How Huawei silent chip progress helping to revive smartphone market share
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Huawei has made a significant comeback in the smartphone market despite strict US sanctions.
- The primary driver behind this resurgence is **Huawei silent chip progress helping to revive smartphone market share** through in-house development.
- Huawei’s HiSilicon division has successfully doubled its revenue market share, demonstrating the effectiveness of its internal strategy.
- This internal chip capability is fueling Huawei’s return to the top spot in China and contributing to its global market position.
- The company’s resilience highlights the strategic importance of supply chain independence in the face of geopolitical challenges.
Table of contents
- How Huawei silent chip progress helping to revive smartphone market share
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction
- The Challenge – Navigating US Sanctions
- The “Silent Progress” – Investing in In-House Chip Capabilities
- HiSilicon’s Resurgence – Concrete Evidence of Success
- Direct Impact on Smartphone Market Share
- A Comeback Despite Sanctions – Resilience in Action
- Rising Globally – The In-House Chip Advantage
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
In a surprising turn of events that has captivated the tech industry, Huawei has begun to stage a remarkable resurgence in the global smartphone market. This comeback is particularly noteworthy given the stringent US sanctions that have significantly impacted the company’s operations since 2019. While many observers expected Huawei to fade from prominence under such pressure, the company has instead found a way to not only survive but *thrive* again. The key question on everyone’s mind is: How?

This post will delve into the critical factor enabling this turnaround: **Huawei silent chip progress helping to revive smartphone market share**. Far from admitting defeat, Huawei doubled down on internal innovation. We will explore the details of Huawei’s intensive, largely under-the-radar efforts in developing its own in-house semiconductor capabilities and how this strategic pivot has had a profound and measurable impact on the company’s market position. This is the story of a Huawei comeback despite US sanctions, driven by technological self-reliance.
The Challenge – Navigating US Sanctions
The path to Huawei’s current resurgence was anything but easy. Beginning in 2019, the United States implemented a series of increasingly stringent sanctions against the Chinese tech giant. These restrictions were designed to curb Huawei’s access to crucial American technology and components, citing national security concerns. The impact was immediate and severe, fundamentally altering Huawei’s supply chain and business model.
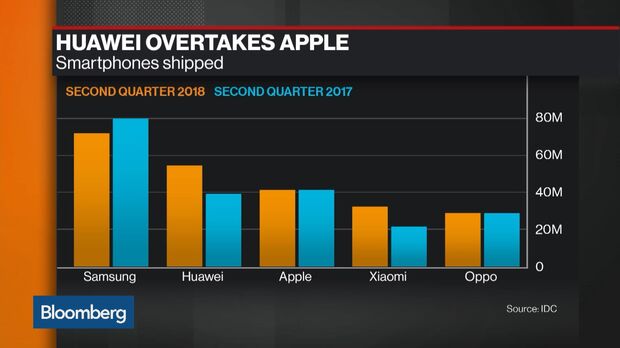
A central pillar of these sanctions was the effective blocking of Huawei’s access to cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturing facilities, particularly those using US technology or software. This meant that companies like TSMC, the world’s leading contract chip manufacturer, were prohibited from producing advanced chips for Huawei. Furthermore, restrictions limited Huawei’s ability to procure essential US-based tech components and even utilize certain software critical for chip design and manufacturing. This created a *chokehold* on Huawei’s ability to power its devices with the high-performance, cutting-edge processors necessary to compete at the top tier of the global smartphone market.
The consequence of these measures was devastating initially. Huawei, once a dominant force challenging Samsung and Apple, saw its smartphone shipments plummet as it struggled to secure adequate supplies of advanced chips. Its supply chain was crippled, and its global market standing was under severe threat. The situation made it appear nearly impossible for Huawei to sustain its position, forcing the company to confront an existential challenge. This period of intense pressure, however, also sowed the seeds for its subsequent recovery by forcing Huawei to seek drastic, internal solutions to remain competitive. This difficult journey is a testament to the Huawei comeback despite US sanctions, highlighting the immense obstacles it had to overcome.
The “Silent Progress” – Investing in In-House Chip Capabilities
Faced with unprecedented external constraints, Huawei made a strategic decision that would define its future: *deep investment in domestic, in-house chip development*. Instead of scaling back or giving up its hardware ambitions, the company quietly, yet intensely, focused its vast resources on building its own semiconductor ecosystem from the ground up. This push became known as “silent chip progress” because much of the foundational work and strategic planning occurred away from the international spotlight, shrouded in the necessity of overcoming sanctions.
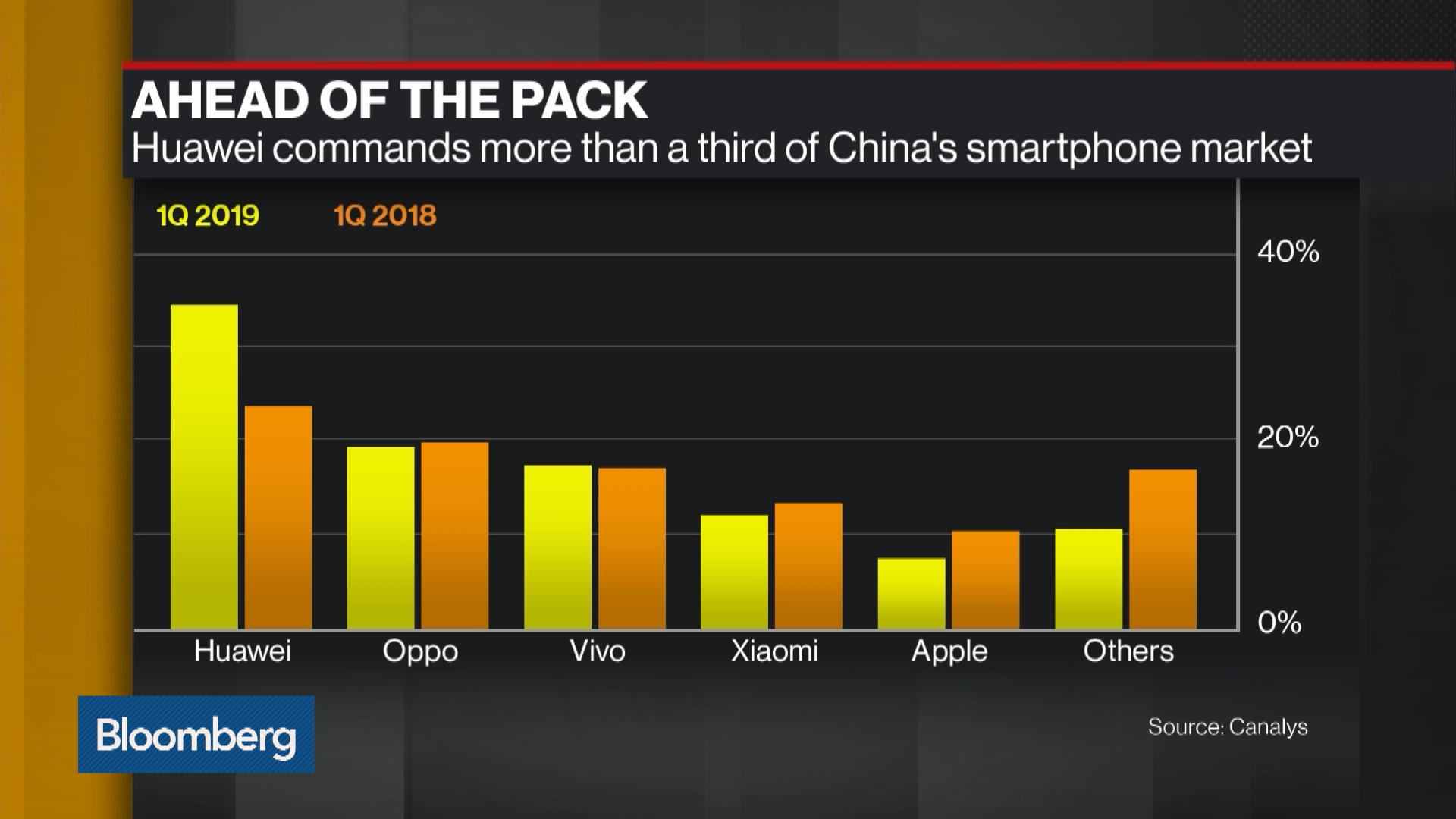
This “silent chip progress” represents Huawei’s methodical, largely under-the-radar initiative to design and, crucially, *manufacture* its own advanced smartphone processors. The primary engine driving this initiative is its semiconductor design arm, HiSilicon. For years, HiSilicon was known for its Kirin processors, but sanctions severely hampered its ability to get them manufactured. The new focus involved not just design but also working closely with domestic Chinese semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) to push the boundaries of their capabilities and establish reliable production lines free from direct reliance on restricted foreign technologies.

Technical innovation was paramount. Huawei leveraged its expertise in areas like AI and 5G integration, focusing on developing chips that could deliver competitive performance and unique features despite manufacturing limitations compared to the absolute bleeding edge elsewhere. These proprietary chips became *crucial* for several reasons: they allowed Huawei to navigate many international restrictions, maintain product differentiation in its devices (offering features and performance not possible with generic components), and gain significantly greater control over its volatile supply chains. While the initial chips produced under these constraints might not have always matched the absolute latest performance benchmarks set by Western or Taiwanese rivals, Huawei’s continuous iteration and investment have led to a *rapid evolution* in their capabilities, helping to close the gap faster than many expected. This formidable in-house capability is foundational to understanding how **Huawei in-house smartphone chips helping it rise globally**. It is the engine of their independence and their competitive edge.
HiSilicon’s Resurgence – Concrete Evidence of Success
The most tangible evidence of the effectiveness of Huawei’s intensive internal chip development strategy is the remarkable resurgence of its HiSilicon division. After several years of decline, marked by severe restrictions that crippled its ability to supply chips to its parent company, HiSilicon has experienced a significant recovery. This isn’t just a minor uptick; the data shows a substantial shift.
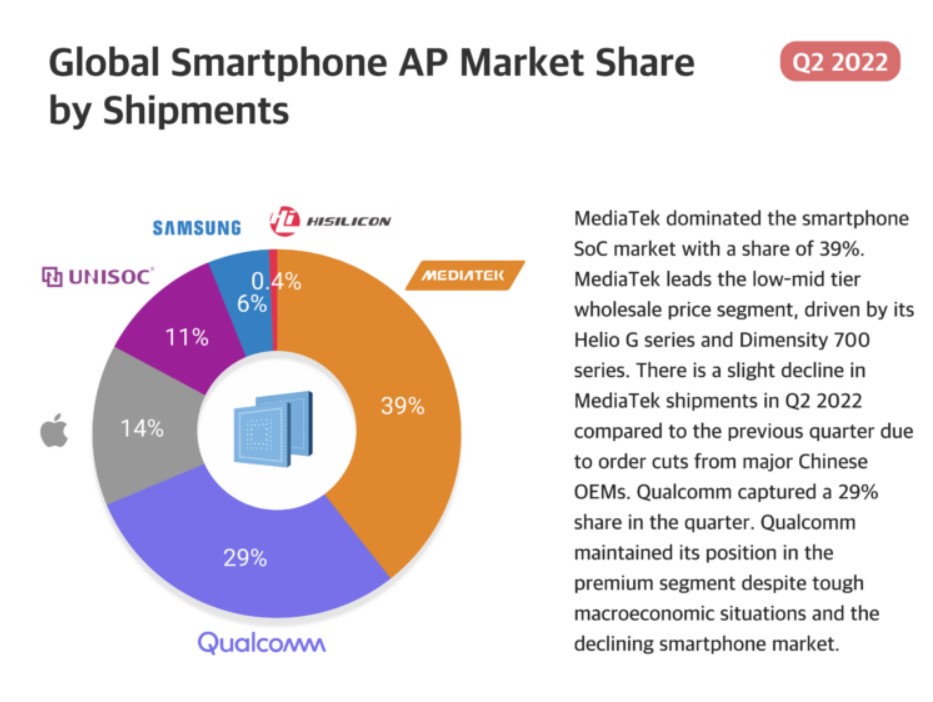
According to industry analysis, HiSilicon has managed to *double* its revenue market share in recent periods. This impressive recovery is largely thanks to renewed demand from Huawei’s latest flagship and mid-range devices, which are now successfully incorporating these internally developed chips. This internal supply chain, built through perseverance and significant investment, has become the lifeline enabling Huawei to power its devices when external sources were cut off.
This resurgence of HiSilicon – proof that Huawei HiSilicon doubles revenue market share – clearly demonstrates the success of Huawei’s strategic pivot. By relying heavily on self-developed semiconductor solutions, Huawei has significantly reduced its vulnerability to external supply shocks and export restrictions. This strategic independence provides a more stable foundation for its smartphone business and is a direct outcome of the **Huawei silent chip progress helping to revive smartphone market share**. It shows that the investment in internal capabilities is not just a survival mechanism but a pathway to renewed strength and competitiveness in the market.
Direct Impact on Smartphone Market Share
The advances Huawei has made in developing and utilizing its own chips are not merely technical achievements; they are having a *direct and profound impact* on its standing in the global smartphone market. The availability of internally sourced, capable processors has allowed Huawei to ramp up production and release competitive new devices, directly fueling its recovery.

Globally, the company has seen a consistent positive trend. Its global smartphone shipments rose for the eighth consecutive quarter, reaching a significant 15.1 million units in Q1 2025, according to TechInsights. This sustained growth trajectory is a strong indicator of the company’s recovery.
The impact is perhaps most dramatic and visible in its home market, China. In Q1 2025, Huawei’s sales saw a remarkable 28.5% year-on-year increase, as reported by Counterpoint Research and corroborated by TechInsights. This surge was enough to propel Huawei back to the top spot in the domestic China smartphone market, a position it hadn’t held since 2021, according to multiple sources including Counterpoint Research and TechInsights. The company’s market share surged to its highest level in years, capturing significant share from competitors like Apple and local brands.
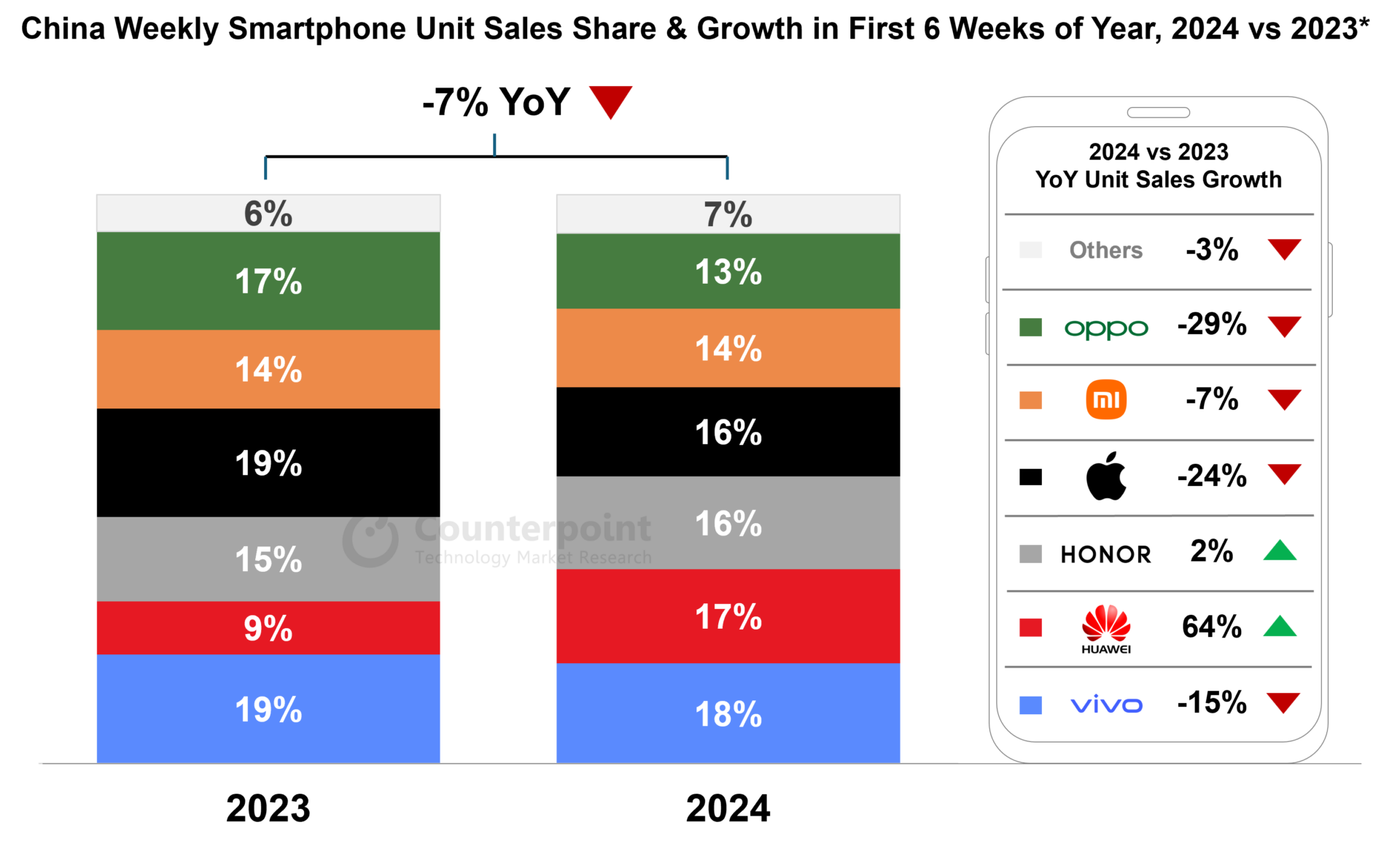
This market share surge is driven by a combination of factors, critically including its technological innovations – *specifically the performance and availability enabled by its in-house chips* – and, in some instances, supportive government-backed subsidies that have made purchasing Huawei devices more appealing and affordable for consumers. Sources like Huawei Central, Counterpoint Research, TechInsights, and Canalys all point to these drivers. This dramatic shift frames the ongoing narrative around Huawei smartphone market share 2024 (using the latest Q1 2025 data as the current benchmark for the year), demonstrating how internal chip progress is translating directly into competitive success.
Furthermore, the availability of these chips has allowed Huawei to diversify its product portfolio, releasing everything from flagship models like the Pura 70 series to mid-range and even foldable devices, ensuring there’s a competitive Huawei option across various price points. This breadth of offering, only possible with a stable supply of processors, directly contributes to capturing broader market segments. The ability to launch new models consistently and in sufficient volume is a testament to the robustness of their re-engineered supply chain, powered significantly by HiSilicon. This contrasts sharply with the periods when component shortages crippled their launch cycles. The success in China, the world’s largest smartphone market, acts as a powerful launchpad and sends a clear signal to the global industry about Huawei’s renewed capabilities and ambition. It signifies that Huawei is no longer just surviving the sanctions but actively regaining lost ground, powered fundamentally by its domestic technology base and the advancements in its internal chip design and manufacturing processes.

A Comeback Despite Sanctions – Resilience in Action
The narrative surrounding Huawei’s recent performance is undeniably a story of resilience, a definitive Huawei comeback despite US sanctions. This recovery isn’t happening because the sanctions have been lifted or significantly eased; it’s occurring against the persistent backdrop of strict US trade restrictions and ongoing geopolitical tension that continues to impact its access to the most advanced global semiconductor technology.
Huawei’s ability to regain significant market share, particularly reclaiming the top position in the intensely competitive Chinese market, serves as a *strong testament* to the efficacy and resilience of its supply chain reengineering and its unwavering strategic focus on domestic technology development. While external pressures remain, Huawei has managed to build a parallel system capable of powering its core business.
Despite the significant constraints imposed by sanctions, which have forced compromises in certain areas compared to competitors with unrestricted access to the absolute latest global tech, Huawei has managed to outpace both global competitors operating in China (like Apple) and domestic rivals. This success highlights not just technological achievement but also operational excellence and strategic foresight in adapting to a challenging environment.
The critical role of internal chip production cannot be overstated in enabling this Huawei comeback despite US sanctions. It is the engine that provides the necessary components, reduces dependency on volatile external sources, and allows Huawei to control the integration of hardware and software in a way that differentiates its devices. The success seen in market share data, confirmed by sources like Counterpoint Research and TechInsights, underscores that Huawei has found a viable path forward, demonstrating remarkable adaptability and determination in overcoming formidable adversity through technological self-sufficiency. This isn’t merely bouncing back; it’s a restructuring of their entire operational core to become less vulnerable to future external shocks.
Rising Globally – The In-House Chip Advantage
Huawei’s self-sufficiency in semiconductor technology is not just a story confined to the Chinese market; it is actively establishing the foundation for renewed global ambitions. While international expansion faces continued geopolitical hurdles, Huawei’s internal chip capabilities provide a crucial strategic advantage that could facilitate its rise outside China in the long term.
By controlling its own chip development and supply chain, Huawei can better mitigate the risks associated with external component availability. This stability allows the company to focus on innovation and delivering competitive products. With their own processors, Huawei is empowered to design and integrate unique features tailored specifically for both premium high-end devices and more accessible mass-market smartphones, making its offerings more attractive and competitive on the international stage. This technological independence means Huawei is less reliant on the fluctuating availability and pricing of components from third parties, giving them more control over product roadmaps and costs.

This strategic position enables Huawei to capitalize on future global opportunities, particularly if trade restrictions evolve or if new markets become more receptive to its products. The success in China, powered by their chips (Source: TechInsights), serves as a powerful proof point of their capabilities. It demonstrates that Huawei can produce competitive, high-quality smartphones using a predominantly domestic supply chain. This is a compelling narrative for markets looking for alternatives to existing dominant players.
While significant challenges remain in markets heavily influenced by US policy, the fundamental technological independence achieved through their “silent progress” is precisely what makes the prospect of **Huawei in-house smartphone chips helping it rise globally** a real possibility. This self-reliance is not just about survival; it’s about building a sustainable, competitive platform for future growth, potentially allowing Huawei to gradually expand its footprint and challenge established players in more regions as geopolitical and market conditions allow. Their consistent global shipment growth over eight quarters, while still recovering, hints at the gradual rebuilding of their international presence, anchored by this newfound chip self-sufficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the remarkable turnaround witnessed in Huawei’s smartphone business is largely attributable to one essential factor: the company’s determined and successful focus on developing internal chip technology. This **Huawei silent chip progress helping to revive smartphone market share** has been the linchpin of its recent revival. By making significant, strategic investments in building in-house semiconductor design and manufacturing capabilities, Huawei has effectively navigated and overcome the formidable external pressures imposed by stringent US sanctions.

This strategic pivot has yielded tangible results, most notably enabling Huawei to reclaim domestic market leadership in China – a significant milestone that underscores its resilience and adaptability. The recovery of its HiSilicon division, which saw Huawei HiSilicon doubles revenue market share, provides concrete evidence that their internal strategy is bearing fruit. This resurgence positions Huawei strongly for potential sustained future growth, both domestically and potentially in select international markets where conditions permit.
The Huawei comeback despite US sanctions is a powerful case study in corporate resilience and strategic adaptation. It highlights the critical strategic value of achieving supply chain independence, especially for global technology companies operating in an era of geopolitical volatility. The story of **Huawei silent chip progress helping to revive smartphone market share** and its subsequent rise in Huawei smartphone market share 2024 (drawing on Q1 2025 data from sources like Huawei Central, Counterpoint Research, TechInsights, and Canalys) underscores the power of relentless innovation and the strategic importance of self-reliance when facing significant adversity. The success of **Huawei in-house smartphone chips helping it rise globally** demonstrates a blueprint for navigating complex international trade environments through technological self-sufficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How have US sanctions specifically impacted Huawei’s access to chips?
US sanctions, implemented primarily since 2019, have significantly restricted Huawei’s ability to access cutting-edge semiconductor technology and manufacturing services. This included prohibiting companies that use US equipment or software from producing advanced chips for Huawei, effectively cutting them off from leading foundries like TSMC. It also limited their access to essential US-based components and chip design tools, creating a major challenge for their smartphone production.
Q2: What is the “silent chip progress”?
The “silent chip progress” refers to Huawei’s largely under-the-radar, intensive investment and development effort focused on creating and manufacturing its own advanced smartphone processors and related semiconductor components. This was a strategic response to being cut off from international chip suppliers, aimed at achieving technological self-sufficiency through its HiSilicon division and collaboration with domestic fabrication plants.
Q3: How has HiSilicon contributed to Huawei’s comeback?
HiSilicon, Huawei’s chip design arm, is central to the comeback. By successfully developing chips that can be manufactured domestically, HiSilicon has enabled Huawei to secure a reliable supply of processors for its smartphones. This has allowed Huawei to launch new, competitive devices consistently, leading to increased sales and market share, and demonstrating a significant resurgence in HiSilicon’s own revenue market share.
Q4: What is the current state of Huawei’s smartphone market share?
As of Q1 2025, Huawei has seen a significant increase in its smartphone market share, particularly in China, where it reclaimed the top position for the first time since 2021. Its sales in China grew by 28.5% year-on-year, driven by strong demand for its new models powered by in-house chips, and supported in some cases by government subsidies. Globally, shipments have also shown consistent growth over multiple quarters.
Q5: Can Huawei compete globally with its in-house chips?
Huawei’s in-house chips provide the technological foundation necessary for global competition by ensuring a stable supply chain and enabling product differentiation. While challenges remain due to sanctions impacting access to the absolute latest manufacturing nodes, their rapid progress and the performance of their current chips allow them to offer competitive devices. Their ability to control their own chip development positions them strategically for potential future growth outside of China, particularly in markets less impacted by US restrictions.
Q6: Are Huawei’s new chips as advanced as those from leading global suppliers?
Current analysis suggests that Huawei’s latest chips, while significantly advanced and sufficient for competitive performance, may not yet be manufactured at the absolute latest process node (like 3nm or 4nm) used by industry leaders like Apple or Qualcomm due to sanctions. However, Huawei has demonstrated remarkable progress in leveraging available domestic manufacturing capabilities and optimizing their chip designs (e.g., using techniques like advanced packaging) to close this gap rapidly and deliver strong performance, especially in areas like AI and connectivity. The key is that they are *good enough* and *available* when other options are not.
Q7: What role have government subsidies played in Huawei’s comeback?
In addition to its technological advancements, some reports indicate that government-backed subsidies or supportive policies in China have played a role in boosting Huawei’s sales by making its devices more affordable or attractive to consumers compared to international brands. While the in-house chips provide the necessary hardware capability, these external factors can also influence consumer choice and market share dynamics within the domestic market. Sources like Counterpoint Research and Huawei Central have mentioned subsidies as a contributing factor alongside technological innovation.
Q8: What does Huawei’s comeback mean for the global smartphone market?
Huawei’s successful comeback, fueled by its chip progress, signals a potential shift towards greater regional self-reliance in technology. It demonstrates that it is possible for a company, supported by its domestic ecosystem, to overcome significant external pressure and regain competitiveness. This could encourage other regions or companies to invest more heavily in domestic semiconductor capabilities, potentially leading to a more fragmented but also more resilient global supply chain landscape in the long term. It also reintroduces a major competitor at the high end, increasing pressure on established players like Apple and Samsung, especially in key markets like China.






