Ingram Micro Ransomware Attack Details: A Deep Dive into the Cybersecurity Incident and Its Impact on IT Distribution

Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- The Ingram Micro ransomware attack details reveal a critical cybersecurity incident involving SafePay ransomware.
- This event caused a significant Ingram Micro system outage lasting nearly two days, disrupting global IT supply chains.
- SafePay ransomware exploited vulnerabilities in legacy systems and misconfigurations, encrypting critical business platforms, including Xvantage.
- The incident resulted in substantial financial losses, estimated at over $136 million per day, and considerable reputational damage.
- Key lessons emphasize the urgent need for continuous monitoring, regular patching, robust incident response plans, and advanced proactive cybersecurity measures.
- The attack highlights the increasing threat of IT distribution ransomware attacks 2025 and beyond, necessitating continuous adaptation and investment in defense.
Table of contents
- Ingram Micro Ransomware Attack Details: A Deep Dive into the Cybersecurity Incident and Its Impact on IT Distribution
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction: The Ingram Micro Ransomware Incident
- Unpacking the Ingram Micro Cybersecurity Incident Explained
- The Malicious Software: SafePay Ransomware Impact on Ingram Micro
- The Aftermath and Business Disruption
- Lessons Learned from the Ingram Micro Cybersecurity Incident
- The Evolving Threat Landscape: IT Distribution Ransomware Attacks 2025 and Beyond
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction: The Ingram Micro Ransomware Incident
The Ingram Micro ransomware attack details have emerged as a profoundly significant event within the highly interconnected world of IT distribution. Ingram Micro, a veritable giant in the industry, stands as one of the largest global IT distributors, playing a pivotal role in connecting technology vendors with resellers and end-users worldwide. This particular cybersecurity incident involved the surreptitious infiltration of SafePay ransomware deep into their critical systems, marking a concerning escalation in the sophistication of cyber threats targeting vital supply chain links.

The significance of this incident cannot be overstated. It did not merely disrupt Ingram Micro’s internal operational rhythm; its ripple effects permeated the entire broader IT supply chain, creating widespread apprehension and tangible delays. A substantial Ingram Micro system outage ensued, crippling essential functions for nearly two exhaustive days. This outage severely hampered both internal operational efficiency and, more critically, customer-facing services, leading to a cascade of challenges for countless businesses reliant on Ingram Micro’s vast network.
The entire ordeal serves as a stark, unequivocal reminder of the pervasive vulnerability of the IT sector to the relentless and evolving onslaught of modern ransomware attacks. In an age where digital infrastructure forms the backbone of global commerce, such incidents underscore the urgent need for continuous vigilance, robust defensive strategies, and proactive measures to safeguard against increasingly sophisticated cyber adversaries.
Unpacking the Ingram Micro Cybersecurity Incident Explained
To fully grasp the magnitude of this event, it is crucial to delve into the precise chronology and initial response to the Ingram Micro cybersecurity incident explained. Understanding the progression of the attack provides invaluable insights into the rapid decision-making and immediate actions undertaken by the organization.
Chronology of the Attack
The initial signs of trouble emerged on *July 2, 2025*, when Ingram Micro’s security monitoring systems first flagged suspicious network activity. These systems, designed to detect anomalies and potential intrusions, began to indicate irregular patterns of data access and unusual traffic flows. This early detection was a crucial first step, triggering a heightened state of alert within the cybersecurity team. By the morning of *July 3, at 8:00 AM ET*, the grim reality became undeniable: the presence of ransomware within Ingram Micro’s internal systems was officially confirmed. This confirmation marked a critical pivot point, shifting from suspicion to validated threat, demanding immediate and decisive action.
Initial Response and Containment
Upon this confirmation, Ingram Micro’s response was swift and methodical, aligning with best practices for critical incident management. The paramount concern was immediate containment. This involved promptly taking affected systems offline to isolate the threat and prevent further lateral movement of the ransomware across the network. Such a drastic step, while disruptive, is indispensable in limiting the damage and preserving the integrity of unaffected systems. Simultaneously, the company took the critical step of notifying relevant law enforcement agencies, recognizing the criminal nature of the attack and the need for external expertise and investigative support.
Beyond containment and notification, Ingram Micro rapidly initiated comprehensive incident response protocols. This multifaceted approach involved deploying both their highly skilled internal cybersecurity teams, who possess intimate knowledge of the company’s infrastructure, and engaging specialized third-party cybersecurity experts. The collaboration of internal and external expertise ensured a robust and thorough forensic investigation, meticulously tracing the ransomware’s entry point, propagation, and overall impact. These combined efforts were aimed at understanding the full scope of the breach, eradicating the threat, and preparing for recovery.
What Caused the Ingram Micro System Outage?
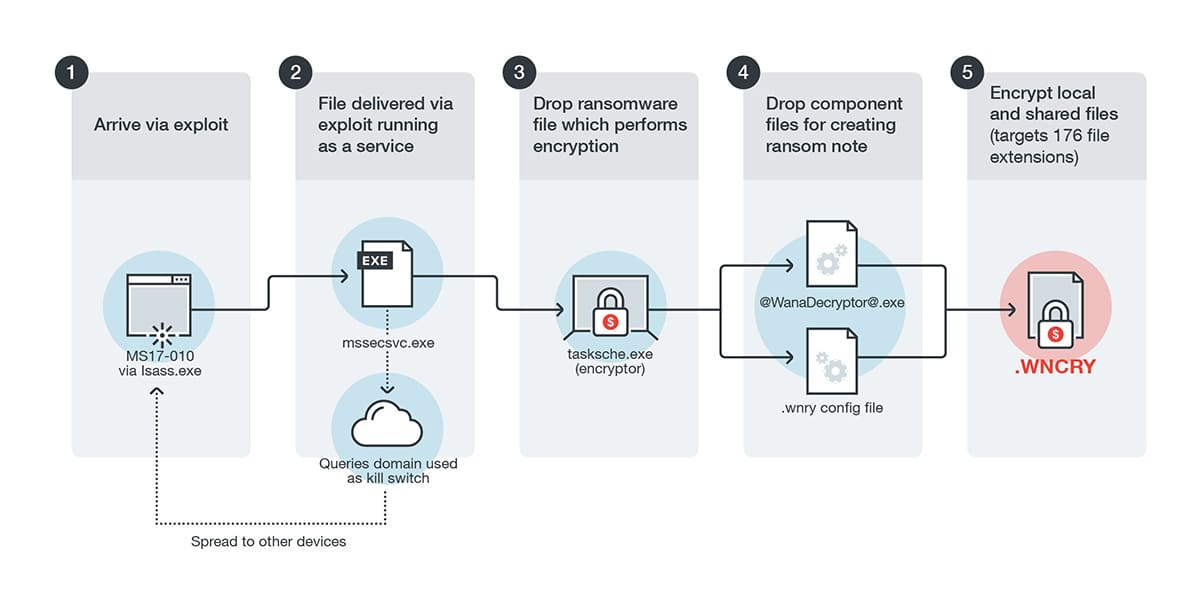
A central question arising from this event is what caused Ingram Micro system outage. The forensic analysis conducted post-attack provided clear answers. It revealed that the attackers skillfully exploited specific vulnerabilities embedded within Ingram Micro’s *legacy systems*. These older systems, while functional, often lack the advanced security features and regular patch updates of newer infrastructure, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Furthermore, the investigation identified critical *misconfigurations in key business applications* as significant contributing factors. These misconfigurations, potentially due to human error or oversight during setup and maintenance, could have created unintentional pathways or weak points that the attackers leveraged to gain initial access or escalate privileges. This dual vulnerability – legacy systems and misconfigurations – provided the perfect storm for the SafePay ransomware to infiltrate and spread. The immediate and direct consequence of this breach was a widespread system outage that crippled operations globally, impacting every facet of Ingram Micro’s vast distribution network.

The Malicious Software: SafePay Ransomware Impact on Ingram Micro
Understanding the specific characteristics of SafePay ransomware and its direct impact on Ingram Micro is crucial to appreciating the severity of this cyberattack.
SafePay Ransomware Characteristics
SafePay ransomware is a nefarious variant known for its efficacy in exploiting system vulnerabilities and existing misconfigurations. Its core modus operandi revolves around the ruthless encryption of files and the subsequent demand for a ransom payment—typically in cryptocurrency—in exchange for the decryption key. This variant often initiates its attack by gaining initial access through vulnerable endpoints, which can include unpatched software, weak remote desktop protocols, or even successful phishing attempts that trick employees into divulging credentials or executing malicious files. Once initial access is achieved, SafePay then demonstrates a sophisticated ability to move laterally across networks. This lateral movement is key to its destructive potential, allowing the ransomware to spread from one compromised system to another, escalating its privileges and encrypting a broader swathe of critical data and applications, thereby maximizing disruption and impact across the targeted organization.

Specific Impact on Ingram Micro
The deployment of SafePay ransomware had a devastating effect on Ingram Micro’s digital ecosystem. It systematically encrypted both their internal business systems, which are essential for day-to-day operations like finance, HR, and internal communications, as well as their external-facing platforms. This widespread encryption led to a significant and immediate disruption of normal workflows and severely hampered order processing capabilities. Partners and customers, accustomed to seamless digital interactions, suddenly found themselves unable to place new orders, track existing shipments, or access crucial information. Notably, Ingram Micro’s flagship Xvantage platform, which is designed to automate crucial functions such as quoting, order management, and tracking, was among the severely affected systems. Given Xvantage’s central role in facilitating transactions and information flow between Ingram Micro and its vast network of partners and customers, its compromise amplified the attack’s impact, creating bottlenecks and delays across the entire IT distribution chain.
Scope of Disruption
The immediate consequences of the SafePay ransomware attack were far-reaching. To contain the rapidly spreading threat, Ingram Micro was forced to undertake the drastic but necessary measure of isolating critical systems. This meant taking major portions of their network offline, effectively creating a digital cordon sanitaire to prevent further encryption and data exfiltration. This isolation was followed by intensive emergency patching to close the exploited vulnerabilities and in-depth forensic analysis to understand the full extent of the breach and identify any lingering threats. The cumulative effect of these necessary actions was a widespread system outage that lasted approximately *48 hours*. During this crucial business period, the entire machinery of order fulfillment and IT supply chain operations came to a grinding halt, underscoring the profound operational paralysis that ransomware can inflict on a global enterprise.
The Aftermath and Business Disruption
The reverberations of the Ingram Micro system outage extended far beyond the company’s internal operations, manifesting as a significant disruption across the global IT distribution landscape.
Extent of the Outage and Impact on the Supply Chain
The *system outage* had a profound and immediate impact on Ingram Micro’s core ability to process and ship orders. For a company that serves as a vital conduit in the technology supply chain, this meant an immediate bottleneck in the flow of essential IT products and services. The disruption cascaded down to a wide array of affected entities, including:
- Resellers: Small and large IT resellers, who depend on Ingram Micro for inventory, pricing, and expedited delivery, faced immediate shortages and delays in fulfilling their own customer orders. This directly impacted their revenue and customer satisfaction.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs, which manage IT infrastructure and services for their clients, often rely on Ingram Micro for hardware and software procurement. The outage meant delays in new client setups, system upgrades, and critical hardware replacements, impacting their service level agreements.
- Technology Vendors: Global technology giants and smaller innovators alike, who utilize Ingram Micro’s vast distribution network to get their products to market, experienced significant backlogs in their sales pipelines.
The incident underscored how interconnected our digital infrastructure truly is, echoing concerns raised by other significant disruptions, such as a massive internet outage affecting Google Cloud and Cloudflare, which similarly highlighted vulnerabilities in global connectivity.

Response and Recovery Procedures
Ingram Micro’s comprehensive response efforts and recovery procedures were crucial in mitigating the long-term damage. Following the initial containment, their teams immediately focused on:
- System Isolation: Ensuring all compromised systems were fully isolated to prevent any further spread of the ransomware or data exfiltration attempts. This involves meticulous network segmentation and strict access controls.
- Emergency Patching: Rapidly deploying emergency patches to address the specific vulnerabilities that the attackers exploited. This proactive measure was vital to prevent re-infection once systems were brought back online.
- Gradual Service Restoration: Implementing a phased approach to restoring services, prioritizing critical functions first. This meticulous process ensures stability and validates the integrity of restored data before full operational capacity is resumed.
The tireless efforts of their cybersecurity and IT teams paid off, with most major systems returning to operation by *July 5*. However, the recovery process didn’t end there. Continuous monitoring for any residual threats and ongoing validation from independent cybersecurity experts became a standard practice to ensure the environment remained secure and resilient against future attacks.

Quantifying the Business Impact
The financial implications and broader business disruption of the outage were substantial. Given Ingram Micro’s immense scale, with a reported $12.28 billion in quarterly sales, the daily revenue loss during the approximate 48-hour outage was staggering. It is estimated that the company incurred losses of *over $136 million per day* in potential sales during this period. This figure highlights not only the immediate financial blow but also the significant ripple effect on the numerous businesses that rely on Ingram Micro for their own operations. Beyond the direct sales losses, the event also incurred significant longer-term reputational risks for the company. Trust, once eroded, is difficult to rebuild, and such incidents can lead to partners seeking alternative distribution channels or questioning the reliability of the supply chain. This underscores that the true cost of a cyberattack extends far beyond the immediate operational downtime and includes lasting impacts on brand image and market position.
Lessons Learned from the Ingram Micro Cybersecurity Incident
The Ingram Micro cybersecurity incident offers a wealth of critical lessons for businesses across all sectors, but particularly for those operating within the intricate web of IT distribution and the global supply chain.
Key Takeaways for Businesses
The incident powerfully underscores several non-negotiable necessities for modern organizations:
- Continuous Monitoring of IT Systems: It’s no longer sufficient to merely react to alerts. Organizations must implement sophisticated, real-time monitoring solutions that can detect even subtle anomalies indicative of an intrusion. This involves leveraging AI and machine learning to analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs constantly.
- Regular Patching of All Systems (Especially Legacy Ones): The exploitation of legacy system vulnerabilities was a key factor in the Ingram Micro breach. Older systems, while perhaps still functional, often have known security weaknesses that become prime targets if not consistently updated with the latest security patches. A robust patch management program, encompassing all hardware and software, is paramount.
- Robust Incident Response Plans: Having a detailed, well-rehearsed incident response plan is critical. This plan must outline clear roles and responsibilities, communication strategies (internal and external), steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. The speed and effectiveness of Ingram Micro’s initial response, in taking systems offline, demonstrated the value of such a plan.
These three pillars form the foundational defense against the dynamic nature of contemporary cyber threats, particularly for organizations whose operational integrity is deeply intertwined with a complex global supply chain.
Prioritizing Proactive Cybersecurity Measures
Beyond reactive measures, businesses must fundamentally shift towards a proactive cybersecurity posture. This includes:
- Regular Vulnerability Assessments: Consistently conducting internal and external vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. These assessments should simulate real-world attack scenarios to uncover hidden flaws in network configurations, applications, and security controls.
- Comprehensive Employee Training: Recognizing that the human element remains a significant vulnerability, providing ongoing and comprehensive employee training on cybersecurity best practices is vital. This includes training on identifying phishing attempts, safe browsing habits, strong password policies, and the importance of reporting suspicious activity. Empowering employees with knowledge transforms them into the first line of defense against ransomware risks. For example, understanding how to secure a smartphone in 2025 or adhering to general cybersecurity tips to stay safe online can significantly mitigate risks.
Such proactive frameworks are not merely deterrents; they are essential investments in operational continuity and long-term business resilience.

Mitigating Future Risks: Advanced Defenses
To reduce exposure to similar sophisticated attacks, organizations must adopt specific technical and organizational measures:
- Advanced Endpoint Protection Solutions: Moving beyond traditional antivirus, next-generation endpoint protection uses behavioral analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to detect and block malicious activity on devices before it can cause harm.
- Network Segmentation: Dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments dramatically limits the lateral movement of threats. If one segment is compromised, the attacker’s ability to spread to other critical parts of the network is severely restricted, thus containing the “blast radius” of an attack.
- Robust Third-Party Risk Management Programs: As supply chain attacks become more prevalent, it’s crucial to assess the security posture of partners and vendors. This involves due diligence, regular security audits, and contractual agreements outlining cybersecurity requirements.
- AI-Driven Threat Detection Systems: These systems, leveraging artificial intelligence, can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying complex attack patterns and anomalous behavior that might evade traditional security tools, offering a new frontier in breakthrough AI cyber defense.
- Zero-Trust Architectures: A paradigm shift in security, zero-trust models assume no user or device can be trusted by default, regardless of their location inside or outside the network. Every access request is verified, fostering a more granular and secure environment. This approach is becoming foundational for unbeatable AI cloud security.
- Collaborative Information-Sharing Networks: Participating in industry-specific threat intelligence sharing groups allows organizations to learn from the experiences of peers, share indicators of compromise, and collectively enhance their defensive capabilities against common adversaries.
These measures represent the forefront of cybersecurity, becoming increasingly essential tools in combating the ever-evolving tactics of ransomware gangs.
The Evolving Threat Landscape: IT Distribution Ransomware Attacks 2025 and Beyond

The Ingram Micro incident is not an isolated event but rather a stark illustration of a broader, escalating trend of ransomware attacks specifically targeting IT distributors. Understanding this context is vital for preparing for future challenges.
Trend Context: The Surge in Ransomware Against IT Distribution
Ransomware attacks against IT distributors have witnessed a significant surge in recent years. This phenomenon is driven by two primary factors: the sector’s critical place in the technology supply chain and the growing sophistication of ransomware groups. IT distributors, like Ingram Micro, act as central hubs, managing vast amounts of sensitive data, financial transactions, and critical inventory. A successful attack on such an entity can have a cascading effect, disrupting thousands of downstream businesses and creating a lucrative target for cybercriminals. The scale of this problem is underscored by alarming statistics: *March 2023 alone saw a record-breaking 459 ransomware incidents globally*, a figure that unequivocally indicates a persistent upward trend in cybercriminal activity. This surge is part of a broader landscape of explosive cybersecurity threats in 2025, emphasizing that no industry is immune, and those at the heart of critical infrastructure are particularly vulnerable.
Projected Threats for IT distribution ransomware attacks 2025 and Beyond
Looking ahead, the outlook for IT distribution ransomware attacks 2025 suggests a continued and intensified threat. As the IT distribution industry continues its relentless drive to digitize and automate its processes—embracing cloud solutions, AI-driven logistics, and interconnected platforms—new attack surfaces inevitably emerge. Attackers are expected to increasingly exploit both the *lingering legacy vulnerabilities* that remain in older systems and the *potential weaknesses in new system integrations*. The complex interdependencies inherent in modern, digitized supply chains create numerous points of entry and avenues for lateral movement for sophisticated threat actors. Consequently, the industry is projected to remain a prime target through 2025 and well beyond, necessitating not just reactive defense but continuous adaptation and substantial investment in cutting-edge cybersecurity measures. This ongoing arms race demands constant innovation on the part of defenders.
Emerging Defenses in the Face of Evolving Threats
In response to the escalating threat landscape, defensive innovations are rapidly becoming essential tools for organizations. These include:
- AI-Driven Threat Detection Systems: These advanced systems utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyze massive datasets of network traffic, user behavior, and system logs in real-time. This allows them to identify subtle anomalies, complex attack patterns, and nascent threats that might bypass traditional signature-based detection methods, enabling proactive identification and response.
- Zero-Trust Architectures: A fundamental shift from the traditional perimeter-based security model, zero-trust assumes that no user, device, or application, whether inside or outside the network, can be implicitly trusted. Every single access request is meticulously verified and authenticated, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and limiting the “blast radius” of a breach by preventing lateral movement within the network.
- Collaborative Information-Sharing Networks: Recognizing that collective defense is stronger than individual efforts, organizations are increasingly participating in industry-specific threat intelligence sharing networks. These platforms allow peers to share vital information about new attack vectors, indicators of compromise (IOCs), and defensive strategies, fostering a united front against common cyber adversaries. This collaboration is crucial for staying ahead of rapidly evolving ransomware tactics.
Embracing these emerging defenses is paramount for IT distributors to build resilient operations capable of withstanding the complex and persistent cyber threats of the future.
Conclusion
The Ingram Micro ransomware attack details provide a vivid and sobering illustration of the profound operational, financial, and reputational risks posed by sophisticated cyber threats in our interconnected world. The subsequent Ingram Micro system outage and the extensive business disruption it caused underscore that no organization, regardless of its size or market dominance, is immune to the destructive power of ransomware. For the entire IT distribution industry, this incident serves as a critical call to action, emphasizing the absolute necessity of maintaining continuous vigilance, proactively modernizing IT infrastructure, and implementing adaptive security strategies. These measures are not merely best practices; they are fundamental requirements for defending against the escalating threat of ransomware in 2025 and beyond, ensuring resilience and continuity in an increasingly digital and dangerous landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: What exactly happened in the Ingram Micro cybersecurity incident?
A1: Ingram Micro experienced a significant ransomware attack starting on July 2, 2025, when SafePay ransomware infiltrated its systems. This led to a widespread system outage, encrypting internal business systems and customer-facing platforms like Xvantage, causing major operational disruptions for nearly two days.
- Q2: What caused the Ingram Micro system outage?
A2: Analysis revealed that attackers exploited vulnerabilities within Ingram Micro’s legacy systems and leveraged misconfigurations in key business applications. These weaknesses allowed the SafePay ransomware to gain access and propagate, directly triggering the global system outage.
- Q3: How much revenue did Ingram Micro lose during the outage?
A3: Given Ingram Micro’s scale of $12.28 billion in quarterly sales, it is estimated that the company lost over $136 million per day in potential revenue during the approximately 48-hour system outage.
- Q4: What is SafePay ransomware, and how does it operate?
A4: SafePay ransomware is a variant known for exploiting system vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. It encrypts files and demands a ransom for decryption. It typically gains initial access through vulnerable endpoints and then moves laterally across networks to maximize disruption and impact by encrypting a wide range of systems.
- Q5: What are the key lessons other businesses can learn from this incident?
A5: Key lessons include the critical need for continuous IT system monitoring, regular patching of all systems (especially legacy ones), and the development of robust incident response plans. Proactive measures such as regular vulnerability assessments, comprehensive employee cybersecurity training, advanced endpoint protection, network segmentation, and adopting zero-trust architectures are also crucial.