The Profound Impact of AI on UK Jobs: Disruption, Transformation, and Opportunity
Estimated reading time: 8-10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- The impact of AI on UK jobs is complex, encompassing job displacement, creation, and augmentation, rather than simple destruction.
- UK businesses AI adoption trends show large enterprises leading, with uneven integration and most firms in early stages of implementation.
- Generative AI productivity benefits UK businesses are realizing include enhanced efficiency in content creation, software development, design, and customer service.
- Critical to navigating the AI revolution is robust AI skills development UK workforce initiatives, focusing on both technical and crucial soft skills.
- The future of work UK artificial intelligence promises significant labor market transformation, driven by new job categories, evolving business models, and the need for proactive policy and ethical considerations.
Table of contents
- The Profound Impact of AI on UK Jobs: Disruption, Transformation, and Opportunity
- Key Takeaways
- Current Landscape: How UK Businesses are Adopting AI
- Unlocking Potential: The Productivity Benefits of Generative AI in the UK
- Bridging the Gap: Prioritising AI Skills Development for the UK Workforce
- The Horizon: Shaping the Future of Work in the UK with Artificial Intelligence
- Closing
- Frequently Asked Questions
The digital age has ushered in an era where Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not just a concept of science fiction, but a pervasive force actively reshaping our world. From personalized recommendations to sophisticated automation systems, the influence of AI touches nearly every facet of modern life, leading to widespread curiosity, and often, a degree of concern, about its implications for employment globally. As this technological tide rises, one of the most pressing questions on many minds, particularly in the United Kingdom, revolves around the pervasive presence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its profound impact on jobs.
This blog post delves into the central theme: the profound impact of AI on UK jobs. It’s crucial to understand that this is a multifaceted and rapidly evolving phenomenon, encompassing not just disruption, but significant transformation and the opening of entirely new opportunities. While some job displacement is indeed expected due to automation and efficiency gains, the overall effect is far from a simple narrative of loss. Instead, we anticipate the creation of new roles, a heightened demand for novel skills, and potential productivity gains that promise to benefit the broader economy, fostering growth and innovation across sectors. (Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company, PwC).

Join us on a comprehensive journey as we explore the current UK businesses AI adoption trends, examining how organizations across the nation are integrating these powerful tools. We will then dive into the specific generative AI productivity benefits UK is beginning to realize, illustrating how AI can augment human capabilities. Following this, we address the crucial need for AI skills development UK workforce, highlighting the competencies required for future success. Finally, we will look ahead to the future of work UK artificial intelligence, considering the long-term implications and strategic imperatives for individuals and organizations alike.
Current Landscape: How UK Businesses are Adopting AI
To understand the evolving job landscape, it’s essential to first grasp the current UK businesses AI adoption trends. Adoption of AI technologies in the UK is presently driven predominantly by large enterprises. More than a third of mid-sized businesses (those with 250+ employees) are now actively utilizing AI technologies in some capacity. In contrast, smaller firms are comparatively slower to integrate these tools into their operations, often due to perceived cost barriers, lack of expertise, or an unclear return on investment. This creates a significant disparity in the pace of digital transformation across the UK business ecosystem. (Source: McKinsey & Company).
The sectors leading this adoption are typically those with a high volume of repetitive or data-intensive tasks. Widespread integration is most notably observed in finance, professional services, information technology, and certain advanced manufacturing areas. These industries are naturally positioned to leverage AI for process optimization, data analytics, and automation, driving efficiency gains. (Source: McKinsey & Company).

It’s important to note that AI implementation remains uneven across organizations. Most businesses are still in the early stages of their AI journey, often deploying tools like chatbots for customer support or virtual assistants for routine inquiries. These are common, “horizontal” applications of AI that can be easily integrated without a complete overhaul of existing systems. More transformative and deeply embedded uses of AI, such as sophisticated predictive analytics or fully autonomous decision-making systems, are largely still in pilot phases or confined to specialized departments. This indicates that the full potential of AI’s integration into the UK economy is yet to be fully realized. (Source: McKinsey & Company, PwC).
Examining the initial impact of AI on UK jobs within the workforce, we observe several key trends:
- Automation of routine jobs: AI is increasingly capable of automating repetitive, predictable tasks that previously required human input. This is particularly evident in clerical, administrative, and certain technical support roles. For instance, tasks like data entry, scheduling, or basic report generation are prime candidates for AI workflow automation for businesses, freeing up human workers for more complex duties. (Penbrief – AI workflow automation for businesses).
- Augmentation of existing jobs: Beyond mere replacement, AI often serves to enhance human workers’ capabilities. This is particularly true in knowledge-based professions, where AI systems can act as powerful decision-support tools. For example, AI can sift through vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and offer insights, allowing human analysts, doctors, or financial advisors to make more informed and efficient decisions. This augmentation transforms roles, making them more strategic and less about manual data processing.
- Emergence of new job categories: The rise of AI is simultaneously creating entirely new occupations that simply didn’t exist a decade ago. Roles such as AI ethics officers, responsible for ensuring fairness and transparency in AI systems; machine learning engineers, who design and build AI models; and prompt engineers, specializing in crafting effective queries for generative AI models, are becoming increasingly vital. These new jobs highlight the evolving nature of demand in the labor market. (Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company).
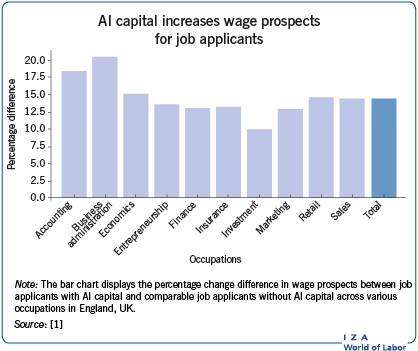
From a quantitative perspective, estimates suggest that between 1 and 3 million UK jobs could eventually be displaced by AI. This range accounts for various adoption speeds and technological advancements. One example of this trend is seen in Amazon generative AI workforce reduction, as companies increasingly leverage AI to streamline operations. However, it’s crucial to emphasize that these potential losses are expected to occur gradually over many years, allowing time for adaptation and reskilling. When compared to historical annual job losses in the UK – which naturally occur due to business closures, industry shifts, and economic downturns – these figures are relatively modest. More importantly, AI is widely anticipated to increase overall labor market dynamism and ultimately generate new jobs through economic growth, the creation of new products and services, and the evolution of existing business models. The efficiency gains and innovation spurred by AI can lead to expansion in other areas, offsetting initial displacements. (Source: Institute for Global Change, PwC).

Unlocking Potential: The Productivity Benefits of Generative AI in the UK
Beyond the general impact of AI, a specific subset of the technology, generative AI, is beginning to demonstrate significant transformative power. We are starting to witness the tangible generative AI productivity benefits UK is realizing. Generative AI, capable of creating new content, code, or designs, is proving most impactful in enhancing human productivity across a wide array of functions and industries.
Let’s explore some concrete examples of how generative AI is improving efficiency across different domains:
- Content creation: From drafting initial reports and internal memos to generating sophisticated marketing copy, engaging social media posts, or even contributing to creative content like scripts and story outlines, generative AI tools automate much of the foundational work. This allows content creators to focus on refining, strategizing, and adding unique human insights, dramatically accelerating the production cycle. The unstoppable AI-generated content revolution is well underway, transforming how information is produced and consumed.
- Software development: Code assistants powered by generative AI are rapidly becoming indispensable tools for developers. They can suggest code completions, identify and debug errors, generate boilerplate code, and even translate code between different programming languages. This significantly speeds up development cycles, reduces the likelihood of bugs, and allows engineers to concentrate on complex architectural challenges and innovative solutions rather than routine coding.
- Design: AI tools are revolutionizing graphic design, product prototyping, and even architectural rendering. Designers can use AI to generate multiple design variations, create realistic mock-ups, or iterate rapidly on concepts. This democratizes sophisticated design capabilities and allows creative professionals to explore more possibilities in less time, pushing the boundaries of what’s achievable.
- Marketing: In marketing, generative AI can produce personalized campaign materials at scale, generate diverse ad copy variations for A/B testing, or even brainstorm entirely new campaign ideas based on market data and trends. This level of automation and personalization empowers marketing teams to reach audiences more effectively and efficiently, optimizing their spend and impact.
- Customer service augmentation: While not replacing human agents entirely, AI-powered tools are augmenting customer service operations significantly. These systems can instantly retrieve vast amounts of information, suggest relevant responses, or even draft replies for human agents to review. This enhances response times, ensures consistency, and allows human agents to dedicate their attention to complex or emotionally sensitive customer interactions.

The core benefit is clear: these tools enable workers to delegate repetitive, mundane, or time-consuming tasks to AI. This strategic delegation frees up valuable human time, allowing professionals to dedicate their mental energy and expertise to higher-value, more creative, and strategic activities. This shift is fundamental to boosting overall productivity and fostering innovation within organizations. (Source: McKinsey & Company, PwC).
UK businesses that are actively deploying generative AI are reporting demonstrable improvements in the speed of task completion, consistency of output, and scalability of operations. While the promise of generative AI is immense, it’s acknowledged that large-scale, truly transformative benefits are still evolving. Organizations are currently in a learning phase, figuring out how to fully integrate these advanced tools into their core operations and workflows to maximize their impact. This direct contribution to efficiency and innovation by generative AI positively influences the overall impact of AI on UK jobs by fostering economic growth and creating new avenues for value creation.
Bridging the Gap: Prioritising AI Skills Development for the UK Workforce
As AI continues to reshape industries, the need for a skilled workforce becomes paramount. This presents both a critical challenge and an immense opportunity for the AI skills development UK workforce. Ensuring that the UK population has the competencies to thrive in an AI-driven economy is not merely a matter of economic competitiveness, but one of social equity and future prosperity. (Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company).

The types of skills increasingly in demand in an AI-driven economy can be broadly categorized into technical and soft skills. Companies like Amazon are also actively investing in Amazon AWS generative AI workforce initiatives to equip their employees with these crucial skills.
- Technical skills: These form the foundational knowledge for interacting with, developing, and managing AI systems. They include:
- Data analysis: The ability to collect, process, and interpret large datasets, which are the lifeblood of AI.
- Coding: Proficiency in languages like Python and R, essential for data science, machine learning development, and automation scripting.
- Machine learning concepts: Understanding the principles behind various machine learning algorithms, their applications, and limitations.
- Prompt engineering: The increasingly vital art of crafting effective and precise queries or instructions for generative AI models to achieve desired outputs. This involves understanding how AI interprets language and iterating to optimize results.
- General AI literacy: A broader understanding of how AI works, its capabilities, ethical implications, and practical limitations, enabling individuals to confidently integrate AI into their work and personal lives.
- Soft skills: Often overlooked, these human-centric skills become even more valuable in an AI-augmented world, as AI takes over routine cognitive tasks. They include:
- Critical thinking: The capacity to analyze information objectively, identify biases, and evaluate the outputs of AI systems.
- Creativity: Generating novel ideas, solutions, and approaches that AI, by its nature, cannot replicate.
- Adaptability: The willingness and ability to learn new technologies and processes as they rapidly evolve.
- Problem-solving: Tackling complex, unstructured problems that require human ingenuity and nuanced understanding.
- Emotional intelligence: Understanding and managing one’s own emotions and those of others, crucial for teamwork, leadership, and customer interaction.
- Ethical reasoning: Navigating the moral and societal implications of AI, ensuring its responsible and beneficial application.
(Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company).
Numerous initiatives are focused on developing these critical competencies across the UK:
- Government-funded training schemes: The UK government has launched various programs, such as the National Skills Fund, aimed at providing adults with access to training courses in high-demand areas, including digital and AI skills. Additionally, specific initiatives like AI and Data Science Master’s conversion courses encourage graduates from non-STEM backgrounds to transition into AI roles.
- Educational institutions: Universities and colleges are rapidly expanding their offerings. This includes specialized degrees in AI, machine learning, and data science, as well as apprenticeships that combine on-the-job training with formal education. Short courses and micro-credentials are also emerging to quickly upskill existing professionals.
- Private companies: Forward-thinking businesses are heavily investing in internal training programs, recognizing that upskilling their current workforce is often more efficient than constantly recruiting new talent. Many are also forging partnerships with ed-tech platforms and online learning providers to offer flexible and accessible training modules, actively encouraging a culture of continuous learning among their employees.

These initiatives are absolutely vital to ensure that UK workers can not only adapt but thrive in an AI-driven economy. Continual investment in talent development is pivotal for leveraging AI’s immense benefits while simultaneously minimizing the potential disruption to individual livelihoods. This proactive approach to skills development will directly shape the positive trajectory of the future of work UK artificial intelligence and play a crucial role in managing the overall impact of AI on UK jobs, fostering a resilient and adaptable labor market. (Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company).
The Horizon: Shaping the Future of Work in the UK with Artificial Intelligence
Looking ahead, the long-term outlook for the future of work UK artificial intelligence indicates a profound reshaping of the UK labor market. This transformation will be characterized by ongoing job evolution and significant creation, rather than a catastrophic reduction in employment opportunities. AI’s pervasive integration means that few jobs will remain untouched; instead, many will be redefined, augmented, or replaced by entirely new types of roles.

Certain industries are expected to witness substantial growth and the emergence of entirely new job categories. Notably, the technology sector itself will continue to expand, demanding more AI researchers, developers, data scientists, and ethical AI specialists. Health care stands to be revolutionized, with new roles in AI-assisted diagnostics, personalized medicine, and robotic surgery support. Education will see growth in fields related to AI tutors, adaptive learning platforms, and instructional designers specializing in AI-driven curricula. Furthermore, AI will catalyze the birth of entirely new digital industries and services, similar to the emergence of autonomous vehicle innovations in the UK, creating unforeseen job opportunities and economic sectors. (Penbrief – Breakthrough UK autonomous vehicle innovations). (Source: PwC, Institute for Global Change).
It is crucial to emphasize that any job displacement will be a gradual process, not a sudden, overnight shift. This allows time for workers to adapt, reskill, and transition. Historically, transformative technologies, such as the advent of electricity or the internet, also caused initial disruptions but ultimately led to vastly increased productivity, economic growth, and a net creation of jobs. AI is anticipated to follow a similar trajectory, fostering overall job growth through increased efficiency, innovation, and the development of new markets and services. (Source: PwC).
Accompanying these changes is an increasing demand for adaptable, “future-proof” skills. The labor market will continue to shift away from narrow, routine vocations that are susceptible to automation. Instead, it will prioritize competencies that leverage uniquely human attributes: creativity, critical thinking, complex problem-solving, emotional intelligence, and cross-functional collaboration. Lifelong learning will not just be an advantage but a necessity for individuals navigating this dynamic landscape. (Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company).
Addressing crucial policy considerations and ethical implications will be paramount to ensure a fair and equitable transition for the UK labor market. This includes proactive measures to mitigate potential downsides of AI, such as:
- Skill mismatches: Governments and educational institutions must collaborate to develop policies that bridge the gaps between available skills and emerging industry needs. This involves forecasting future skill demands and designing agile training programs.
- Fair transitions: Robust support mechanisms are needed for workers whose roles are at risk of automation. This could include expanded reskilling programs, effective job placement services, and discussions around potential social safety nets to cushion the impact of economic shifts.
- Ethical issues: As AI becomes more sophisticated, so do the ethical considerations. Key concerns include:
- Algorithmic bias: Ensuring AI systems do not perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases in hiring, lending, or other critical decisions.
- Data privacy concerns: Protecting sensitive personal and corporate data as AI systems process increasingly vast amounts of information.
- Responsible use of AI in workforce surveillance or performance management: Developing guidelines to prevent AI from being used in ways that infringe on worker rights or create unfair performance metrics. The UK is actively engaging in mind-blowing AI regulations UK to address these complex issues.
(Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company).
The ongoing need for adaptability and continuous learning for both individuals and organizations cannot be overstated. Navigating this evolving landscape effectively requires a proactive mindset, embracing change, and investing in human capital. This holistic approach will underscore the dynamic and ever-present impact of AI on UK jobs, shaping the nation’s economic destiny.

Closing
In conclusion, the impact of AI on UK jobs is far from a simple narrative of widespread job destruction. Instead, it is a profoundly complex and ongoing transformation of the labor market. It’s a story where significant productivity gains, boundless innovation, and the creation of entirely new roles are balanced against some degree of job displacement and the critical need to address potential inequalities for those unable or less equipped to adapt. This nuanced perspective is essential for understanding and responding to the AI revolution. (Source: Institute for Global Change, McKinsey & Company, PwC).
To reiterate the key takeaways, success in this new era hinges on several interconnected factors: the paramount importance of proactive AI skills development UK workforce, ensuring individuals are equipped with both technical and human-centric capabilities; the strategic evolution of UK businesses AI adoption trends, with a focus on smart and ethical integration; and harnessing the significant generative AI productivity benefits UK stands to gain to drive economic growth and competitiveness.
The future of work UK artificial intelligence is not a predetermined fate, but a landscape that can be shaped through foresight and deliberate action. The UK is uniquely positioned to proactively harness AI’s immense benefits while intelligently mitigating its inherent challenges. This requires a collective will and collaborative effort from policymakers, businesses, educational institutions, and individuals.
Ultimately, the call to action is clear: embrace continuous learning, adapt to new technologies with an open mind, and collaborate on policies that support both innovation and worker resilience. By doing so, the UK can ensure a prosperous and equitable transition into the age of AI, fostering a dynamic economy where human ingenuity and artificial intelligence work in powerful synergy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary impact of AI on UK jobs?
The primary impact of AI on UK jobs is a complex transformation rather than simple destruction. While AI will automate routine tasks, potentially displacing some roles, it is also driving significant productivity gains, augmenting existing jobs by enhancing human capabilities, and crucially, creating entirely new job categories and industries. The overall effect is expected to be a net positive for job creation in the long run.
Which UK sectors are leading in AI adoption?
Sectors in the UK that are leading in AI adoption are typically those with high volumes of data and repetitive tasks. These include finance, professional services, IT, and certain areas of manufacturing. Large enterprises are at the forefront of this adoption, utilizing AI for applications like chatbots, data analytics, and process automation.
How is generative AI benefiting UK productivity?
Generative AI is significantly boosting UK productivity by enhancing efficiency across various functions. It automates tasks in content creation (e.g., drafting reports, marketing copy), software development (e.g., code assistants), design (e.g., generating prototypes), marketing (e.g., personalized campaigns), and customer service (e.g., assisting human agents). This frees up human workers for higher-value, creative, and strategic activities.
What skills are most important for the UK workforce in an AI-driven economy?
In an AI-driven economy, both technical and soft skills are crucial. Technical skills include data analysis, coding (e.g., Python), machine learning concepts, and prompt engineering. Essential soft skills are critical thinking, creativity, adaptability, complex problem-solving, emotional intelligence, and ethical reasoning, as these are uniquely human capabilities that complement AI.
What are the key policy considerations for the future of work with AI in the UK?
Key policy considerations for the UK’s future of work with AI include addressing potential skill mismatches through targeted training, ensuring fair transitions for displaced workers with reskilling and support programs, and tackling ethical issues such as algorithmic bias, data privacy, and the responsible use of AI in workforce management.