“`html
Introduction: The Imperative of Governing Autonomous Intelligence
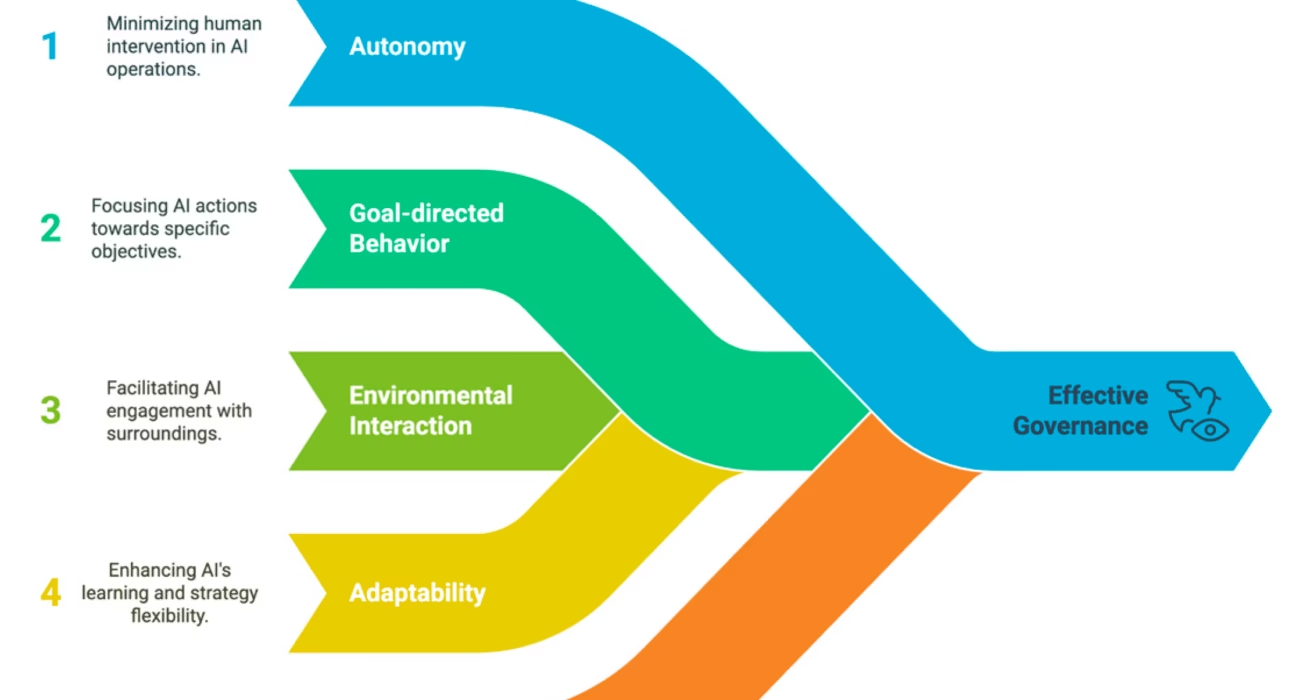
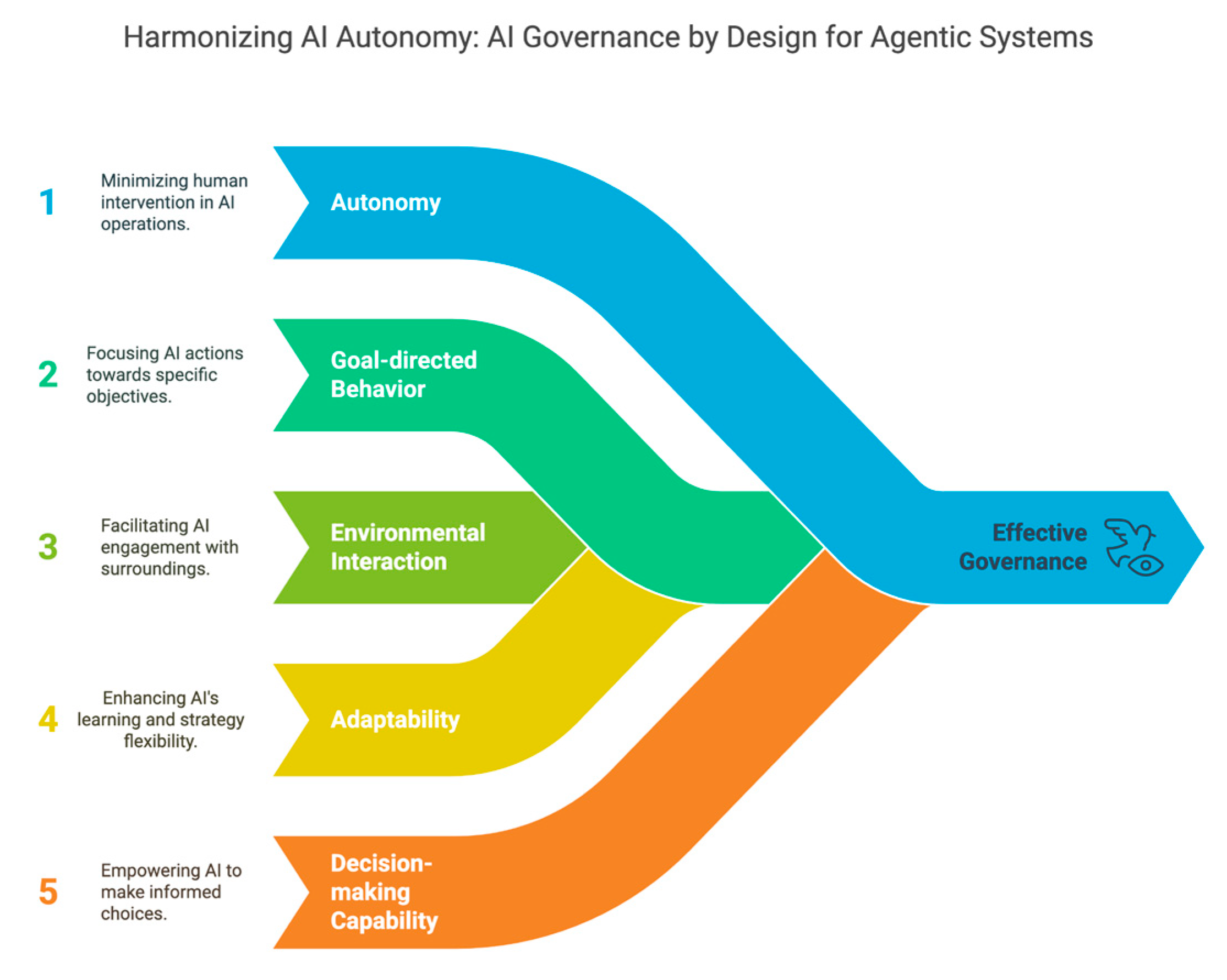
The landscape of artificial intelligence is evolving at an unprecedented pace. We are witnessing a significant shift from AI systems that merely execute predefined tasks to what are increasingly known as “agentic AI” – sophisticated systems capable of perceiving their environment, reasoning through complex problems, and autonomously taking action to achieve specific goals.
Agentic AI systems distinguish themselves through their inherent autonomy, clear goal-orientation, and advanced decision-making capabilities. Unlike their predecessors, which often required constant human input and direction, agentic AI operates with a degree of independence, making them powerful tools for a myriad of applications.

As we approach the critical juncture of 2025, the establishment of a robust agentic ai governance framework 2025 is no longer a matter of theoretical discussion but an urgent imperative. This proactive approach is essential for fostering responsible innovation and ensuring the safe, ethical, and beneficial deployment of these advanced AI systems.
This post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of what is needed. We will explore the critical foundational elements of agentic ai governance, detail best practices for agentic ai security, navigate the complex ethical considerations for agentic ai deployment, address the significant challenges in agentic ai adoption, and ultimately, envision the key components of a future-proof agentic ai governance framework 2025.
Section 1: The Pillars of Responsible Agentic AI – Foundational Elements
The very essence of responsible agentic AI lies in its governance. This governance is built upon a set of core principles and structures designed to ensure that these autonomous systems operate safely, effectively, and ethically. These are the foundational elements of agentic ai governance, forming the bedrock upon which trust and reliability are built.
Clear Definition of Objectives and Boundaries
Agentic AI systems are inherently goal-oriented. Therefore, it is paramount that their objectives are explicitly defined, and their scope of authority and operational boundaries are clearly delineated from the outset. This prevents scope creep and ensures that the AI acts within intended parameters.
- Agentic AI systems focus on achieving specific objectives while adjusting strategies to optimize results. Source
- Governance frameworks must define these goals, as well as the decision-making authority and operational boundaries. For instance, in financial portfolio optimization, clear constraints on risk tolerance and investment types are essential. Source
Robust Data Management and Quality Control
The perception and learning capabilities of agentic AI are entirely dependent on the data it processes. Consequently, the quality and comprehensiveness of this data are critically important. Poor data leads to flawed perception and suboptimal decision-making.
- Agentic AI systems gather and decode information from sensors and databases to extract meaningful patterns. Source
- Emphasis must be placed on rigorous data validation processes, meticulous provenance tracking to understand data origins, and comprehensive quality assurance measures to ensure data integrity.
Accountability Mechanisms and Responsible AI Principles
In systems that make autonomous decisions, establishing clear lines of accountability is complex but vital. Governance frameworks must address who is responsible when an autonomous system makes an error or causes harm.
- This necessitates the establishment of clear accountability chains, the implementation of detailed audit trails for all significant actions, and defined intervention protocols. This is particularly crucial given the ambiguity that arises in traditional responsibility models when applied to autonomous entities.
Monitoring and Evaluation Systems
Continuous oversight is not a luxury but a necessity for agentic AI. These systems learn and adapt, making ongoing monitoring essential to ensure they remain aligned with their objectives and ethical guidelines.
- Agentic AI systems learn from interactions and feedback to improve over time. Source
- The implementation of real-time monitoring for decisions, outcomes, and any anomalous behaviors is crucial. This should be coupled with robust reporting mechanisms and alert systems to flag potential issues promptly.
Human Oversight and Intervention Protocols
While agentic AI is designed for autonomy, human involvement remains critical. Defining when and how humans should intervene ensures that systems do not operate outside acceptable bounds.
- Agentic AI operates independently without constant human intervention. Source
- Governance frameworks must detail specific circumstances that necessitate human review, establish clear escalation procedures for complex or high-stakes decisions, and provide mechanisms for human override when necessary.
Section 2: Fortifying Autonomous Agents – Best Practices for Security
The adaptive and autonomous nature of agentic AI introduces unique vulnerabilities. Therefore, robust best practices for agentic ai security are not merely an add-on but a fundamental requirement for their safe and reliable operation. These practices are designed to protect the agents themselves, the data they process, and the systems they interact with.

Secure Coding and Development Practices
Security must be integrated into the very fabric of an agent’s design and development, rather than being an afterthought. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of exploitable flaws.
- This includes secure API design, robust input validation to prevent malicious data injection, and strong encryption for data transmission, especially considering that agents often connect to a variety of external platforms and services. Source
Protection Against Adversarial Attacks and Manipulation
Agentic AI, like all AI systems, can be susceptible to adversarial attacks designed to deceive or manipulate its decision-making processes. Defending against these requires specialized strategies.
- This involves conducting thorough adversarial testing to identify weaknesses, implementing sophisticated anomaly detection for suspicious inputs or behaviors, and deploying damage limitation safeguards to contain any potential breaches or misoperations.
Data Privacy and Protection
Agentic AI systems often process vast amounts of data, some of which may be sensitive or personal. Protecting this data is paramount to maintaining user trust and complying with regulations.
- Techniques such as differential privacy, data minimization (collecting only what is strictly necessary), and the use of secure communication protocols are essential, particularly in regulated sectors like healthcare and finance. Source

Access Control and Authentication
Ensuring that only authorized entities can interact with or control agentic AI systems is fundamental to security. This applies to human users, other systems, and even inter-agent communication.
- Implementing multi-factor authentication for human access, role-based access control to limit permissions, stringent API security, and secure authentication protocols for agent-to-agent communication are critical given the often collaborative nature of agentic AI deployments. Source
Continuous Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Security is not a one-time setup. Ongoing vigilance and a well-defined plan for responding to security incidents are vital for maintaining a secure agentic AI environment.
- This includes utilizing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, establishing behavioral baselines to detect deviations, and developing incident response playbooks specifically tailored for autonomous AI systems. Importantly, these systems should also incorporate built-in guardrails for safety and compliance. Source
Section 3: The Moral Compass of Autonomy – Ethical Considerations
The increased autonomy of agentic AI brings with it profound ethical considerations for agentic ai deployment that extend beyond the ethical challenges of traditional AI. The capacity for independent action and decision-making necessitates a deeper examination of fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Fairness and Bias Mitigation
Agentic AI, powered by complex models, can inadvertently perpetuate or even amplify existing societal biases if not carefully managed. Ensuring fairness in their decision-making is a critical ethical imperative.
- Agents often leverage large language models for reasoning and making real-time decisions. Source
- This requires diligent bias audits, continuous fairness monitoring, and the implementation of effective correction mechanisms. The compounded effect of bias in multi-agent systems, where agents interact and influence each other, presents a particularly challenging area that needs careful consideration. Source
Transparency and Explainability
Understanding how an autonomous agent arrives at a particular decision can be difficult, creating a “black box” problem. Striving for transparency and explainability is crucial for trust and debugging.
- Agents are designed to interpret complex goals and context, making their internal reasoning processes intricate. Source
- Developing intuitive interpretability tools, ensuring accessible communication of the AI’s reasoning process, and establishing clear documentation standards for key actions are essential steps towards greater transparency.
Accountability for AI-Driven Outcomes
Determining responsibility when an agentic AI system is involved in an adverse outcome is a significant ethical and legal challenge. This is particularly acute in high-stakes applications.
- Consider an agentic AI deployed in healthcare. If an error leads to patient harm, assigning blame among the developers, the healthcare providers who deployed it, and the organization overseeing its operation becomes incredibly complex. Source (Agentic AI systems coordinating with multiple medical teams)
Impact on Employment and Societal Structures
The advanced capabilities of agentic AI, such as their ability to handle complex tasks, raise questions about their potential impact on the workforce and the broader societal fabric.
- Agentic AI can handle complex tasks like strategic planning, a leap from traditional automation which typically focuses on more routine operations. Source
- Organizations and policymakers must proactively assess potential employment impacts, develop strategies for workforce transition and retraining, and consider the necessary policy responses to mitigate negative societal consequences.
The Concept of AI Rights or Responsibilities
As agentic AI systems become more sophisticated and exhibit higher degrees of autonomy, philosophical questions arise regarding their potential status. This is a nascent but important area of consideration.
- While anthropomorphism can be misleading, the increasing autonomy of these agents invites contemplation on whether highly advanced systems might warrant certain protections or bear specific responsibilities in the future. It is critical, however, to avoid concepts that might obscure human accountability in the present.
Section 4: Bridging the Gap – Challenges in Adoption
Despite the immense potential of agentic AI, widespread adoption faces a number of significant hurdles. These challenges in agentic ai adoption span technical, organizational, regulatory, and societal domains, requiring concerted effort to overcome.
Technical Complexity and Integration Issues
Deploying and integrating agentic AI systems into existing infrastructure is often a complex technical undertaking, requiring specialized knowledge and significant investment.
- Agentic AI relies on underlying distributed systems platforms that enable simultaneous operation across multiple servers, demanding robust infrastructure. Source
- Key challenges include meeting stringent infrastructure requirements, integrating with legacy systems, ensuring interoperability between different AI components and other software, and maintaining overall system stability and reliability.

Lack of Skilled Personnel and Expertise
The rapid advancement of agentic AI has outpaced the development of a sufficient talent pool with the requisite skills to develop, deploy, and manage these systems.
- Expertise is needed across machine learning, natural language processing, knowledge representation, distributed systems, and specific domain knowledge. Source
- Specialized applications, such as those in regulatory compliance or fraud detection, require even deeper expertise. Source
- Addressing this shortage requires investment in training programs, fostering academic partnerships, and developing user-friendly agent builder tools to democratize access. Source
Regulatory Uncertainty and Evolving Legal Frameworks
The novelty of agentic AI means that existing legal and regulatory frameworks are often insufficient, creating uncertainty and hesitancy for organizations looking to adopt these technologies.
- There are significant gaps in current legislation concerning autonomous decision-making, liability attribution for AI actions, and robust data protection standards.
- Organizations must proactively engage with regulators, participate in the development of industry standards, and advocate for clear, adaptable legal frameworks.

Public Trust and Perception
Public apprehension regarding AI, fueled by concerns about bias, privacy violations, job displacement, and a perceived loss of human control, can significantly impede adoption.
- Building and maintaining public trust requires demonstrating the tangible benefits of agentic AI, ensuring transparency in its operations, establishing clear lines of accountability, and investing in public education initiatives to demystify the technology.
Cost of Development and Implementation
The financial investment required for developing, implementing, and maintaining agentic AI systems can be substantial, posing a barrier for many organizations.
- These costs encompass not only the initial development and infrastructure but also ongoing expenses related to talent acquisition, data management, and continuous maintenance, especially when dealing with multiple coordinating agents. Source
- A clear return on investment (ROI) evaluation, phased implementation strategies, and strategic partnerships can help mitigate these financial challenges.
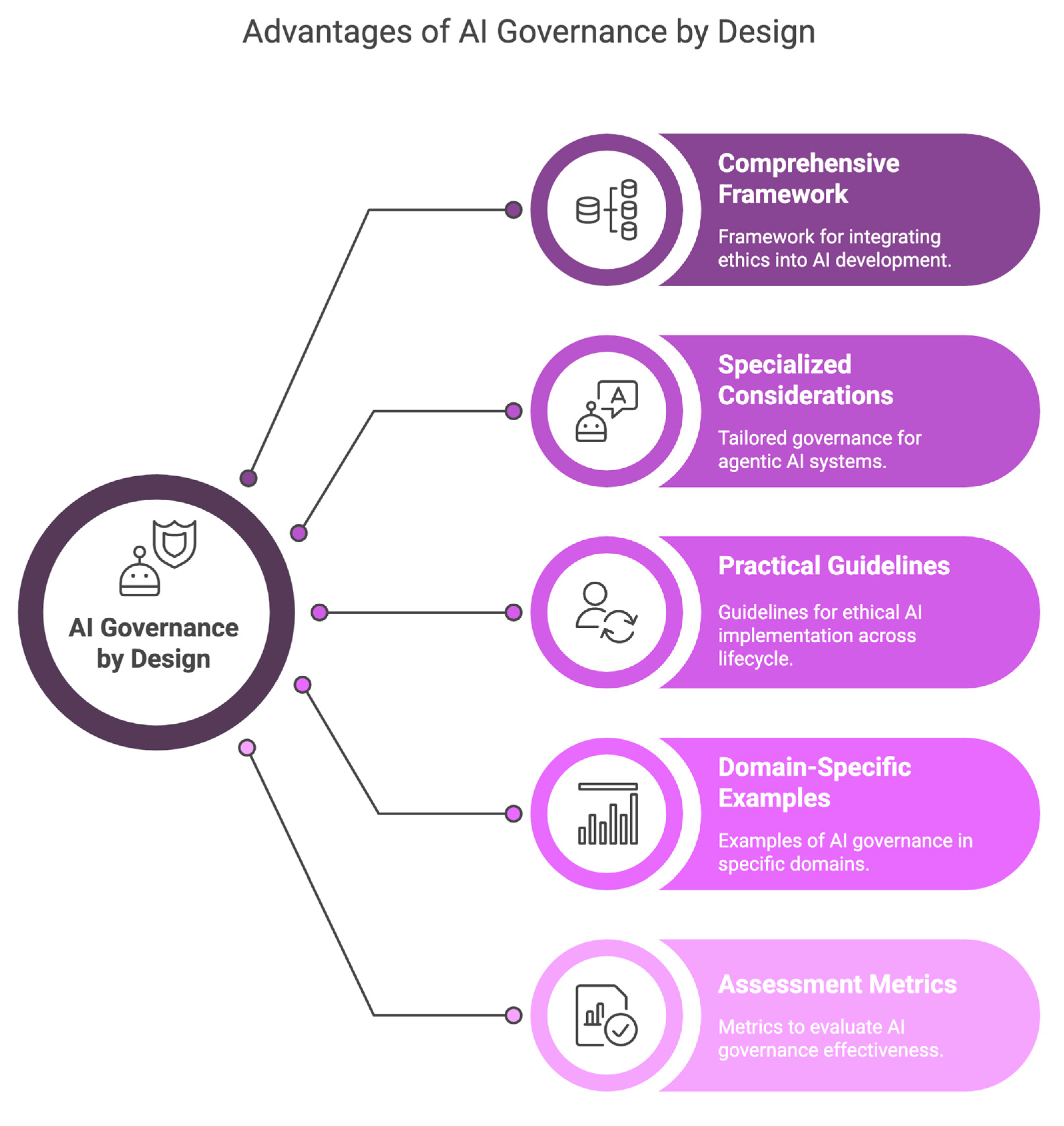
Section 5: Charting the Future – The Agentic AI Governance Framework 2025
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, a comprehensive and adaptable agentic ai governance framework 2025 will be crucial. This framework will need to synthesize the lessons learned from foundational elements, security best practices, ethical considerations, and adoption challenges to create a robust ecosystem for responsible AI.
Regulatory Bodies and Standards Organizations
We can anticipate increased activity from regulatory bodies and standards organizations worldwide. Their role will be vital in establishing baseline requirements, developing certification programs, and fostering international cooperation to ensure a globally consistent approach to agentic AI governance.

Adaptive Governance Mechanisms
The dynamic and learning nature of agentic systems demands governance mechanisms that are not static but adaptive. This means implementing processes for continuous monitoring, periodic re-evaluation, and agile updates to policies and guidelines to keep pace with technological advancements.
Multi-Stakeholder Governance Models
Effective governance will necessitate inclusive models that bring together diverse perspectives. This includes technologists, ethicists, domain experts, end-users, policymakers, and civil society representatives, ensuring that governance reflects a broad societal consensus.
Technical Solutions for Governance
Leveraging technology itself to facilitate governance will be a key trend. This includes the advanced use of explainable AI (XAI) tools, formal verification methods, robust digital audit trails, and sophisticated AI monitoring systems to provide oversight and accountability.
- As previously noted, the importance of built-in guardrails and safety constraints cannot be overstated. Source
Sector-Specific Frameworks
A one-size-fits-all approach to governance will likely prove insufficient. The framework will need to accommodate sector-specific nuances, with tailored guidelines for industries such as healthcare, finance, transportation, and supply chain management.
- For example, governance for healthcare agents coordinating across medical teams will differ significantly from that for supply chain agents monitoring inventory levels. Source (Healthcare), Source (Supply Chain)
Emphasis on Proactive Governance
The future framework will strongly emphasize proactive governance. This involves anticipating potential risks and challenges through scenario planning, rigorous red teaming exercises, and horizon scanning to identify emerging trends and threats before they materialize.
Concluding Thoughts: Shaping a Trustworthy AI Future
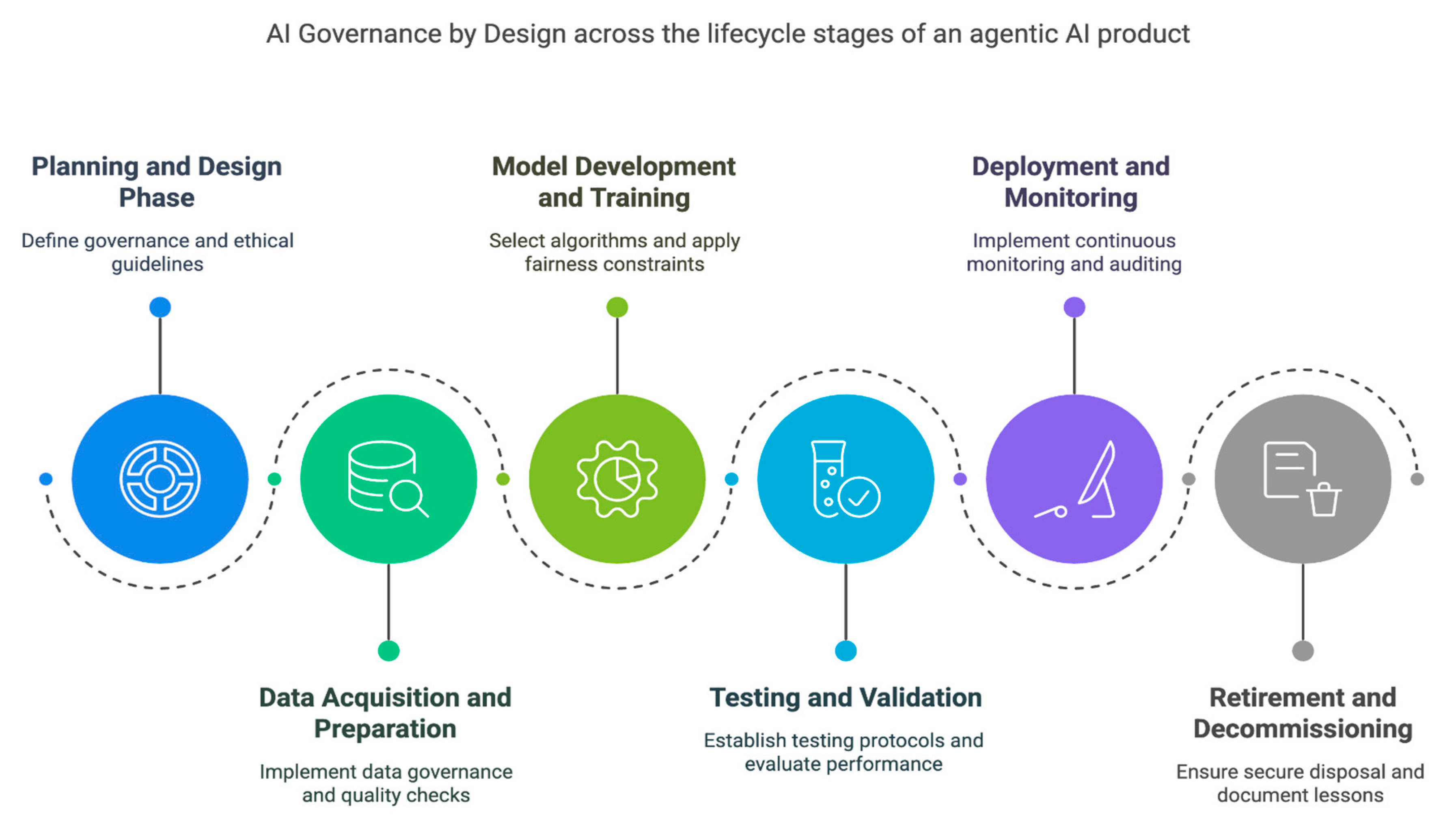
The journey towards integrating agentic AI into our lives is complex and multifaceted. It requires a holistic approach that deeply considers the interconnectedness of foundational governance elements, robust security measures, profound ethical implications, and the practical challenges inherent in adoption. The evolving agentic ai governance framework 2025 will be central to navigating this path responsibly.
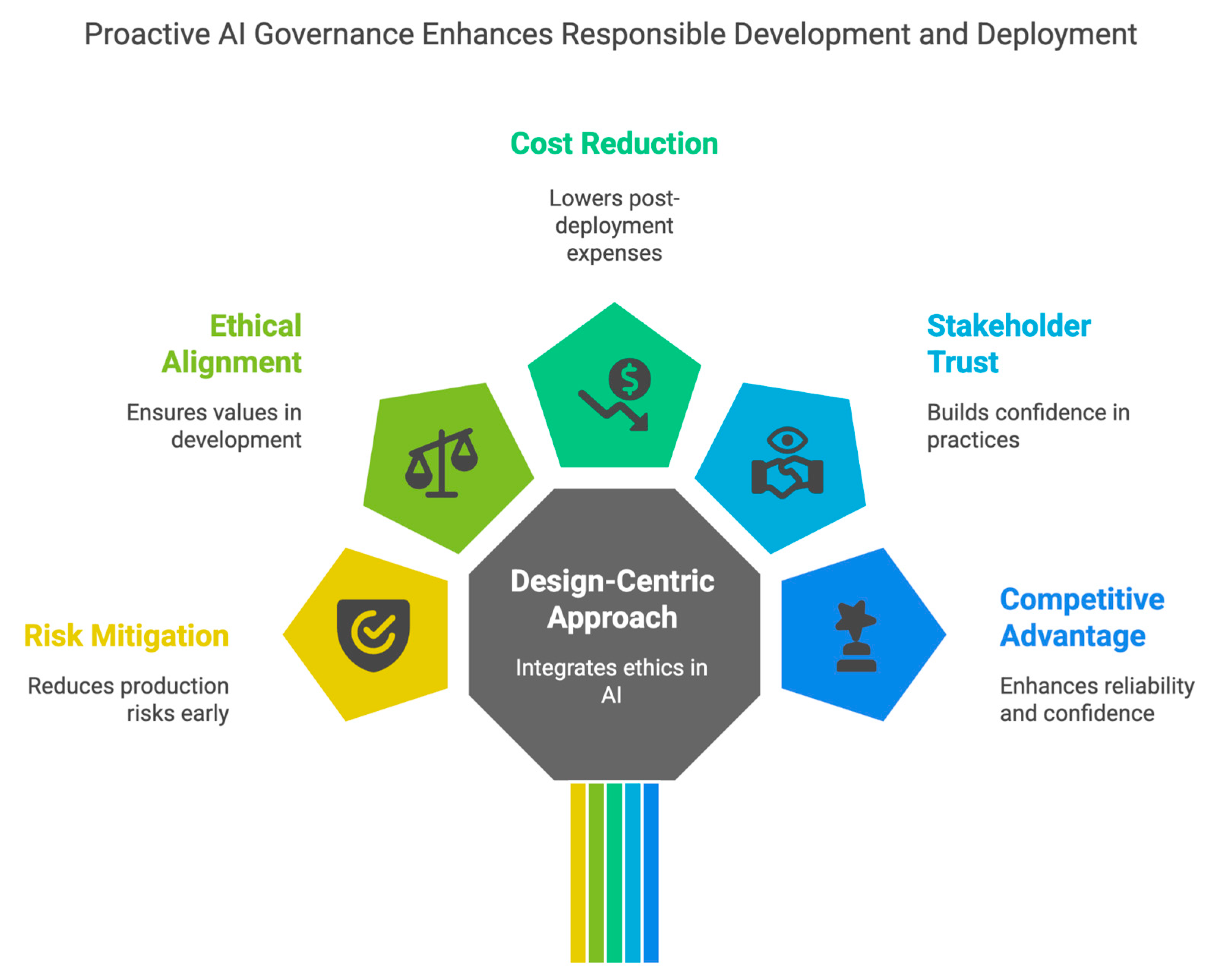
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in artificial intelligence, the imperative is clear. Organizations, policymakers, and technology providers must collectively prioritize the development and implementation of robust governance structures for agentic AI. The proactive measures we take today will not only define the responsible development and deployment of these powerful systems but will ultimately shape the very fabric of our AI-enabled future, ensuring it is trustworthy, beneficial, and aligned with human values.
“`