Brain-Computer Interfaces: Unpacking the Latest Neuralink N1 News and 2025 Milestones
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- The Neuralink N1 brain-computer interface is enabling patients to control computers with their minds, marking a revolutionary step in BCI technology.
- Clinical trials in 2025, such as the GB-PRIME study, are showing promising results with rapid patient adaptation and minimal complications.
- Technical advancements include high-bandwidth signals, bidirectional capabilities, and automated surgery, paving the way for future applications like vision restoration.
- Elon Musk’s updates outline an ambitious roadmap, with plans to scale electrode counts and integrate AI for human-AI symbiosis.
- While offering immense benefits, BCIs pose risks such as surgical invasiveness, ethical concerns, and the need for long-term stability.

Table of contents
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: Unpacking the Latest Neuralink N1 News and 2025 Milestones
- Key Takeaways
- From Concept to Reality: A Brief History of BCI
- Neuralink N1 Brain Computer Interface News: 2025’s Defining Moments
- A Deep Dive into Neuralink Clinical Trials 2025
- Unpacking the Latest Brain Computer Interface Technology
- Elon Musk Neuralink Updates 2025: The Visionary Roadmap
- Analyzing Neuralink GB-Prime Study Results
- Neuralink vs. The Competition: A Balanced View
- Implications, Benefits, and Risks
- Frequently Asked Questions
The field of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) is experiencing a revolutionary moment, promising a future where thought alone controls technology. This potential is why neuralink n1 brain computer interface news is dominating headlines in 2025, as the first patients demonstrate fluid control of computers with their minds. For anyone tracking the intersection of neuroscience and technology, staying updated on these developments is crucial to understanding the future of healthcare and human capability.
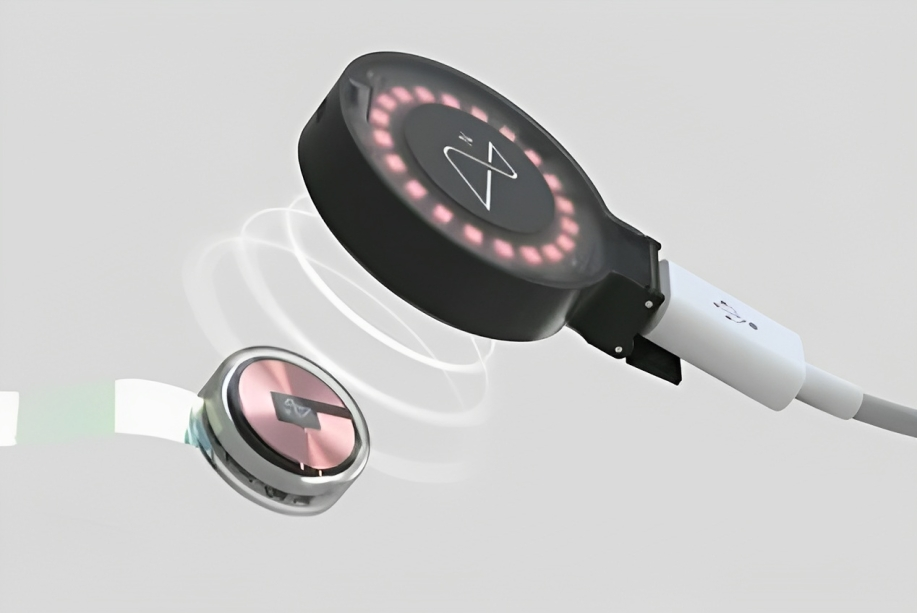
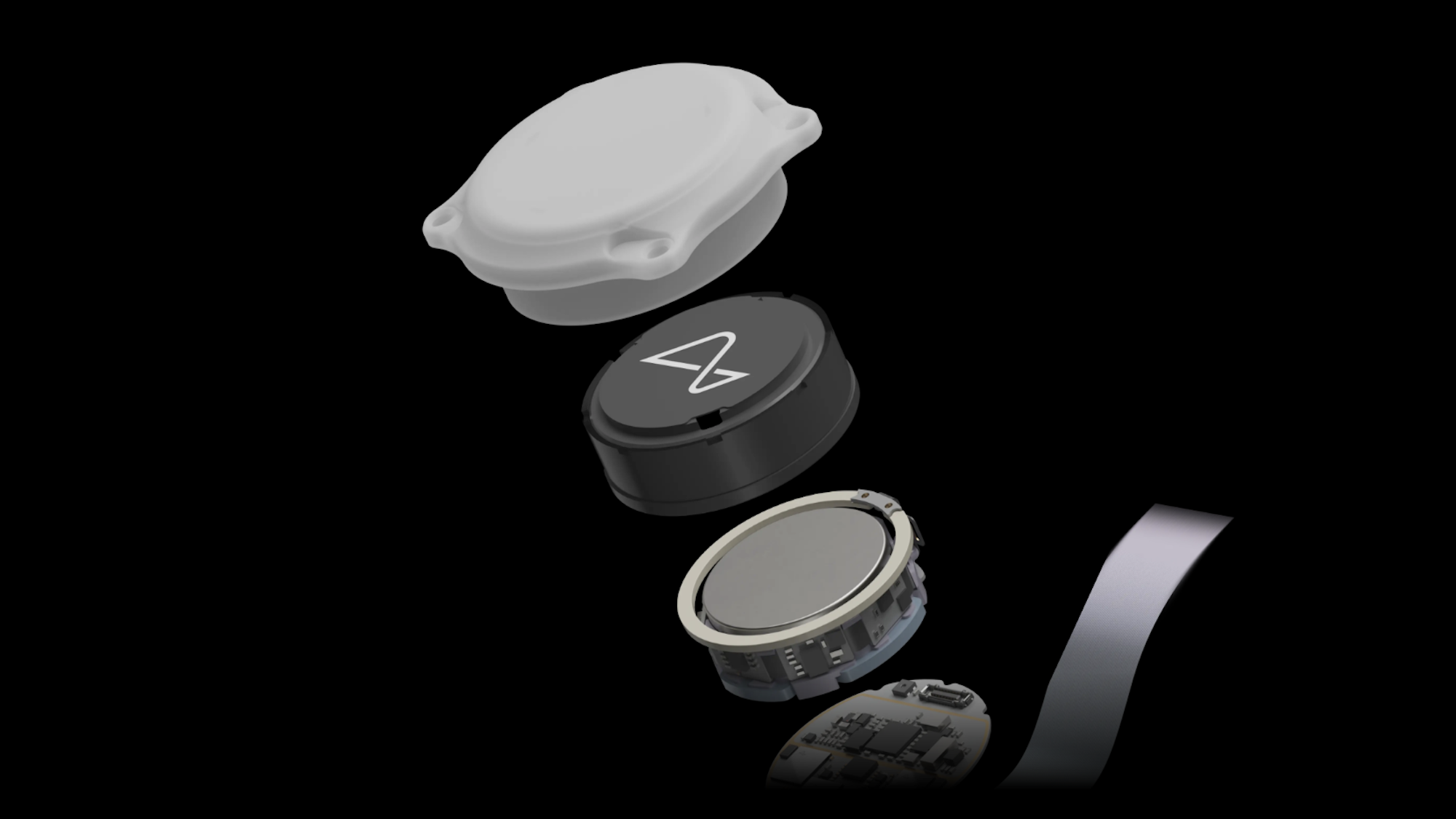
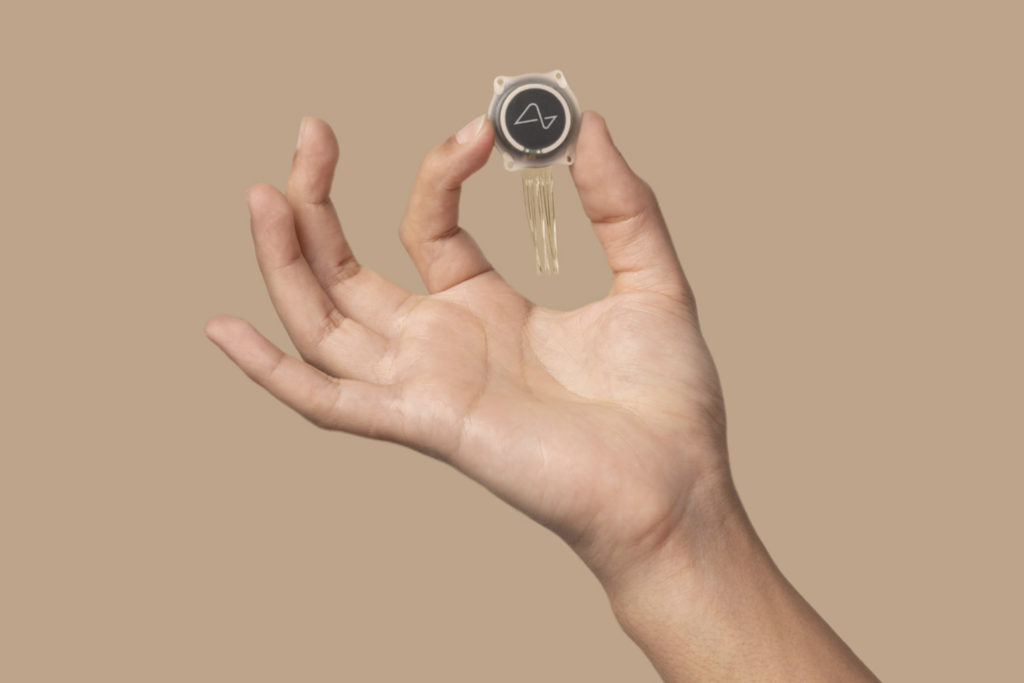
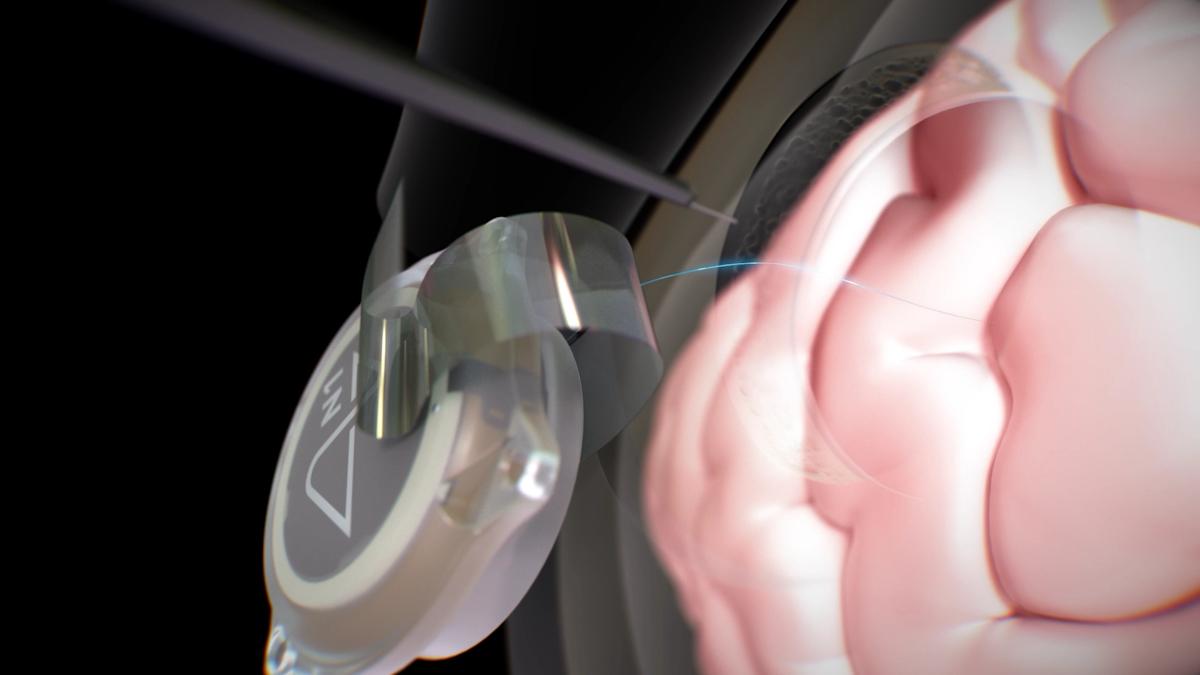
At its core, a BCI is a system that enables direct communication between the brain and an external device, like a computer or robotic arm. It works by using implantable electrodes to record neural signals, which are then decoded by advanced algorithms into commands. The leadership of Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk, has brought this technology into sharp focus with its N1 Implant. This fully implantable, intracortical BCI uses over 1,000 electrodes on ultra-thin threads, placed with micron precision by the R1 Robot surgical system. Its initial target is to restore independence to individuals with paralysis from conditions like spinal cord injuries or motor neurone disease.

From Concept to Reality: A Brief History of BCI
The journey to this point has been decades in the making. The evolution of BCIs has progressed from rudimentary systems with bandwidths of about 1 bit per second to today’s high-bandwidth, intracortical interfaces. Understanding how BCIs work is key: tiny threads containing electrodes are implanted near neurons to record electrical activity. Sophisticated AI then decodes these signals in real-time, translating a user’s intention to move a cursor, type, or even speak into immediate action on a connected device. This represents the pinnacle of latest brain computer interface technology.
Neuralink N1 Brain Computer Interface News: 2025’s Defining Moments
The most compelling neuralink n1 brain computer interface news revolves around tangible patient outcomes. The N1 implant allows for thought-based control of computers, smartphones, and cursors. Remarkably, users are achieving fluid operation in as little as 15 minutes post-implant—a staggering improvement over earlier research trials that required hours of calibration. A landmark moment came in October 2025, when the UK’s first patient, a person with motor neurone disease, controlled a computer cursor the day after implantation at UCLH’s National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery and returned home soon after. Parallel trials in the U.S. and Canada show patients using the system for daily devices, with ambitious expansion plans to increase electrode counts from 1,000 in 2026 to over 25,000 by 2028 for multi-implant access to motor, speech, and visual cortices.

A Deep Dive into Neuralink Clinical Trials 2025
To provide comprehensive updates, let’s explore the key neuralink clinical trials 2025. The GB-PRIME study is a multi-site early feasibility trial evaluating the N1’s safety and functionality. The UK’s first implant in October 2025 is part of this study, with patients undergoing ongoing monitoring. Another key study is the CONVOY Study, launched in November 2024, which is testing the N1 for controlling assistive robotic arms. Furthermore, Summer 2025 updates on the Telepathy trials for phone and computer control revealed rapid user adaptation, with plans for speech cortex implants to decode words into speech slated for the following quarter. These trials are part of a broader wave of revolutionary AI medical breakthroughs transforming patient care.

Unpacking the Latest Brain Computer Interface Technology
The latest brain computer interface technology, led by Neuralink, involves several technical leaps. The most significant is a monumental bandwidth boost—from historic rates of ~1 bit/second to modern systems capable of megabits or even gigabits per second. This enables what researchers call “conceptual telepathy,” high-dexterity computer control, and lays the groundwork for future AI integration for thought storage and retrieval. Innovations include:
- Bidirectional (read/write) capabilities for two-way communication between brain and device.
- Mixed-signal custom chips that allow for more recording channels and efficient data processing.
- Fully automated surgery via the R1 Robot, ensuring safe and precise implantation for 24-hour use.
- Adaptive machine learning algorithms that maintain stable long-term signal decoding.
An exciting upcoming application is “Blindsight,” which aims to restore vision in blind users via cortical stimulation, with navigation trials planned for 2026. These advancements are central to the 10 cutting edge AI technologies shaping our future.

Elon Musk Neuralink Updates 2025: The Visionary Roadmap
Engaging with elon musk neuralink updates 2025 provides insight into the company’s ambitious trajectory. In Summer 2025, Musk emphasized aggressive scaling: tripling electrodes to 3,000 in 2026, targeting 10,000 by 2027 with multiple implants, and demonstrating early body reanimation and robot control. His long-term vision includes gigabit-speed brain-machine links, full sight restoration via cortical stimulation, and creating intuitive AI interfaces that are faster than manual input. In a significant December 2025 announcement, Musk unveiled plans for a new BCI designed for human testing, signaling continued rapid innovation.

Analyzing Neuralink GB-Prime Study Results
For credibility, examining specific neuralink gb-prime study results is essential. The initial outcomes from the UK’s first patient are promising: successful thought-control of a computer cursor was achieved just hours post-surgery in October 2025, with no reported surgical complications and a discharge home soon after. The patient now collaborates with engineers on daily autonomy tasks like device control. Follow-up assessments are focused on learning curves and long-term functionality, with early data from U.S. and Canada sites supporting the potential for practical, daily use.

Neuralink vs. The Competition: A Balanced View
While Neuralink leads in areas like electrode density (1,000+), robotic surgical precision, and scalability, it’s important to acknowledge a vibrant competitive landscape. Rivals like Paradromics are advancing with high-channel-count systems, while established companies continue with less invasive, lower-bandwidth approaches. The intracortical approach offers superior signal resolution and bandwidth for complex control but involves higher surgical invasiveness compared to non-invasive EEG headsets, which remain crucial for various applications.

Implications, Benefits, and Risks
The implications of this technology are vast. It promises to accelerate BCI adoption in healthcare for speech and mobility restoration, and could revolutionize gaming, education, and work through high-bandwidth links. The primary benefits include:
- Regained independence for paralyzed individuals through control of assistive devices.
- Future vision restoration for the blind via cortical stimulation techniques.
- A new era of human-AI symbiosis, where thought and machine interaction become seamless.
However, significant risks and challenges exist:
- Inherent risks of brain surgery, including infection and tissue damage.
- Long-term electrode stability and the body’s immune response.
- Ensuring signal decoding accuracy to prevent misinterpretation of neural commands.
- Managing channel limits amid growing competition and technological demands.
Ethical considerations are paramount, particularly regarding the privacy of neural data, informed consent, and equitable access. All trials require rigorous approval from bodies like the UK’s MHRA and HRA.
The industry impact will be profound, particularly in healthcare for applications like speech restoration and controlling robotic arms, and in gaming/education for enabling entirely new forms of thought-based interaction. This integration of intelligence into devices is a trend also seen in the evolution of smart home ecosystems and represents the next frontier in latest innovations in wearable tech.

The Dawn of Human-AI Symbiosis
In summary, the transformative neuralink n1 brain computer interface news of 2025, marked by pioneering clinical trials and tangible study results, signals a new chapter in human-technology interaction. We are witnessing the dawn of a potential human-AI symbiosis, powered by direct neural links. To stay informed on this fast-moving field, monitor neuralink.com/trials for participation opportunities and news, and follow the latest elon musk neuralink updates 2025 for announcements on future breakthroughs. The progress in neuralink clinical trials 2025 and the encouraging neuralink gb-prime study results are not just scientific milestones; they are stepping stones to a future where the boundaries between mind and machine become seamlessly integrated, much like the most advanced wearable tech gadgets aim to do today. This technology, once matured, could become as integrated into daily life as the most sophisticated tech gadgets available, fundamentally redefining human potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a brain-computer interface (BCI)?
A brain-computer interface is a system that enables direct communication between the brain and an external device. It works by recording neural signals via electrodes, which are then decoded by algorithms to control computers, robotic arms, or other devices.
How does Neuralink’s N1 implant work?
The N1 implant is a fully implantable BCI that uses over 1,000 electrodes on ultra-thin threads, surgically placed near neurons by the R1 Robot. It records neural activity, which is processed by custom chips and AI to translate thoughts into commands for devices like computers or smartphones.
What are the main benefits of BCIs?
BCIs offer transformative benefits, including restoring independence to individuals with paralysis, enabling communication for those with speech impairments, and potentially restoring vision. They also pave the way for enhanced human-AI interaction in various fields.
What are the risks associated with Neuralink implants?
Risks include the invasiveness of brain surgery, potential for infection or tissue damage, long-term stability of electrodes, ethical concerns about neural data privacy, and the need for accurate signal decoding to avoid errors.
How can I participate in Neuralink clinical trials?
Information on clinical trial participation is available on Neuralink’s official website at neuralink.com/trials. Eligibility criteria and application processes are detailed there for interested candidates.
What ethical issues surround BCIs?
Key ethical issues include ensuring informed consent for participants, protecting the privacy and security of neural data, addressing equitable access to the technology, and considering the long-term societal impacts of human enhancement.






