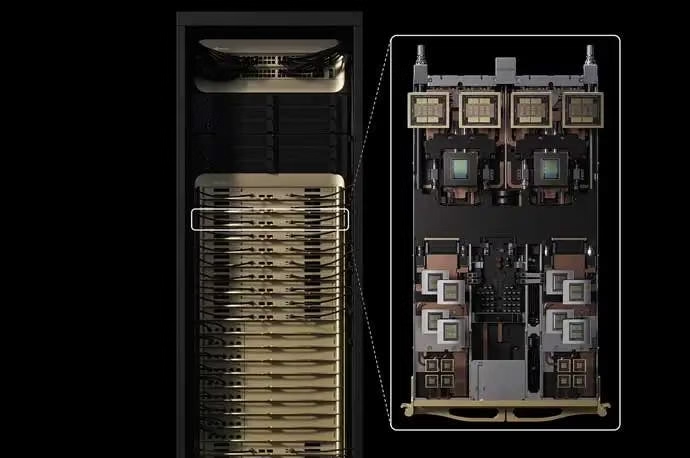
NVIDIA Vera Rubin: The AI Hardware Platform Redefining Compute
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- The explosive demand for AI is pushing silicon to its limits, and NVIDIA’s answer is the groundbreaking nvidia vera rubin ai hardware platform, unveiled at CES 2026 as the successor to Blackwell.
- Built on an “extreme co-design” philosophy, Rubin integrates six custom components—Vera CPU, Rubin GPU, NVLink 6, ConnectX-9 SuperNIC, BlueField-4 DPU, and Spectrum-6 switch—into a unified system for unmatched ai workload acceleration.
- Specs are staggering: a single Rubin GPU delivers 5x the inference performance of Blackwell, while the rack-scale NVL72 system offers 3.6 exaFLOPS, redefining benchmarks for enterprise ai compute chips.
- For enterprises, the platform promises radical cost efficiency, including 10x lower cost per token for inference and game-changing reliability features for continuous operation.
- In cloud ai infrastructure, Vera Rubin enables new tiers of scalable AI-as-a-Service, with nine major hardware and cloud partners already building compatible platforms to meet surging demand.
- Applications from scientific research and autonomous systems to massive LLM training will see transformative gains, accelerating the pace of AI innovation across every industry.
Table of contents
- NVIDIA Vera Rubin: The AI Hardware Platform Redefining Compute
- Key Takeaways
- The AI Compute Crisis and NVIDIA’s Answer
- Deconstructing the Vera Rubin Architecture: Extreme Co-Design
- The Rubin GPU: A Leap in Raw Performance
- The Vera CPU: Agentic AI and the End of the Bottleneck
- Rack-Scale Power: The NVL72 Supercomputer
- Security and Resilience Built from the Silicon Up
- Enterprise Impact: Why Specialized AI Compute Chips Are Non-Negotiable
- The Four Pillars of Enterprise AI Demand
- The TCO Argument: Unbeatable Economics
- Engineering for Zero Downtime
- Transforming Cloud AI Infrastructure for the Next Decade
- A Growing Ecosystem of Partners
- Scalability and Density Redefined
- Power and Cooling: The Infrastructure Challenge
- AI Workload Acceleration: Real-World Applications and Use Cases
- Scientific Research and Grand-Challenge Simulations
- The Autonomous Future: Robots, Vehicles, and More
- LLM Training and Inference: A New Efficiency Frontier
- Frequently Asked Questions
The insatiable hunger of artificial intelligence for more compute power is the defining technological challenge of our time. As models grow from billions to trillions of parameters, and as every industry races to deploy generative and agentic AI, the silicon that powers this revolution is being pushed to its absolute limits. The response to this crisis is not an incremental step, but a seismic shift: the introduction of nvidia vera rubin ai hardware.

Unveiled at CES 2026 as the successor to the formidable Blackwell platform, Vera Rubin isn’t just a new GPU—it’s a completely reimagined, ground-up architecture for high-performance AI silicon. It sets a new benchmark for what’s possible in enterprise ai compute chips and the very foundation of cloud ai infrastructure. This platform is engineered for one purpose: to demolish the bottlenecks that constrain today’s most ambitious AI projects.
This deep-dive explores the specs, the architecture, and the profound implications of the Vera Rubin platform. We’ll dissect how its “extreme co-design” philosophy delivers unprecedented ai workload acceleration, analyze its transformative value for enterprise decision-makers, and map out its role in building the next generation of AI cloud services. For anyone tracking the frontier of AI hardware, understanding Vera Rubin is essential.
Deconstructing the Vera Rubin Architecture: Extreme Co-Design

NVIDIA’s core innovation with Vera Rubin is a philosophy it calls “extreme co-design.” This moves beyond simply connecting best-in-class components. Instead, six elements—the Vera CPU, Rubin GPU, NVLink 6 Switch, ConnectX-9 SuperNIC, BlueField-4 data processing unit, and Spectrum-6 Ethernet switch—are designed as a single, cohesive system. The result is a holistic architecture where the whole is exponentially greater than the sum of its parts, engineered explicitly for superior ai workload acceleration.
The Rubin GPU: A Leap in Raw Performance
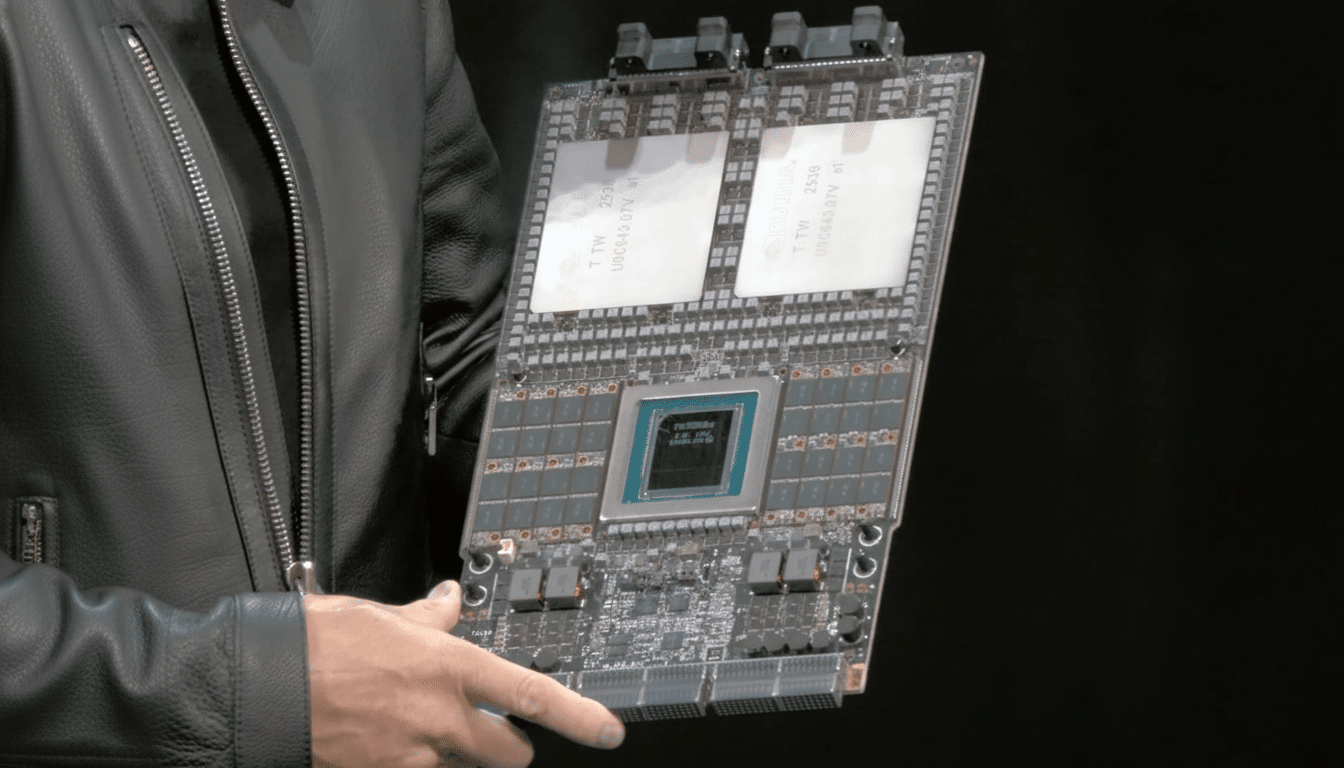
The heart of the platform is the Rubin GPU, a monster of computational density. Each Rubin GPU delivers a staggering 50 PFLOPS of inference performance using the new NVFP4 data type—a figure that represents a 5x increase over the Blackwell GB200. For training, it offers 35 PFLOPS of NVFP4 performance, 3.5x that of its predecessor.
But raw FLOPs are only part of the story. AI performance is often limited by memory, and here Rubin makes a generational leap. It features eight stacks of next-generation HBM4 memory, providing:
- 288GB of total capacity per GPU.
- A colossal 22 TB/s of memory bandwidth.
This represents a 2.8x boost in bandwidth over Blackwell’s already-impressive HBM3e, ensuring that the vast computational engines are constantly fed with data, eliminating a critical bottleneck in both training and inference workloads [1] [2].
The Vera CPU: Agentic AI and the End of the Bottleneck
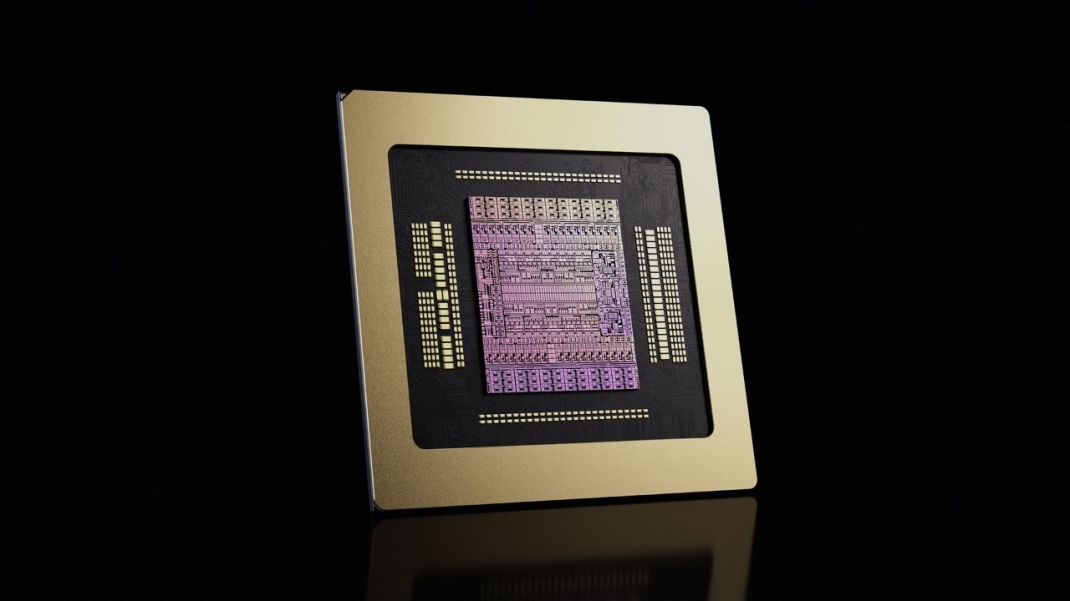
While GPUs accelerate matrix math, the rise of complex, multi-step agentic AI requires sophisticated reasoning and state management—tasks traditionally handled by CPUs. The Vera CPU is built from the ground up for this new era. It features 88 custom Olympus ARM cores that, via spatial multi-threading, can handle 176 simultaneous threads.
Its most critical innovation is its connection to the Rubin GPUs. Instead of relying on the slower PCIe bus, Vera uses a ultra-fast NVLink Chip-to-Chip (C2C) interconnect running at 1.8 TB/s. This doubles the bandwidth of the Grace CPU in Blackwell and completely bypasses traditional I/O bottlenecks [1]. For memory, it accesses a massive 1.5TB of LPDDR5X memory at 1.2 TB/s bandwidth, a 3x increase over the Grace platform, providing ample space for complex agent state and KV caches [3] [2].
Rack-Scale Power: The NVL72 Supercomputer
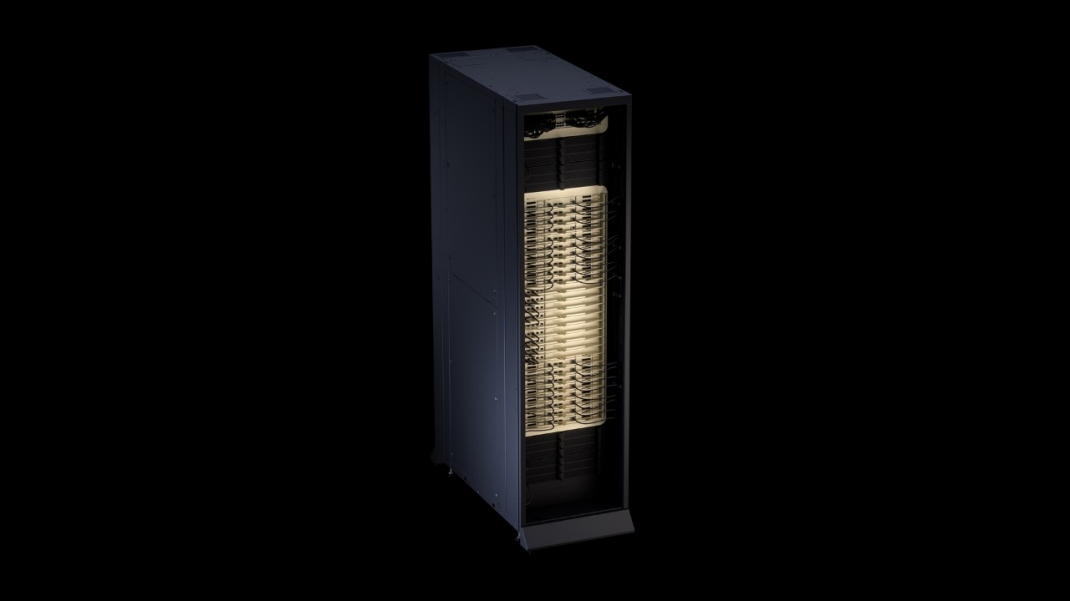

The full potential of nvidia vera rubin ai hardware is realized at rack scale in the NVL72 configuration. This isn’t just a collection of chips; it’s a unified AI supercomputer in a single rack:
- Compute: 3.6 exaFLOPS of NVFP4 inference performance and 2.5 exaFLOPS for training.
- Memory: A staggering 54TB of LPDDR5X (from the Vera CPUs) combined with 20.7TB of HBM4 (from the GPUs).
- Bandwidth: An aggregate memory bandwidth of 1.6 PB/s.
The glue that holds this behemoth together is the NVLink 6 switch, which provides a mind-boggling 260 TB/s of GPU-to-GPU bandwidth within the rack—a figure NVIDIA notes is “more than global internet capacity.” This fabric allows all 72 GPUs in the rack to operate as a single, colossal compute entity, making model partitioning a thing of the past for single-rack deployments [1] [4].
Security and Resilience Built from the Silicon Up
With AI models becoming proprietary crown jewels, security is paramount. The Vera Rubin platform expands trusted execution environments (TEEs) across the entire stack—from the individual chip to the fabric and network. This provides a hardware-rooted chain of trust designed to protect sensitive AI models and data throughout the compute lifecycle, a critical feature for enterprises and cloud providers hosting multi-tenant workloads [1].
Enterprise Impact: Why Specialized AI Compute Chips Are Non-Negotiable

The era of running cutting-edge AI on generalized compute is over. Enterprise ai compute chips like those in the Vera Rubin platform are critical because AI workloads have unique, punishing demands for memory bandwidth and sustained computational throughput that CPUs and standard datacenter GPUs cannot efficiently meet.
The Four Pillars of Enterprise AI Demand
Vera Rubin is engineered to address four core enterprise needs:
- Generative AI at Scale: Serving thousands of concurrent users with low-latency, high-quality inference requires immense throughput. Rubin’s 5x inference leap directly tackles this.
- Agentic AI: AI agents that perform complex, multi-step tasks require persistent state management and massive KV caches. The Vera CPU’s huge memory pool and fast link to the GPU are purpose-built for this.
- Scientific Computing & Simulations: Fields like computational fluid dynamics, quantum chemistry, and climate modeling need sustained double-precision (FP64) performance and massive data movement, which Rubin’s memory subsystem delivers.
- Large Language Model Development : Training ever-larger models requires not just FLOPs, but training efficiency to enable faster research iteration cycles.
The TCO Argument: Unbeatable Economics

The business case for nvidia vera rubin ai hardware is compelling. For Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model training, NVIDIA claims enterprises will need only 1/4 the number of GPUs compared to a Blackwell system. For inference on those same MoE models, the cost per token plummets by a factor of 10x [1]. This means a single rack delivers more AI capacity than before, radically improving total cost of ownership (TCO) and enabling projects that were previously economically unviable.
Engineering for Zero Downtime
For enterprises running 24/7 AI inference pipelines, reliability is as important as performance. Vera Rubin introduces several key innovations:
- Cable-Free Modular Trays: For quick, tool-less swaps of failed components.
- Improved NVLink Resiliency: Allows for maintenance and component replacement without taking the entire system offline.
- Second-Gen RAS Engine: Provides more robust reliability, availability, and serviceability features for continuous health monitoring and zero-downtime operations [1].
Transforming Cloud AI Infrastructure for the Next Decade

The shift to cloud ai infrastructure is accelerating, and Vera Rubin is the engine for its next phase. The platform’s design directly addresses the core challenges of cloud providers: multi-tenancy, scalability, efficiency, and power density.
A Growing Ecosystem of Partners
Adoption is already underway. Nine major hardware and cloud companies have committed to building Vera Rubin-based platforms, signaling a rapid and broad-based ecosystem rollout that will make this powerful enterprise ai compute chips technology widely accessible [5].
Scalability and Density Redefined
Cloud builders can scale Vera Rubin in powerful increments. A single DGX SuperPOD, composed of eight NVL72 racks, aggregates:
- 576 Rubin GPUs and 288 Vera CPUs.
- 28.8 ExaFLOPS of NVFP4 performance.
This massive pool of unified compute enables cloud providers to offer tiered AI-as-a-Service offerings—from small, isolated instances for fine-tuning to entire SuperPODs dedicated to training frontier models—all with strong performance isolation [2].
Power and Cooling: The Infrastructure Challenge
The power of Vera Rubin comes with significant infrastructure demands. A standard NVL72 rack operates in the 120-130 kW range. However, NVIDIA also announced a Rubin Ultra variant pushing an astonishing 600 kW per rack [3]. This necessitates advanced cooling solutions like rear-door heat exchangers and will likely be deployed only in the most advanced, high-density data centers built for AI (those supporting 80+ kW/rack).
| Configuration | Estimated Power per Rack | Cooling Requirement |
| Standard Vera Rubin NVL72 | 120 – 130 kW | Advanced air cooling / liquid cooling doors |
| Vera Rubin Ultra | Up to 600 kW | Direct-to-chip liquid cooling mandatory |
AI Workload Acceleration: Real-World Applications and Use Cases

The abstract specs of nvidia vera rubin ai hardware translate into tangible breakthroughs across industries. Its unprecedented ai workload acceleration will redefine what’s possible.
Scientific Research and Grand-Challenge Simulations
Fields like astrophysics, climate science, and molecular dynamics are constrained by the ability to move vast datasets. Vera Rubin’s 1.6 PB/s aggregate rack bandwidth and exaflop-scale compute will enable simulations with higher fidelity and larger scales than ever before. Drug discovery pipelines, where moving molecular interaction data between CPU and GPU memory is a major bottleneck, could see time-to-solution slashed dramatically.
The Autonomous Future: Robots, Vehicles, and More
The Vera CPU is a game-changer for autonomous systems. In robotics, self-driving cars, and industrial automation, the need for real-time sensor fusion, path planning, and complex decision-making requires powerful, deterministic CPU performance. The Vera CPU’s high core count, huge low-latency memory, and ultra-fast link to the Rubin GPU for perception tasks create an ideal integrated platform for the next generation of autonomous stacks.
LLM Training and Inference: A New Efficiency Frontier

For AI labs and companies building large language models, Vera Rubin offers a dual advantage. The 3.5x training performance boost means faster iteration cycles, allowing researchers to test new architectures and techniques more rapidly. For deployment, the 10x reduction in inference cost per token for MoE models makes serving powerful LLMs to millions of users economically sustainable for the first time [1]. Furthermore, the rack’s 54TB of LPDDR5X memory can be used as a massive, shared KV cache, dramatically improving the efficiency of serving multiple concurrent agentic AI sessions.
The trajectory of AI chip demand is a key driver of technological and economic growth, a trend powerfully illustrated in the analysis of Nvidia stock AI growth. Platforms like Vera Rubin solidify this leadership, building on a legacy of GPU innovation seen in products like the GeForce RTX 40 series. However, the competitive landscape is fierce, with significant challenges emerging from companies like Huawei, underscoring the strategic importance of NVIDIA’s breakthroughs. The profound influence of these milestones, including achieving record market valuations as discussed in NVIDIA’s influence on AI impact, demonstrates the transformative power of investing in foundational AI hardware.
Frequently Asked Questions
When will NVIDIA Vera Rubin AI hardware be available?
NVIDIA has stated that the Vera Rubin platform is scheduled for release in the second half of 2026, following its unveiling at CES 2026.
How does Vera Rubin compare to the previous Blackwell platform?
Vera Rubin represents a generational leap. Key improvements include 5x higher inference performance per GPU, 3.5x higher training performance, 2.8x more memory bandwidth, a new Vera CPU with 3x more memory bandwidth than Grace, and a rack-scale system (NVL72) with over 3 exaFLOPS of performance.
What is “extreme co-design” and why is it important?
Extreme co-design is NVIDIA’s philosophy of architecting the CPU, GPU, network switch, DPU, and interconnect as a single, unified system rather than separate components. This holistic approach eliminates traditional bottlenecks (like PCIe) and optimizes the entire data path, resulting in vastly superior performance and efficiency for AI workloads compared to assembling discrete best-in-class parts.
What are the main use cases for the Vera CPU?
The Vera CPU is specifically designed for complex, sequential reasoning tasks that are less suitable for GPUs. Its primary use cases include:
– Running the orchestration logic for agentic AI systems.
– Managing massive Key-Value (KV) caches for large language model inference.
– Handling control plane and state management in autonomous machines like robots and vehicles.
– Providing high-performance host processing for scientific simulation codes.
What does Vera Rubin mean for the cost of AI?
NVIDIA projects significant cost reductions. For training Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models, they claim only 1/4 the number of GPUs are needed compared to Blackwell. For inference on MoE models, the cost per token is projected to be 10x lower. This dramatically improves the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and can make large-scale AI deployment economically feasible for more enterprises.
What are the infrastructure requirements for deploying Vera Rubin?
Deploying Vera Rubin, especially at scale, requires advanced data center infrastructure. A standard NVL72 rack consumes 120-130 kW, necessitating robust power delivery and advanced cooling (like liquid cooling doors). The high-performance “Ultra” variant can draw up to 600 kW per rack, requiring direct-to-chip liquid cooling and facilities built for extreme density.
How will Vera Rubin affect cloud AI services?
Vera Rubin will enable cloud providers to offer more powerful, efficient, and scalable AI-as-a-Service tiers. Its unified architecture simplifies multi-tenant deployment. The massive performance per rack allows providers to offer isolated instances with enormous compute and memory resources, facilitating everything from large-scale fine-tuning to frontier model training for cloud customers.