Bone Conduction Audio While Eating: The Ultimate Guide to Hands-Free Sound
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Bone conduction audio while eating offers a novel, hygienic way to enjoy music or podcasts without blocking your ear canals.
- This technology transmits music through vibrations directly through your skull bones to the inner ear, bypassing the eardrum.
- It excels during meals by maintaining situational awareness, preventing earbuds from falling out, and avoiding hygiene issues.
- As part of the growing ecosystem of wearable audio gadgets, bone conduction represents a leap in creative sound tech.
- While audio quality may differ from traditional headphones, the benefits for active, awareness-focused scenarios are significant.
Table of Contents
- Bone Conduction Audio While Eating: The Ultimate Guide to Hands-Free Sound
- Key Takeaways
- The Lunchtime Dilemma: A Relatable Hook
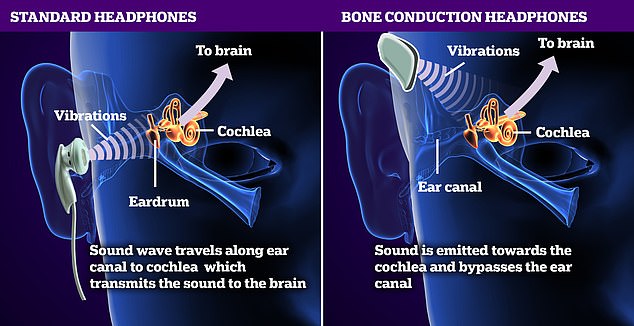
- What Is Bone Conduction Audio?
- The Science Behind the Vibrations
- Why It’s Perfect for Meals
- Bone Conduction vs. Traditional Headphones: A Comparison
- Wearable Audio Gadgets: The Bigger Picture
- Beyond Eating: Versatility of Creative Sound Tech
- Pros, Cons, and Technical Limitations
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Lunchtime Dilemma: A Relatable Hook
Picture this: you’re at lunch, ready to unwind with your favorite podcast or playlist. You pop in your earbuds, but within minutes, they’re slipping out as you chew, getting greasy from handling food, or worse—amplifying the sounds of your own chewing until it’s all you can hear. Frustrating, right? This common scenario highlights the need for a hands-free audio solution that blends seamlessly into everyday moments like meals. Enter bone conduction audio while eating, a groundbreaking approach that transmits sound vibrations through your skull bones directly to the inner ear, keeping ear canals open for comfort and awareness. By bypassing the eardrum, this wearable audio gadgets innovation uses transducers on your cheekbones to convert audio into vibrations, ideal for meals where traditional earbuds cause inconvenience from chewing, food handling, or hygiene issues. Learn more about the basics from Wikipedia, Salusu Health, and HearView.

What Is Bone Conduction Audio?
At its core, bone conduction audio while eating is a method of sound transmission that leverages your body’s natural anatomy. Instead of sending sound waves through the air into your ear canals, devices like bone conduction headphones vibrate against your cheekbones, sending these vibrations through the skull to the cochlea in the inner ear. This process skips the outer and middle ear entirely, making it a unique form of music through vibrations. As explained by Soundcore and Shokz, this technology is particularly useful for maintaining situational awareness—you can hear your surroundings, including conversations or potential spills, while still enjoying your audio content. It’s a perfect example of how wearable audio gadgets are evolving to fit modern lifestyles.

The Science Behind the Vibrations
To truly appreciate this creative sound tech, let’s dive into the science. How does music through vibrations work? In traditional air conduction, sound waves travel through the air, vibrate the eardrum, and are amplified by tiny bones in the middle ear before reaching the cochlea. Bone conduction shortcuts this by directly agitating the cochlear fluid with vibrations transmitted through the skull’s bones—primarily the temporal bone. These vibrations are converted by hair cells into neural signals for the brain, as detailed by HearView. Interestingly, bones naturally transmit lower frequencies more effectively than higher ones, a property enhanced in devices like headphones or hearing aids. This natural process is rooted in physics; for a deeper look, check out Wikipedia and Integrated Listening. By contrasting with air conduction, we see how bone conduction offers a distinct auditory experience, especially suited for activities like eating where open ear canals are beneficial.
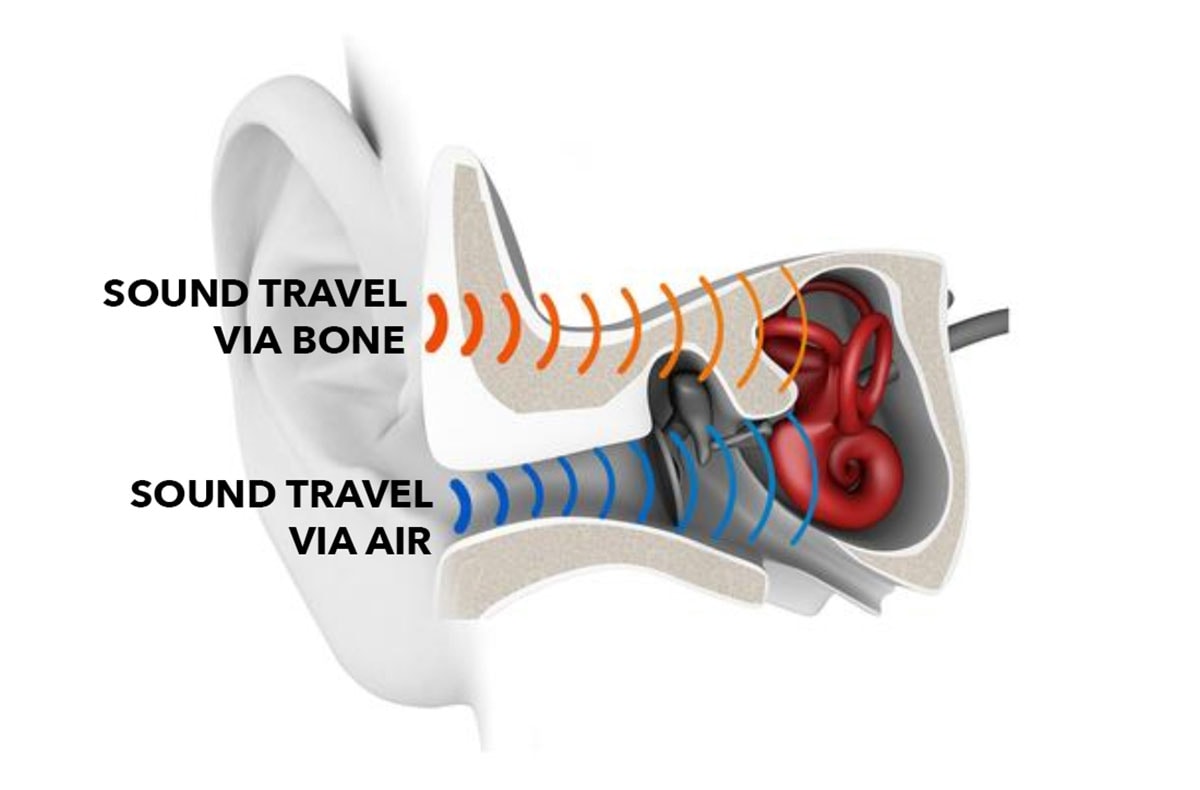
Why It’s Perfect for Meals
Imagine enjoying a meal without constantly adjusting earbuds or dealing with that “plugged-up” feeling. That’s the promise of bone conduction audio while eating. By leaving ear canals unobstructed, this technology prevents pressure, irritation, or wax buildup that often comes with in-ear buds. You remain fully aware of your surroundings—whether it’s a friend’s conversation or the sound of chewing—which enhances safety and social interaction. Users can eat and drink freely without fear of earbuds falling out or getting dirty, a stark contrast to traditional headphones that block canals, cause fatigue, and isolate ambient noise. As Soundcore notes, this makes bone conduction a top choice for wearable audio gadgets designed for daily use. Here’s a quick comparison to illustrate the advantages:

Bone Conduction vs. Traditional Headphones During Meals
| Feature | Bone Conduction Headphones | Traditional Headphones (In-Ear/Over-Ear) |
|---|---|---|
| Ear Canal Impact | Open and unobstructed | Blocked or covered |
| Ambient Awareness | Full (hears surroundings) | Reduced (isolates user) |
| Comfort During Eating | High (no pressure, easy with food/drink) | Low (irritation, dislodging risk) |
| Hygiene | Better (nothing in ears) | Potential issues with prolonged use |
Source: Adapted from HearView
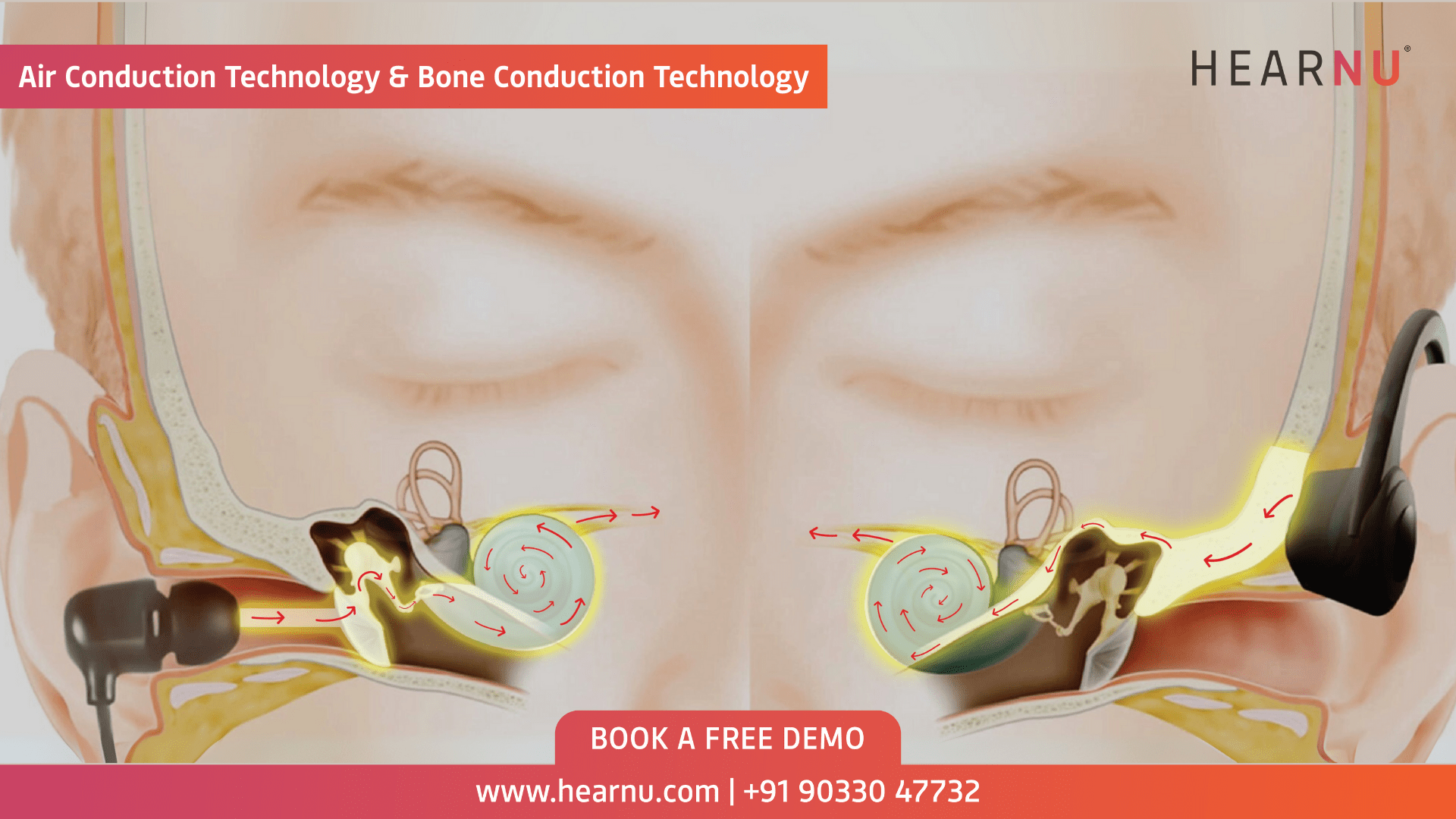
Wearable Audio Gadgets: The Bigger Picture
Bone conduction is just one star in the galaxy of wearable audio gadgets. It fits alongside open-ear designs like air-conduction earbuds, which use speakers to direct sound without sealing canals, and smart glasses with integrated audio. As explored by Bose, these methods prioritize awareness over isolation, making them ideal for daily wear. Pure bone conduction vibrates cheekbones directly, while hybrids may combine methods for features like active noise cancellation (ANC). This evolution reflects broader trends in wearable tech, from fitness trackers to AI-powered devices. For insights into innovations, see PenBrief on wearable innovations, coolest gadgets, health gadgets, and AI-powered wearables. By integrating bone conduction into this ecosystem, we see how creative sound tech is reshaping how we interact with audio in our daily lives.

Beyond Eating: Versatility of Creative Sound Tech
The applications of bone conduction extend far beyond the dining table, showcasing its role as a pinnacle of creative sound tech. Consider these scenarios:
- Swimming: Waterproof models allow audio enjoyment while submerged, as sound travels well through water and bone.
- Running: A secure fit without cords or ear tips prevents discomfort during movement.
- Hearing Assistance: Bone-anchored hearing aids (BAHA) or implants like BONEBRIDGE help those with conductive hearing loss by bypassing damaged outer or middle ears.
Historically, this concept isn’t new. Beethoven famously bit a rod attached to his piano to feel vibrations when his hearing declined, illustrating the roots of music through vibrations in overcoming auditory barriers. Today, as Salusu Health and HearView explain, this technology empowers users in diverse environments, from sports to medical fields. It’s a testament to how innovation can transform simple vibrations into a versatile auditory tool.

Pros, Cons, and Technical Limitations
Like any technology, bone conduction has its trade-offs. On the plus side, it offers unmatched situational awareness, comfort, and hygiene—key for bone conduction audio while eating. However, audio quality may not match traditional headphones for all users. Due to bone transmission limits, bass and high frequencies can be less pronounced, though speech and mids are often clear. There’s also potential for sound leakage in quiet settings because of the open design. Technically, passive transcutaneous devices can lose up to 20dB through skin, though active ones improve fidelity. Fit is crucial; proper placement on cheekbones ensures optimal conduction. As Wikipedia and Soundcore note, these limitations make bone conduction best for active, awareness-needing scenarios rather than critical listening. When evaluating wearable audio gadgets, it’s important to weigh these factors against your needs.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is bone conduction audio safe for long-term use?
Yes, bone conduction audio is generally safe. It bypasses the eardrum, reducing risk of damage from loud volumes, but as with any audio device, it’s wise to listen at moderate levels to protect your hearing. For more, see HearView’s explanation.
2. Can I use bone conduction headphones while eating messy foods?
Absolutely! Since nothing goes in your ears, they’re easy to wipe clean if they get dirty. This makes them ideal for meals where traditional earbuds might get greasy or fall out.
3. How does bone conduction compare to open-ear air conduction headphones?
Both keep ear canals open, but bone conduction uses vibrations on bones, while air conduction uses speakers near the ears. Bone conduction often offers better awareness but may have different sound quality. Learn more from Bose.
4. Are bone conduction devices good for people with hearing loss?
They can be beneficial for conductive hearing loss, where sound bypasses damaged areas. However, for sensorineural loss, consult an audiologist. Devices like BAHA use similar principles.
5. What’s the future of bone conduction in wearable tech?
Expect advancements in integration with other wearable audio gadgets, such as smart glasses or AR headsets, blending vibration tech for seamless audio experiences. For insights, check Soundcore and Shokz.

Imagine a world where meals, workouts, and daily chaos all come with your personal soundtrack—bone conduction is leading the way. Try a bone conduction device for your next meal and share your experiences, or explore recommended models to start your journey.