“`html
AI Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation
Estimated reading time: 15 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a pivotal technology in addressing the global challenge of climate change.
- Digital technologies, including AI, could cut emissions by up to 20% by 2050 in key sectors (source: climatepolicylab.org).
- AI applications in climate actions could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 4% by 2030, equivalent to the combined yearly emissions of Australia, Canada, and Japan (source: carboncredits.com).
- AI revolutionizes climate action by analyzing vast datasets, optimizing complex systems, and accurately predicting environmental patterns.
- AI is crucial for **AI driven decarbonization strategies 2025**, which involve a proactive approach to reducing carbon emissions across various sectors.
- AI offers specific solutions in energy optimization, transportation, industrial processes, and climate adaptation.
- The **environmental impact of generative AI** is a significant consideration, requiring energy-efficient solutions.
- AI plays a vital **role in achieving net zero emissions** through monitoring, R&D acceleration, and carbon management.
- The **future of AI in climate tech innovation** promises more sophisticated applications and discoveries.
- Challenges like the digital divide and data limitations need addressing for equitable AI deployment in climate action.
Table of contents
- AI Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding AI’s Transformative Power in Climate Action
- Specific AI Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation
- Energy and Grid Optimization
- Transportation and Urban Planning
- Industrial Process Optimization
- Climate Adaptation and Early Warning Systems
- Addressing the Environmental Impact of AI Itself
- The Role of AI in Achieving Net Zero Emissions
- The Future of AI in Climate Tech Innovation
- Challenges and Considerations for AI in Climate Action
- Concluding Thoughts on AI and a Sustainable Future
The urgency of climate change is no longer a distant threat; it is a present reality demanding immediate and innovative solutions. In this critical battle, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a pivotal technology, offering powerful **AI solutions for climate change mitigation**. From driving decarbonization efforts to understanding and mitigating its own environmental footprint, AI is set to play a multifaceted role in achieving global net-zero goals.
The potential impact is substantial: digital technologies, including AI, could cut emissions by up to 20% by 2050 in sectors like energy, materials, and mobility (source: climatepolicylab.org). Furthermore, AI applications specifically focused on climate actions could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by a remarkable 4% by 2030. This reduction is equivalent to the combined yearly emissions of nations like Australia, Canada, and Japan (source: carboncredits.com). The integration of AI into climate strategies represents a paradigm shift, moving towards more data-driven, optimized, and effective interventions.

Understanding AI’s Transformative Power in Climate Action
AI technologies are fundamentally revolutionizing how we approach climate action. Their capacity to analyze vast, complex datasets far exceeds human capabilities, enabling the optimization of intricate systems and the accurate prediction of environmental patterns. This analytical prowess allows for more precise and effective interventions than traditional methods can achieve.
Central to this transformation are **AI driven decarbonization strategies 2025**. This concept defines a proactive, comprehensive approach aimed at significantly reducing carbon emissions across all sectors. AI, particularly machine learning, is instrumental in pinpointing emission hotspots, optimizing energy usage in real-time, and accelerating the deployment and integration of renewable energy sources. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) highlights AI’s potential in this domain, while also acknowledging the associated risks and challenges, especially for developing countries (source: unfccc.int).

The ability of AI to process and derive insights from enormous volumes of data leads to more targeted and impactful climate solutions. This data-driven approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively and that mitigation efforts are grounded in robust scientific understanding and predictive analysis.
Specific AI Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation
AI offers a diverse range of **AI solutions for climate change mitigation** across several critical sectors:
Energy and Grid Optimization
- AI-powered energy management systems are significantly improving grid efficiency. These systems precisely forecast power demand, enabling better integration and optimization of renewable energy sources like solar and wind (source: unfccc.int).
- AI excels at predicting solar and wind energy generation, identifying optimal locations for new renewable energy facilities, and conducting predictive maintenance on green energy infrastructure. This ensures maximum output and minimizes downtime (source: news.mit.edu).
- The electrical grid is one of the largest and most complex machines ever built. AI plays a vital role in monitoring transmission wire capacity to maximize efficiency and reduce energy waste by intelligently managing power flow (source: news.mit.edu).

Transportation and Urban Planning
- AI tools analyze vast amounts of traffic data to optimize traffic flow and routing. This leads to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions in urban environments (source: unfccc.int).
- AI-driven urban resilience planning identifies infrastructure vulnerabilities to climate impacts and optimizes land use to minimize carbon footprints. This helps cities adapt to and mitigate climate change (source: unfccc.int).
- Smart city initiatives leverage AI to coordinate traffic signals, optimize public transport schedules, and integrate electric vehicle (EV) charging networks, creating more sustainable and efficient urban mobility systems.

Industrial Process Optimization
- AI algorithms are adept at identifying inefficiencies within industrial processes. By analyzing real-time sensor data, AI can optimize operations to minimize energy and material waste, and strategically align production schedules with the availability of renewable energy sources (source: unfccc.int).

Climate Adaptation and Early Warning Systems
- AI significantly strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. It provides greater accuracy and longer lead times, allowing for more effective preparedness and response (source: unfccc.int).
- Google’s Flood Forecasting System is a prime example of AI providing early warnings for risk-informed planning. This system utilizes AI to predict flood events with remarkable precision (source: ecoskills.academy).
- AI is used to analyze satellite and sensor data for biodiversity monitoring, promoting sustainable water management, and supporting land restoration efforts (source: unfccc.int).
- AI’s ability to rapidly measure changes, such as Arctic iceberg melt rates, provides critical data on meltwater release, contributing to a better understanding of climate impacts (source: climatepolicylab.org).

Addressing the Environmental Impact of AI Itself
While AI offers immense potential for climate solutions, it’s crucial to directly address the **environmental impact of generative AI explained**. The very processes of training and deploying large AI models require significant computational resources. This, in turn, leads to considerable energy consumption and associated carbon emissions (source: news.mit.edu).

The carbon footprint of any AI application is not uniform; it varies significantly based on factors such as the size and complexity of the AI model, the duration of its training, and, critically, the source of the electricity used to power the computations. Generative AI, known for its sophisticated capabilities, often comes with particularly high computational demands.
In response, there is a growing focus on developing more energy-efficient AI algorithms and specialized hardware designed to reduce power consumption. Furthermore, the introduction of frameworks like the Net Climate Impact Score is essential for evaluating AI projects. This framework aims to ensure that AI initiatives contribute positively to environmental goals, striving for net positive environmental outcomes (source: news.mit.edu).
The Role of AI in Achieving Net Zero Emissions
The **role of AI in achieving net zero emissions** extends far beyond direct emission reductions. AI is instrumental in sophisticated monitoring, precise measurement, and transparent reporting, which are all foundational to reaching ambitious climate targets (source: penbrief.com).

AI enables precise carbon accounting across entire industries. By analyzing complex data streams, AI increases transparency and accuracy in tracking emissions, making it easier for organizations to understand their impact and identify areas for improvement (source: carboncredits.com).
Furthermore, AI plays a critical role in accelerating research and development (R&D) for new low-carbon technologies and materials. By analyzing vast datasets of material properties and experimental results, AI can significantly speed up the discovery and optimization of innovative solutions (source: penbrief.com).
**AI-driven carbon management** platforms are emerging as powerful tools for organizations. These platforms allow for real-time tracking of emissions, identification of reduction opportunities, and verification of mitigation strategies, streamlining the entire carbon management process (source: penbrief.com).
AI also supports targeted policy interventions. By analyzing economic and environmental data, AI can identify the most impactful approaches for policymakers, ensuring that climate strategies are evidence-based and effective (source: news.mit.edu).
The Future of AI in Climate Tech Innovation
Looking ahead, the **future of AI in climate tech innovation** promises even more sophisticated and transformative applications. We can anticipate AI models capable of simulating complex Earth system interactions with unprecedented accuracy, leading to advanced climate modeling systems (source: penbrief.com).

AI’s ability to accelerate scientific discovery by identifying subtle patterns in large datasets will be crucial in fields like materials science, leading to breakthroughs in sustainable technologies. The increasing sophistication of machine learning (ML) models will enhance our ability to predict long-term climate trends and rigorously evaluate the effectiveness of various mitigation strategies (source: penbrief.com).
Innovative AI applications are also emerging in areas like waste management. Smart waste sorting systems, powered by AI, can significantly improve recycling rates and support the development of a circular economy. Companies like Greyparrot are demonstrating the impact of such AI solutions in this critical sector (source: ecoskills.academy).

Challenges and Considerations for AI in Climate Action
Despite its immense promise, the widespread deployment of AI in climate action faces several significant challenges. One critical issue is the **digital divide** and the unequal access to AI-driven solutions. Developing countries, in particular, may struggle to leverage these technologies due to infrastructure limitations and resource constraints (source: climatepolicylab.org).

Other challenges include limitations in data availability and quality, resource constraints for implementing complex AI systems, and the need for specialized expertise to develop, deploy, and maintain these solutions (source: ecoskills.academy).
There is a clear need for ongoing training and capacity building for professionals to effectively utilize AI in climate resilience efforts. Given the dynamic and complex nature of climate systems, the careful validation and continuous updating of AI climate solutions are paramount to ensure their accuracy and reliability.

Finally, effective development and scaling of AI climate solutions require robust collaboration among companies, regulatory bodies, and research institutions. This interdisciplinary approach is essential for navigating the complexities and ensuring that AI truly serves as a force for positive climate action (source: news.mit.edu).
Concluding Thoughts on AI and a Sustainable Future
The significant potential of AI as a powerful tool for **AI solutions for climate change mitigation** cannot be overstated. It offers a pathway to more effective and efficient strategies for tackling the climate crisis.
We are witnessing a convergence of critical advancements: the implementation of **AI driven decarbonization strategies 2025**, the development of energy-efficient AI technologies, and the increasing understanding of the **role of AI in achieving net zero emissions**. These trends point towards a future where AI is an indispensable partner in our climate efforts.
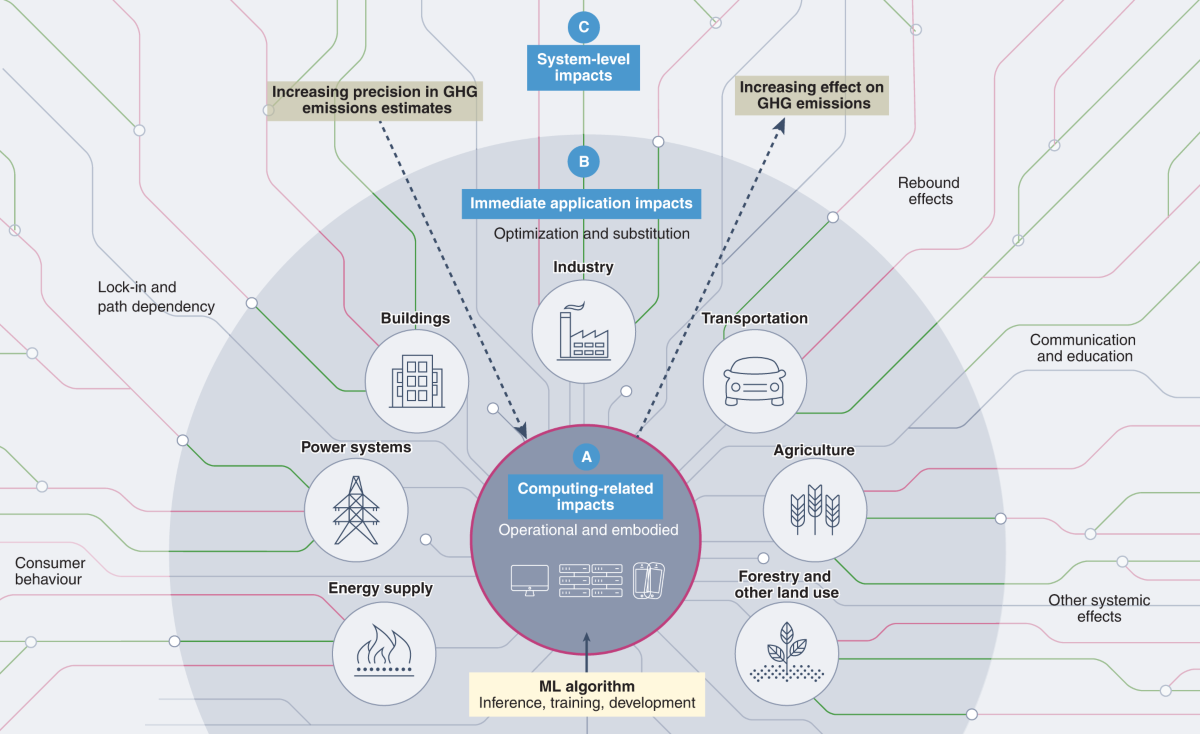
However, it is critically important to emphasize the need for responsible stewardship of AI. We must ensure that AI is developed and deployed in a manner that results in a net positive impact on the environment, carefully considering and mitigating its own footprint.
The transformative power of AI in addressing the climate crisis and building a sustainable future is immense. Yet, this potential can only be fully realized by balancing continuous innovation with a deep commitment to responsibility and equitable access to these groundbreaking technologies.
“`






