; Source). To capitalize on this, strategic planning must immediately address distributed computing needs via Edge AI, secure decentralized data flows through federated data governance implementation, select the right infrastructure (purpose-built platforms vs generic solutions), and redefine human roles using robust human-AI team collaboration strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-agent orchestration moves AI from single tasks to complex, self-directed workflows requiring coordination between specialized models.
- The necessity for low latency mandates a shift to hybrid Edge AI architectures to support real-time decision-making.
- Data security in decentralized systems demands a governance-first approach centered on federated data governance and mandatory XAI auditing.
- Infrastructure choice between purpose-built platforms and generic solutions is critical for scalable, reliable orchestration.
- Successful adoption hinges on redefining roles through structured human-AI collaboration strategies, ensuring human oversight where judgment is paramount.
Table of Contents
- Defining the Future: Deep Dive into Multi-Agent Orchestration AI Trends 2026
- The Distributed Foundation: Enabling Orchestration with Edge AI
- Operationalizing Trust: Implementing Federated Data Governance
- Infrastructure Strategy: Evaluating Platform Choices
- Optimizing Output: Human-AI Team Collaboration Strategies
Defining the Future: Deep Dive into Multi-Agent Orchestration AI Trends 2026
The most significant of the multi-agent orchestration AI trends 2026 is the move toward true systemic autonomy. We are shifting from large language models executing single prompts to interconnected ecosystems of specialized agents. Imagine an agent purely dedicated to risk analysis, another to resource allocation, and a third to scheduling—all coordinating automatically to manage a global supply chain end-to-end (Source; Source).

*This distributed cognitive load offers profound advantages over older monolithic models.* By allowing agents to specialize, organizations can achieve greater accuracy, faster execution, and superior conflict resolution. When an agent encounters a decision that falls outside its training parameters, the orchestration layer routes the conflict to another specialized agent equipped to handle that domain, minimizing human intervention (Source). This complex coordination requires robust communication standards.
To facilitate this, emerging protocols are standardizing interaction. We see frameworks like Anthropic’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) designed for secure, controlled data access and Google’s Agent-to-Agent (A2A) communication facilitating seamless cross-platform dialogue (Source). The operational outcome is a move toward proactive, self-evolving architectures that dynamically reconfigure workflows based on evolving external conditions (Source). This necessitates strategic alignment with revolutionary agentic ai future trends 2025: unlock the power of autonomous action and understanding what is model context protocol (mcp) explained: simplifying ai integrations.
The Distributed Foundation: Enabling Orchestration with Edge AI
Complex, real-time orchestration—a requirement of the multi-agent orchestration AI trends 2026—cannot rely solely on distant cloud servers. Latency introduces unacceptable lag when agents need to communicate instantaneously to manage dynamic situations, such as automated fraud detection or industrial control loops.
This is where Edge AI becomes fundamental. Edge AI refers to processing data locally, directly on the device or a nearby micro-data center, rather than sending everything to a centralized cloud for processing (Source; Source). The dominant architectural pattern emerging is *hybrid distribution*.
The hybrid model intelligently places workloads across the continuum: low-sensitivity, high-volume data is processed at the edge; complex, long-term training and deep analysis remain in the cloud; and specialized chips manage tasks requiring extreme optimization (Source). We can gauge the proliferation of this decentralized power by looking at edge AI smartphone growth statistics, which demonstrate that devices are rapidly gaining the computational muscle necessary to host sophisticated agent components directly. This allows for instantaneous functions, like real-time risk flagging during a transaction, without the cloud bottleneck. Strategic planning must therefore align with revolutionary edge computing breakthroughs: transforming hybrid cloud and ai innovation and the broader unstoppable surge: mastering the 5g smartphone adoption rate 2025.

Operationalizing Trust: Implementing Federated Data Governance
As agents scatter across the network—residing on edge devices, private clouds, and partner systems—the traditional centralized data governance model collapses. Data flows become complex, often crossing regulatory and jurisdictional boundaries, which elevates the risk profile significantly.
Therefore, the success of agentic AI hinges upon rigorous, proactive security structures, primarily focusing on federated data governance implementation. This requires baking governance into the architectural design phase, not bolting it on later (Source; Source). What does this look like in practice?
- Mandatory Explainable AI (XAI): Every agent decision must be auditable. If an agent allocates resources, the system must detail *why* based on specific inputs and logic models.
- Bias Mitigation: Governance frameworks must enforce continuous testing against known biases, especially as agents learn and adapt in decentralized environments.
- Graduated Autonomy: Clearly defining levels of operational independence, each tied to mandatory human override triggers for high-stakes decisions.

This governance layer turns compliance from a hindrance into a competitive edge, especially in verticals like finance and healthcare where adherence to standards like HIPAA is non-negotiable for agent-native operations (Source). Organizations must familiarize themselves with mastering ethical ai deployment strategies for 2025: crucial trends, challenges, and best practices and navigating the evolving technology landscape 2025: your essential guide to emerging innovations.
Infrastructure Strategy: Evaluating Platform Choices
Hosting a fleet of coordinating AI agents is fundamentally different from hosting a traditional monolithic application. Strategists face a critical choice: invest in purpose-built platforms vs generic solutions.
Purpose-built platforms are optimized specifically for complex agent coordination, dynamic task routing, and enforcing multi-step dependencies required for sophisticated workflows. They are generally faster, more accurate in resolution, and designed for vertical compliance (Source; Source). Conversely, generic solutions (like standard cloud VMs or existing application hosting) are useful for initial experimentation but often buckle under the weight of enterprise-scale coordination, leading to cascading failures when agents conflict.
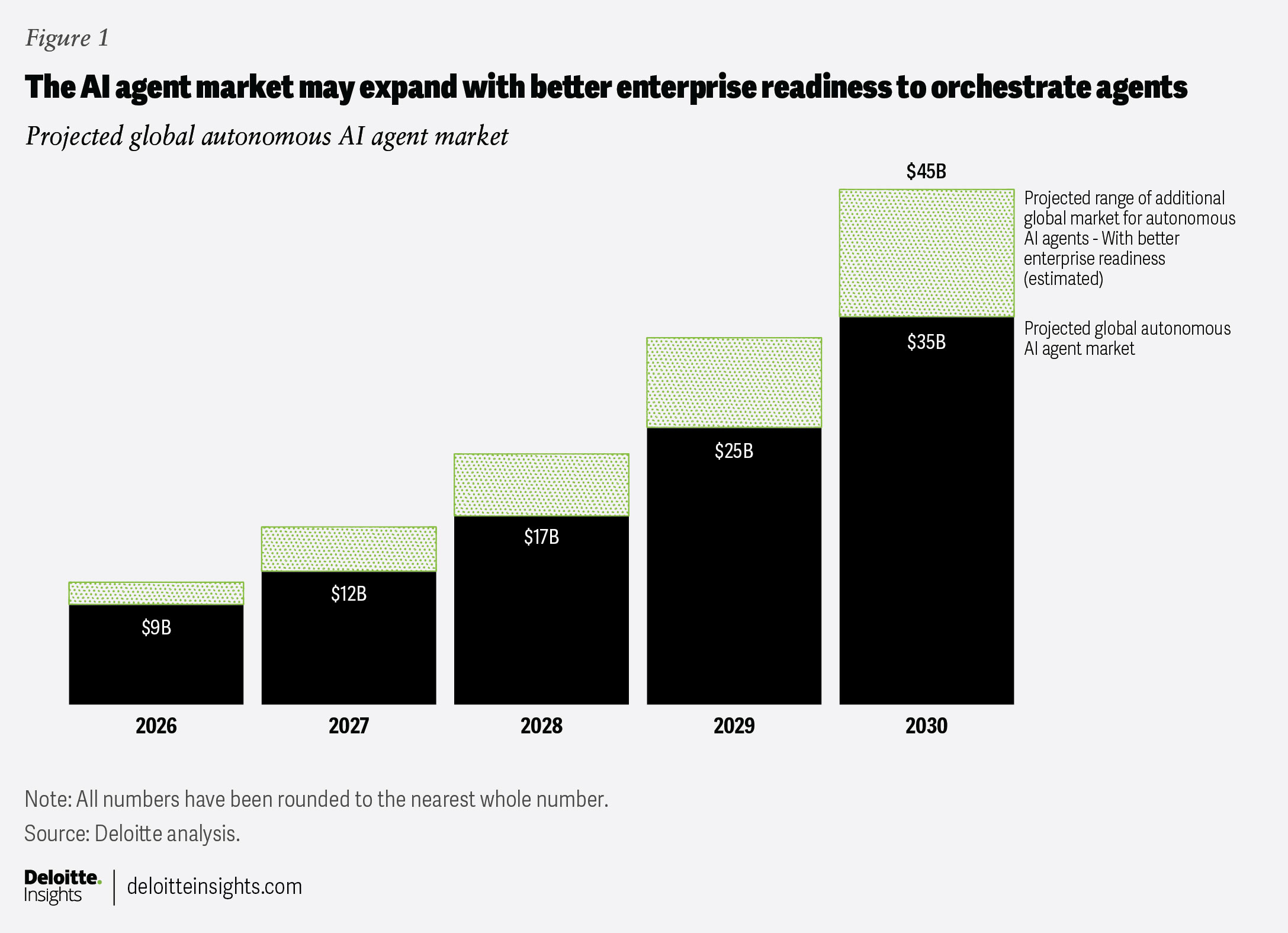
Strategic evaluation must follow clear criteria:
| Criteria | Purpose-Built Platforms | Generic Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | High, designed for dynamic agent loads and rapid reconfiguration (Source). | Limited by traditional scaling mechanisms; orchestration overhead is high. |
| Customization | Deep customization possible within the agent framework, adherence to vertical standards. | High customization of environment, but orchestration logic must be coded externally. |
| Cost & Speed | Higher initial cost, but faster time-to-autonomy and operational efficiency (Source). | Lower initial cost, but slower operational speed and higher debugging costs. |
| Best For | Mission-critical, complex, multi-step workflows. | Pilot projects, simple, single-agent automation tasks. |
For most established enterprises, the pragmatic path involves hybrid modernization: deploying mission-critical orchestration on purpose-built tools while potentially extending legacy systems where immediate overhaul is impractical. Understanding this choice requires diligent research, such as unlocking success: mastering keyword research for explosive growth to identify emerging niche providers.
Optimizing Output: Human-AI Team Collaboration Strategies
The most sophisticated technology fails if organizational culture and processes lag behind. Technological readiness must be matched by operational integration. The future does not feature humans *or* AI; it features integrated ‘collaborative intelligence’ structures defined by robust human-AI team collaboration strategies (Source; Source).
In these structures, AI agents handle the heavy lifting—data crunching, routine execution, and preliminary analysis—freeing human teams to concentrate on strategic oversight, ethical arbitration, and tasks demanding high creativity or nuanced judgment.

Key tactics for embedding this collaboration include:
* Defining explicit Agent Supervisors: Roles accountable for monitoring agent performance, handling exceptions, and authorizing escalations to human review.
* Establishing clear Decision Boundaries: Precise demarcation of which decisions agents can execute autonomously versus which require mandatory human sign-off based on risk levels.
* Skills Mapping: Conducting organizational assessments based on the autonomy spectrum, directing upskilling programs tailored to managing intelligent systems rather than performing routine tasks. For example, in project management, agents forecast delays and identify resource conflicts, but the human project manager retains the final judgment on strategy shifts (Source; Source). This layered approach is essential for building necessary organizational trust.
To implement this successfully, strategists should explore unlocking success: navigating crucial enterprise ai adoption challenges 2025 and leveraging powerful ai-powered collaboration: revolutionizing remote work for unstoppable productivity and smarter teams.
Concluding Strategic Outlook
The trajectory toward advanced AI operations in 2026 is clear: sophistication requires deep integration across infrastructure, security, and personnel. Success in navigating the multi-agent orchestration AI trends 2026 depends on weaving together these five critical pillars:
- Ensuring real-time responsiveness via distributed processing, supported by edge AI smartphone growth statistics as a baseline for decentralized capability.
- Securing complex data pathways through proactive federated data governance implementation.
- Making sound long-term investments by correctly assessing purpose-built platforms vs generic solutions.
- Maximizing reliable output through the structured integration of human oversight via precise human-AI team collaboration strategies.
For the strategic planner, the mandate is immediate action. Begin organizational audits today: review existing governance models against the decentralized nature of future agent systems. Assess current platform flexibility against the need for complex coordination mechanisms. Most importantly, start the cultural shift now by defining cross-functional roles that align human expertise with agent capabilities. Readiness for 2026 starts in the current planning cycle. Explore unlocking tomorrow: incredible ai breakthroughs shaping 2025 and beyond to stay ahead of the curve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between current LLM usage and multi-agent orchestration?
Current LLM usage is primarily prompt-response: a single model handles a single request. Multi-agent orchestration involves multiple specialized AIs coordinating dynamically to complete a complex goal that requires various skill sets (e.g., planning, execution, review) without constant human prompting.
Why is Edge AI adoption critical for orchestration platforms?
Edge AI minimizes latency. For agents making split-second decisions in real-time environments (like manufacturing or high-frequency trading), waiting for cloud round-trips is unfeasible. Edge processing ensures localized, immediate feedback loops necessary for smooth orchestration.
How does federated data governance differ from standard centralized compliance?
Centralized governance assumes data resides in one location or is easily traceable through one authority. Federated governance acknowledges data remains decentralized (e.g., on edge devices or partner servers) and enforces compliance policies locally while reporting status back to a central policy layer, prioritizing data sovereignty.
When should an organization choose a purpose-built platform over a generic solution?
If the use case involves high-stakes workflows requiring complex interaction, conflict resolution between agents, or deep vertical compliance, a purpose-built platform is necessary. Generic solutions are only suitable for testing or isolated, low-risk tasks.
What is the most overlooked aspect of implementing Human-AI collaboration?
The most overlooked aspect is often the necessary cultural and procedural overhaul. It’s not just about training humans on new software; it’s about redefining accountability, establishing trust metrics, and formally integrating autonomous decision points into existing operational SOPs.





