“`html
Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors and Beyond
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Encountering errors with advanced AI tools, especially “Gemini Pro function call tooling errors,” can significantly disrupt development workflows.
- These errors often stem from complex schemas, parameter mismatches, malformed requests, model variability, or underlying API/server issues.
- Troubleshooting involves simplifying schemas, verifying parameters, testing different models, analyzing error codes, and monitoring for known issues.
- Similar errors like “AI unable to fulfill request Amazon” or “Azure DevOps 500 error” require specific checks related to those platforms’ ecosystems and services.
- Features like “Photoshop Generative Fill not working” can be resolved by ensuring software updates, valid subscriptions, stable internet, and correct file/layer formats.
- “Google 2-step verification request failed” often relates to device connectivity, time synchronization, or app updates.
- General best practices include keeping software updated, checking connectivity, monitoring service status, analyzing logs, and knowing when to seek official support.
Table of contents
- Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors and Beyond
- Key Takeaways
- Deep Dive into Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
- Troubleshooting Steps for “Gemini Pro function call tooling errors”
- Troubleshooting “AI unable to fulfill request Amazon”
- Decoding “Azure DevOps 500 Error Troubleshooting”
- Resolving “Photoshop Generative Fill Not Working”
- Addressing “Google 2-Step Verification Request Failed”
- General Best Practices for Error Prevention and Resolution
Deep Dive into Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
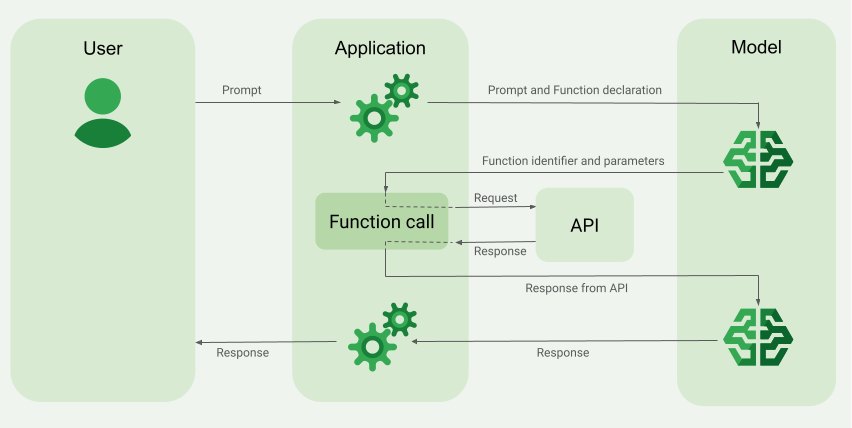
It’s a common frustration for developers: you’ve integrated a powerful AI tool, set up its functions, and then, *bam*, an error message appears, halting your progress. One such specific and often perplexing issue is related to “Gemini Pro function call tooling errors.” These errors occur when the Gemini AI model, particularly when using its function calling capabilities, encounters problems executing or responding to the user-defined functions you’ve provided.
This isn’t just a minor bug; for developers building AI-powered applications, successfully invoking functions is critical for the AI to perform specific actions or retrieve targeted information. When these tooling errors surface, they can prevent your AI system from fulfilling requests as intended, leading to a dead end.

In this post, we’ll not only delve into the intricacies of these “Gemini Pro function call tooling errors” but also explore common issues across other AI and integrated systems. We’ll cover scenarios like an AI unable to fulfill request Amazon, the notorious Azure DevOps 500 error troubleshooting, the sometimes-elusive Photoshop Generative Fill not working, and the annoying Google 2-step verification request failed.
Troubleshooting Steps for “Gemini Pro function call tooling errors”
Understanding “Gemini Pro function call tooling errors” requires a close look at how these models interact with predefined functions. These errors typically arise when the Gemini AI model fails to execute or respond correctly to these function calls, a critical failure point for developers aiming to build sophisticated AI applications.
Let’s break down the common culprits and offer actionable steps:
Common Causes:
- Complex Schemas: When function definitions involve highly nested objects or very large arrays, models like Gemini 2.5 Pro can sometimes struggle. This complexity can lead to internal server errors, often reported as a
500error. Simpler models might handle these schemas without issue, highlighting a potential limitation or sensitivity in the more advanced versions. For more on this, see this discussion on complex schemas. - Parameter Mismatches: Precision is key. If the number of response parts generated by the AI doesn’t precisely match the expected parts for a function call, you might encounter a
400 (INVALID_ARGUMENT)error. This indicates a disconnect between what the AI *thinks* it’s returning and what the function *expects*. Refer to issue #6315 on GitHub for an example. - Malformed Requests: The way you structure your function calls and provide parameters matters immensely. Improperly formed requests can confuse the AI, leading to poor performance or outright failures. This is a recurring theme in discussions, as seen in issue #6315 and this user experience report.
- Model Reliability: AI models, even powerful ones, can exhibit fluctuations in their performance. Their ability to consistently adhere to schemas and correctly make function calls can vary. This variability might occur between different versions of the model, or even between different deployments of the same version. The report on Gemini 2.5 function calling performance touches on this.
- API/Server-Side Issues: Sometimes, the problem isn’t with your code or the schema, but with the underlying infrastructure. Backend services can experience unexpected failures, leading to errors like a
500 INTERNALerror. This was noted in the context of complex schemas as well, as discussed in this Google AI discussion.

Troubleshooting Steps:
- Schema Simplification: If your function schemas are complex, try simplifying them where possible. Removing unnecessary nesting or reducing the size of arrays can alleviate the burden on the model. This is a key recommendation from various developers.
- Parameter Verification: Meticulously check that the parameters you are sending, the structure of the AI’s response, and the resulting function call parts all align perfectly with your function’s defined schema. A single misplaced comma or incorrect data type can cause failure. As emphasized in GitHub issue #6315, precise matching is crucial.
- Model Testing: To diagnose if the issue is model-specific, try using a different Gemini model. For instance, if you’re using Gemini 2.5 Pro, test your schema with Gemini Flash or another available variant. This can quickly reveal if a particular model version is the source of the problem. This approach is suggested in developer forums.
- Error Code Analysis: Don’t just look at the error message; examine the specific error codes provided in the API response. These codes often contain precise information about what went wrong, such as
INVALID_ARGUMENTorINTERNALerrors, pointing you towards the exact misalignment. This GitHub issue highlights the importance of these codes. - Bug & Change Monitoring: Keep an eye on official Gemini API channels, forums, and release notes. Developers sometimes report bugs or changes that affect function calling performance. Being aware of recent updates or known issues, such as those mentioned in performance discussions and the official troubleshooting guide, can save you hours of debugging. Also, see this thread about API changes.
- Official Resources: For comprehensive guidance, always refer to Google’s official documentation. The Gemini API troubleshooting page is an invaluable resource for detailed explanations and solutions.
Troubleshooting “AI unable to fulfill request Amazon”
When you encounter the message “AI unable to fulfill request” within Amazon’s ecosystem—whether it’s with Alexa skills, AWS AI services, or other integrated features—it means the underlying AI backend couldn’t process your command. This can be frustrating, especially when you expect seamless interaction.
Possible Reasons:
- Authentication/Authorization Issues: Your Amazon account might have expired credentials, insufficient permissions, or be in a state that prevents AI services from accessing necessary resources.
- Service Outages or Degraded Performance: Like any cloud service, Amazon’s AI platforms can experience temporary outages or performance issues that prevent requests from being handled correctly.
- Unclear or Invalid Commands: The AI might not understand your request due to ambiguity, incorrect phrasing, or commands that fall outside its programmed capabilities.
- Regional Restrictions: Some AI services or features might not be available in your specific geographic region, leading to fulfillment failures.
Step-by-Step Solutions:
- Verify Account Credentials: Log in to your Amazon account and ensure all payment methods are valid, permissions are correctly set, and there are no security holds or notifications requiring your attention.
- Check Service Health: Visit Amazon Web Services’ Service Health Dashboard (or the relevant status page for the specific Amazon service you’re using) to see if there are any ongoing incidents or advisories.
- Rephrase or Clarify: Try stating your request again, using simpler language or providing more context. For example, instead of “Play music,” try “Play upbeat pop music from the 2000s.”
- Confirm Service Availability: Check the documentation for the specific Amazon AI service or Alexa skill to confirm its availability in your region. You might need to switch regions in your AWS settings if applicable.
Decoding “Azure DevOps 500 Error Troubleshooting”
An Internal Server Error (500) in Azure DevOps is a generic error message indicating that something went wrong on Azure DevOps’ servers, but it couldn’t be more specific about the exact problem. This often means the issue is on their end, but it could also be triggered by your configuration.
Common Causes:
- Transient Server Glitches: Temporary issues within the Azure DevOps infrastructure can cause such errors.
- Project Misconfigurations: Incorrect settings within your project, pipeline, or repository can sometimes lead to server-side processing errors.
- Faulty Extensions: Marketplace extensions installed in Azure DevOps might have bugs or conflicts that cause the system to fail.
- API Rate Limiting: Exceeding the defined API request limits for Azure DevOps can result in errors, though often these are more specific than a 500. However, complex interactions could manifest as a 500.

Troubleshooting Steps:
- Refresh and Retry: The simplest solution is often the best. Refresh the page or retry the operation after a short period. This can resolve issues caused by temporary server hiccups.
- Review Recent Changes: Check any recent modifications made to pipeline definitions, project settings, security configurations, or user permissions. Revert recent changes if the error started occurring after an update.
- Manage Extensions: If you suspect an extension, try disabling it temporarily. You can also check for updates to installed extensions. If disabling resolves the issue, you’ve found your culprit.
- Monitor API Usage: Review your Azure DevOps usage metrics and API call logs to ensure you are not hitting any rate limits or quotas. If you are, you may need to optimize your requests or request an increase.
Resolving “Photoshop Generative Fill Not Working”
Generative Fill is one of Adobe Photoshop’s most powerful AI features, allowing users to add, remove, or extend image content seamlessly. When it’s not working, it’s usually due to a few common factors related to the software, your account, or your connection.
Possible Causes:
- Outdated Photoshop Version: Generative Fill is a feature that receives regular updates. Using an older version means you might be missing critical fixes or even the feature itself.
- Subscription Issues: Generative Fill requires an active Adobe Creative Cloud subscription that includes access to Adobe Firefly generative AI features. A lapsed or invalid subscription will disable it.
- Unstable Internet Connection: Since Generative Fill relies on Adobe’s cloud-based AI models, a poor or intermittent internet connection will prevent it from functioning.
- Corrupted Preferences or Cache: Photoshop’s performance can be affected by corrupted preference files or cached data, leading to features not working as expected.
- Plugin Conflicts: Third-party plugins can sometimes interfere with Photoshop’s core functionalities, including its AI features.
- Unsupported Image Modes/Layers: Generative Fill is designed to work best with specific image formats and layer types. Using unsupported modes like CMYK or attempting to use it on Smart Objects directly can cause failure.
Actionable Solutions:
- Update Photoshop: Open the Creative Cloud desktop application and ensure Photoshop is updated to the latest version.
- Verify Subscription: Log in to your Adobe account on the Adobe website and confirm that your Creative Cloud subscription is active and includes the necessary generative AI features.
- Test Internet Connection: Ensure your internet connection is stable and fast enough for cloud services. Try other online applications to confirm connectivity.
- Reset Preferences: You can reset Photoshop’s preferences by holding down
Ctrl+Alt+Shift(Windows) orCmd+Option+Shift(macOS) immediately after launching Photoshop. Follow the prompts to confirm. - Manage Plugins: Disable all third-party plugins. If Generative Fill starts working, re-enable plugins one by one to identify the conflicting one.
- Check Image Settings: Ensure your image is in RGB color mode. For Generative Fill, it’s best to work on a standard pixel layer. If you’re using a Smart Object, convert it to a regular layer first.
Addressing “Google 2-Step Verification Request Failed”
Google’s 2-Step Verification (2SV) is a vital security layer. When you receive a “Google 2-step verification request failed” error, it means the prompt sent to your device for approval couldn’t be completed or delivered successfully. This can leave you locked out of your account temporarily.
Common Causes:
- Device Connectivity: The phone or device receiving the verification prompt might be offline, have a poor internet connection, or be in Airplane Mode.
- Time Synchronization Issues: For time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) generated by apps like Google Authenticator, incorrect time synchronization between your device and Google’s servers can cause validation failures.
- Google Server Issues: Occasionally, Google’s authentication servers might experience temporary problems, preventing verification requests from being processed correctly.
- Outdated Verification Apps: Using an old version of an authenticator app can lead to compatibility problems.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Ensure Device Connectivity: Verify that the device you’re using for 2SV has a stable Wi-Fi or cellular data connection.
- Synchronize Device Time: On your smartphone or verification device, go to the date and time settings and ensure “Automatic date & time” and “Automatic time zone” are enabled. If using Google Authenticator, check its settings for time correction.
- Reinstall/Update Authenticator App: Uninstall and then reinstall the Google Authenticator app, or check your device’s app store for updates. You will need to re-add your accounts after reinstalling.
- Use Backup Methods: If you have set up backup phone numbers, backup codes, or other verification methods, try using those. Backup codes are particularly useful for one-time access when other methods fail.
- Review 2SV Setup: Log in to your Google Account security settings on a desktop browser and navigate to the “2-Step Verification” section. Review your active methods and ensure they are correctly configured. You can also re-add your phone or authenticator app from here.
General Best Practices for Error Prevention and Resolution
Beyond the specific issues outlined above, adopting a set of general best practices can significantly reduce the occurrence of errors and streamline the troubleshooting process for AI and integrated systems:

- Software Updates: This cannot be stressed enough. Consistently update your operating system, applications, browser, development tools, and any AI models or SDKs you are using. Updates often contain crucial bug fixes, security patches, and performance improvements that can prevent future errors.
- Connectivity Checks: For any online service or AI tool, a stable and reliable internet connection is fundamental. Before diving into complex debugging, perform basic checks: ensure your Wi-Fi is on, you have a strong signal, and your router is functioning correctly. Test connectivity with other sites or services.
- Service Status Monitoring: Many cloud providers and software companies offer status pages that detail ongoing incidents or planned maintenance. Before you assume a problem is on your end, quickly check the official service status page for Google Cloud, AWS, Azure, Adobe, or any other critical service you rely on. This can save you a lot of time by ruling out widespread outages.
- Log and Error Message Analysis: Error messages and logs are your best friends when troubleshooting. Don’t just glance at them; read them carefully. They often contain specific codes, file paths, or descriptions that precisely indicate the root cause of the problem. For AI services, paying attention to API responses and detailed error outputs is crucial, as suggested by resources like Google’s Gemini troubleshooting guide and developer threads. Understanding function calling nuances, as described in Vertex AI documentation, can also be key.
- Seek Official Support: If you’ve exhausted standard troubleshooting steps, encountered an error that seems undocumented, or are facing persistent issues, don’t hesitate to contact the official technical support for the product or service. They have access to internal knowledge bases and can often provide tailored solutions or escalate the problem to their engineering teams.
“`