“`html
Navigating the Complexities of AI Integration for Business Success
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers immense potential for businesses, but most struggle to achieve widespread value.
- Overcoming AI integration challenges is the critical, often underestimated, step for unlocking AI’s true business potential.
- Common obstacles include poor data quality, AI bias, skills gaps, legacy system integration, security concerns, and unclear ROI.
- An effective AI adoption roadmap requires a deliberate strategy, robust data governance, bias mitigation, talent development, and a focus on phased integration.
- Success hinges on a strategic, iterative approach that prioritizes business objectives and continuous adaptation.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- The Landscape of AI Integration Challenges
- 1. Data Quality Issues in AI
- 2. Mitigating AI Bias in Business
- 3. Other Common Challenges in AI Integration
- Building an Effective AI Adoption Roadmap
- 1. Laying the Foundation: A Robust AI Strategy for Businesses
- 2. Addressing Data Quality Issues in AI
- 3. Mitigating AI Bias in Business
- 4. Navigating Other Roadblocks
- Key Strategies for Overcoming AI Integration Challenges
- Conclusion
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands poised to revolutionize businesses, promising unprecedented advancements in productivity, customer experiences, and innovation across virtually every sector. From optimizing supply chains to personalizing marketing campaigns, the potential applications are vast and transformative. Yet, despite this immense promise, a stark reality persists: **most companies struggle to realize AI’s value at scale**. This is a critical point, as **overcoming AI integration challenges** is not merely a technical hurdle but the crucial, often underestimated, step that unlocks AI’s true business potential.

The path to successful AI adoption is fraught with common obstacles. Businesses frequently grapple with issues stemming from **poor data quality**, the pervasive threat of **AI bias**, a significant **skills gap** in the workforce, the complexities of **integration with legacy systems**, critical **security concerns**, and the persistent difficulty in defining a clear **Return on Investment (ROI)**. These challenges, if unaddressed, can transform promising AI pilot projects into costly failures, leaving organizations with a portfolio of underutilized technology and a sense of disappointment.

This article serves as a guide, offering an **effective AI adoption roadmap** designed to steer businesses beyond initial AI pilots and toward scalable, value-generating AI implementations. It emphasizes that successful AI adoption requires a **deliberate AI strategy for businesses**, moving beyond the mere acquisition of new AI tools and towards a holistic integration that aligns with core business objectives and operational realities. By understanding and proactively addressing the common pitfalls, organizations can pave the way for sustainable AI success.
The Landscape of AI Integration Challenges
Integrating AI into the fabric of an organization is rarely a straightforward process. It involves navigating a complex terrain of technical, organizational, and ethical considerations. This section delves into the primary hurdles businesses encounter when attempting to embed AI solutions into their operations, highlighting the specific issues that often derail even the most well-intentioned AI initiatives.
1. Data Quality Issues in AI
At the heart of any AI system lies its data. The performance and reliability of AI models are directly proportional to the quality of the data they are trained on and operate with. Poor data quality is arguably one of the most significant roadblocks to successful AI adoption, acting as a fundamental bottleneck that undermines the entire initiative.
What constitutes poor data quality? It encompasses a wide range of issues, including data that is **inaccurate**, containing factual errors; **incomplete**, missing crucial fields or records; **inconsistent**, using different formats or values for the same information; **outdated**, no longer reflecting current realities; or **irrelevant**, not pertaining to the specific task the AI is designed to perform.

The impacts of **data quality issues in AI** are far-reaching and detrimental:
* **Unreliable AI Model Outputs:** Inaccurate or incomplete data leads to AI models that make erroneous predictions, classifications, or recommendations. This degrades the overall performance of the AI system, rendering it ineffective or even harmful.
* **Poor Business Decisions:** When AI outputs are unreliable, the business decisions made based on them will also be flawed. This can erode stakeholder trust and confidence in AI initiatives, making future investments harder to secure.
* **Lowered ROI and Project Failure:** Ultimately, poor data quality significantly lowers the return on investment (ROI) for AI projects. It can cause AI projects to stall, go over budget, or fail entirely, leading to wasted resources and opportunities.
Consider these relatable examples:
* A sales forecasting model that is trained on incomplete data, perhaps missing crucial sales channels or regional performance metrics, will inevitably produce inaccurate predictions. This can lead to misallocation of resources, missed sales targets, and strategic missteps.
* A customer support chatbot that is trained on outdated FAQs or internal knowledge bases might provide incorrect or irrelevant information. This not only frustrates customers but can also lead to reputational damage and a loss of customer loyalty.
Addressing **data quality issues in AI** requires a proactive and systematic approach, focusing on data governance, cleansing, and validation from the outset.
2. Mitigating AI Bias in Business
While AI promises objectivity, it is susceptible to bias, which can lead to unfair and discriminatory outcomes. **AI bias** refers to systematic and repeatable errors in an AI system that create unfair outcomes, often reflecting existing societal prejudices or imbalances present in the data used to train the AI.
The main sources of AI bias are varied and interconnected:
* **Biased training data:** This is perhaps the most common source. Historical data often reflects societal prejudices, historical inequities, or skewed representation of certain groups. If an AI model is trained on such data without proper mitigation, it will learn and perpetuate these biases.
* **Skewed sampling:** Data collection methods might inadvertently favor certain groups or fail to represent the diversity of the real-world population. This can happen if data is collected from a limited demographic or geographical area.
* **Algorithmic or feature design choices:** The way an AI model is built, the features it prioritizes, or the objective functions it optimizes for can inadvertently introduce bias. For instance, an algorithm designed to maximize efficiency might unintentionally disadvantage certain groups if that efficiency is correlated with biased historical patterns.
It is critical that businesses focus on **mitigating AI bias in business** for several compelling reasons:
* **Ethical Implications:** AI systems can perpetuate and amplify unfairness. This can manifest in discriminatory customer interactions, biased hiring decisions, or unequal access to services, leading to significant ethical concerns and potential harm to individuals and communities.
* **Reputational Damage:** The public exposure of biased AI systems can severely damage a company’s brand image and trust. Consumers and employees are increasingly aware of and sensitive to issues of fairness and discrimination.
* **Legal and Regulatory Risks:** Biased AI can lead to non-compliance with anti-discrimination laws and regulations. This is particularly relevant in sensitive areas such as hiring, lending, pricing, and healthcare, where discriminatory practices can result in substantial legal challenges and penalties.
The manifestations of AI bias in business applications can be concrete and damaging:
* Biased credit scoring systems might unfairly deny loans to individuals from certain demographic groups, even if they are creditworthy, due to historical lending patterns reflected in the training data.
* Hiring recommendation tools could inadvertently favor one gender or ethnicity over others if the historical hiring data shows a bias towards a particular group.
* Discriminatory pricing algorithms might offer different prices to customers based on protected characteristics, leading to unfair and potentially illegal outcomes.
Proactive measures to identify, measure, and correct AI bias are essential for responsible AI deployment.
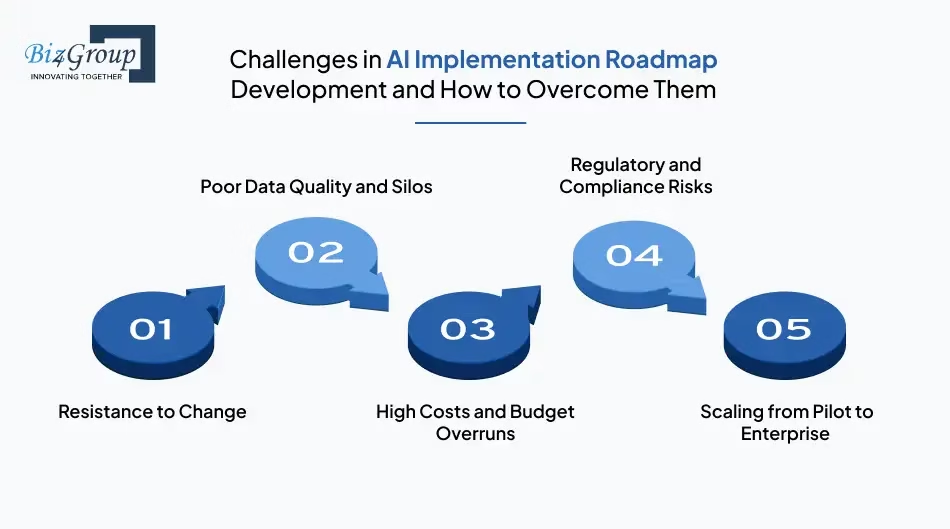
3. Other Common Challenges in AI Integration
Beyond data quality and bias, several other significant roadblocks commonly hinder AI integration:
* **Lack of skilled AI talent and expertise**: There is an ongoing, significant skills gap in the market for specialized AI, data science, and MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) talent. This makes it difficult for organizations to hire, train, or retain the necessary personnel to develop, deploy, and manage AI systems effectively.
* **Integration with existing IT and legacy systems**: Many businesses operate with complex, outdated, or siloed IT infrastructures. Integrating modern AI models and platforms with these legacy systems can be technically challenging, time-consuming, and costly, preventing pilot projects from scaling effectively and hindering seamless connection with existing workflows and essential data sources.
* **Organizational resistance and culture**: Resistance to change is a common human trait, and AI is no exception. Employees may fear job displacement, express skepticism towards new technologies, or engage in “shadow AI” (unofficial, unmanaged AI use). Inconsistent adoption across different departments can also create friction and reduce overall impact.
* **Unclear ROI and success metrics**: A significant hurdle is the difficulty in clearly defining and measuring the ROI of AI initiatives. Without a clear understanding of expected returns and well-defined success metrics, it becomes challenging to justify investment, secure buy-in, and track progress, often leading to underfunded or short-lived pilot programs.
* **Security, privacy, and compliance concerns**: AI systems often process sensitive data, raising critical concerns around data security, privacy, and regulatory compliance. Adhering to strict obligations like GDPR or CCPA, and addressing the increasing cyber risks associated with AI implementations (e.g., model poisoning, adversarial attacks), can significantly slow down adoption and deployment.
Successfully navigating these multifaceted challenges requires a comprehensive and strategic approach that goes beyond simply implementing the technology itself.
Building an Effective AI Adoption Roadmap
Transitioning from AI experimentation to scalable, value-generating implementation demands a structured and deliberate approach. An **effective AI adoption roadmap** is not a rigid, one-size-fits-all plan but a flexible framework that guides businesses through the complexities of AI integration. This section outlines the actionable strategies essential for creating and implementing such a plan.
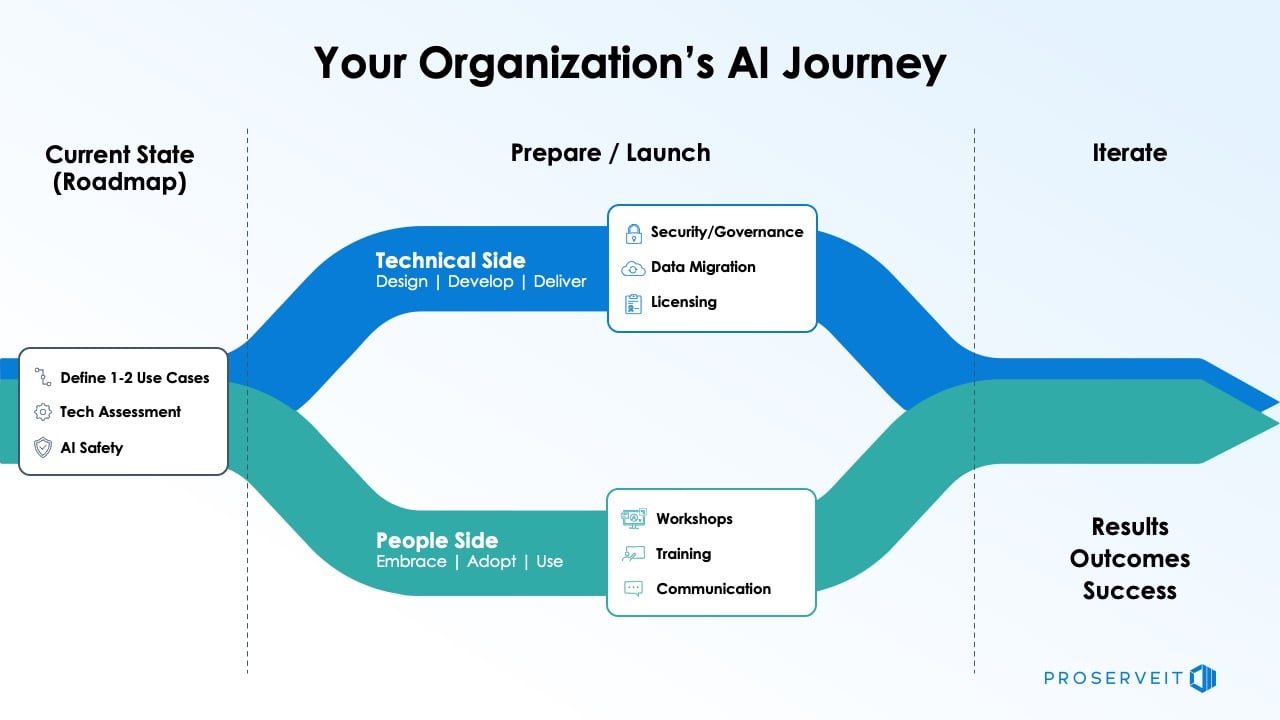
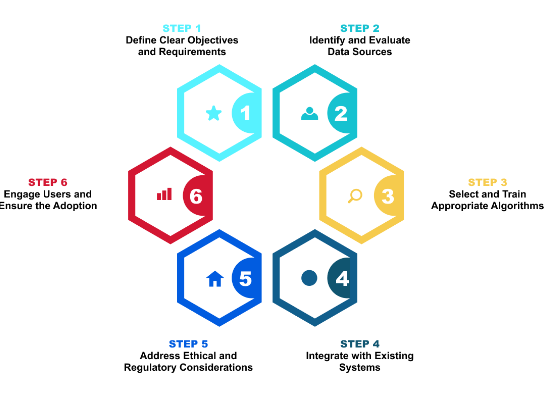
1. Laying the Foundation: A Robust AI Strategy for Businesses
The absolute cornerstone for successfully **overcoming AI integration challenges** is a well-defined **AI strategy for businesses**. This strategy serves as the guiding compass, ensuring that AI initiatives are aligned with overarching organizational goals and deliver tangible business value. A robust AI strategy encompasses several key components:
* **Define Clear Business Objectives:** The primary focus must be on how AI can solve specific business problems or capitalize on opportunities. Initiatives should be directly tied to measurable outcomes such as cost reduction, revenue growth, enhanced customer satisfaction, improved operational efficiency, or mitigated risk. Avoid pursuing AI for its own sake.
* **Identify High-Value Use Cases:** Not all AI applications are created equal. Prioritize use cases where data is readily available and of sufficient quality, the potential business impact is significant and measurable, and the technical complexity is manageable for initial adoption. Start with areas where AI can provide a clear competitive advantage or address a critical pain point.
* **Assess Current Capabilities:** A thorough evaluation of the organization’s existing landscape is crucial. This includes understanding the state of your data infrastructure, the maturity of your IT systems, the skills and readiness of your workforce, the effectiveness of your data governance frameworks, and your overall risk posture concerning AI deployment.
* **Define Success Metrics and ROI Models:** Establish clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure the success of AI initiatives. These might include improvements in cycle time, conversion rates, cost per transaction, error rates, customer retention, or Net Promoter Score (NPS). Develop robust models to track and demonstrate AI’s return on investment over time, ensuring accountability and justifying continued investment.

2. Addressing Data Quality Issues in AI
Given that **data quality issues in AI** are a pervasive problem, specific strategies must be implemented to ensure the reliability of the data feeding your AI systems. Improving data quality is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix, and involves:
* **Implement Robust Data Governance and Ownership:** Establish clear ownership for data assets across the organization. Define data standards, metadata management practices, and formal approval paths for data usage, quality management, and access control. This ensures accountability and consistency.
* **Conduct Thorough Data Cleansing and Validation:** Employ systematic techniques to clean and verify data accuracy. This includes deduplication, standardization of formats, implementation of validation rules at the point of entry, and anomaly detection to identify and rectify errors or outliers.
* **Explore Data Enrichment:** Where appropriate, strategically augment internal data with relevant external data sources or synthetic data. This can provide a more comprehensive and balanced dataset for AI models, filling in gaps and improving their ability to generalize.
* **Invest in Modern Data Infrastructure and Tools:** Utilize contemporary data platforms, efficient data pipelines (ETL/ELT), and sophisticated monitoring tools. These are essential for managing large datasets effectively, ensuring data lineage, and detecting data drift or quality degradation in near real-time.
* **Establish Data Quality Metrics and Continuous Monitoring:** Define key metrics for data completeness, accuracy, timeliness, and consistency. Implement ongoing monitoring processes to ensure data quality is maintained over time, triggering alerts and corrective actions when quality dips below acceptable thresholds.
3. Mitigating AI Bias in Business
Addressing **AI bias in business** is an ethical imperative and a critical risk management activity. It requires a multi-faceted approach that integrates fairness considerations throughout the AI lifecycle:
* **Implement Bias Detection in Datasets and Models:** Utilize fairness metrics (e.g., demographic parity, equalized odds) to systematically identify potential biases in both the training data and the AI models themselves. Compare outcomes across different demographic groups to pinpoint areas of concern.
* **Employ Fairness-Aware Algorithms and Constraints:** Explore and use AI models that are specifically designed or adapted to perform well while adhering to fairness constraints. This might involve incorporating bias mitigation techniques directly into the model training process.
* **Prioritize Diverse and Representative Data Collection:** Actively work to avoid over-reliance on narrow historical patterns. Strive to collect data that reflects the diversity of the real-world population or the target user base. This might involve targeted data collection efforts or data augmentation techniques.
* **Conduct Regular Audits and Establish Ethical Review Processes:** Form cross-functional review boards that include representatives from data science, legal, risk management, HR, ethics, and relevant domain experts. These boards should regularly assess AI systems for fairness, ethical compliance, and potential unintended consequences.
* **Incorporate Human Oversight and Continuous Monitoring:** For high-impact decisions, ensure humans remain in the loop to review and potentially override AI-driven recommendations. Establish robust logging and retraining mechanisms to address emerging biases or data drift over time, maintaining vigilance.
4. Navigating Other Roadblocks
Addressing the remaining common challenges requires strategic planning and operational adjustments:
* **Talent Acquisition and Upskilling:** Focus on a dual approach: upskilling existing employees in data literacy and AI tool usage through comprehensive training programs, while also strategically leveraging external vendors and AI platforms to bridge critical talent gaps for specialized roles.
* **Phased Integration and Pilot Projects:** Begin with narrowly defined pilot projects that are tightly integrated into specific business workflows and demonstrate clear, measurable value. Crucially, design these pilots with a clear, predefined path for scaling to enterprise-wide adoption, rather than treating them as isolated, experimental endeavors. The goal is to build momentum and learn through progressive deployment.
* **Change Management and Training:** Effectively communicate the strategic rationale and the “why” behind AI adoption to all stakeholders. Proactively address employee concerns and fears by emphasizing AI’s role as a co-pilot or assistant that augments human capabilities, rather than as a replacement for human roles. Comprehensive training on how to effectively use and interact with AI tools is essential.
* **Stakeholder Alignment and Communication:** Ensure early and continuous involvement of business leaders, end-users, and IT teams in the AI development and deployment process. Demonstrate quick wins and tangible progress by consistently reporting against agreed-upon KPIs and celebrating successful milestones to build buy-in and momentum.
* **Security, Privacy, and Compliance by Design:** Integrate security, privacy, and regulatory compliance measures from the very inception of AI projects. This is not an afterthought. Implement encryption, anonymization techniques, strict access controls, data minimization principles, and robust governance frameworks from the outset to ensure that AI deployments are secure, private, and compliant with all relevant regulations.
Key Strategies for Overcoming AI Integration Challenges
To consolidate the roadmap, this section distills the core principles into actionable strategies for **overcoming AI integration challenges**. These are the essential tenets that underpin a successful **effective AI adoption roadmap**:
* **Start Small, Then Scale:** This principle emphasizes the importance of launching well-scoped pilot projects. These pilots must be directly linked to real business processes and demonstrate demonstrable value. Crucially, they should be designed with a clear plan for enterprise-wide rollout, rather than existing as isolated experiments. The iterative approach allows for learning and refinement before broader deployment.
* **Foster a Data-Driven Culture:** Cultivating an organizational environment where decisions are consistently informed by data and experimentation is paramount. This involves breaking down silos and promoting strong collaboration between business units, data science teams, and IT departments. It means valuing data as a strategic asset and encouraging curiosity and analytical thinking at all levels.
* **Embrace Continuous Learning and Adaptation:** Position AI systems not as static deployments but as dynamic assets that require ongoing attention. This means establishing processes for continuous monitoring, regular retraining of models to account for changing data patterns, and iterative refinement of the AI-driven processes to maintain and enhance effectiveness over time. The AI landscape evolves rapidly, and so too must your AI implementations.
* **Partner with Experts Where It Matters:** Organizations should strategically leverage external vendors, specialized platforms, and implementation partners, especially for complex, novel, or regulated AI use cases. Attempting to build all AI capabilities in-house can be inefficient and time-consuming. External expertise can accelerate development, bring specialized knowledge, and help bridge critical talent gaps.
* **Keep the ‘Why’ at the Center:** Constantly align every AI initiative with overarching business strategy, demonstrable customer value, and the organization’s risk appetite. Advocate against pursuing “AI for AI’s sake.” Every AI project should have a clear, articulated business purpose and a measurable impact on key organizational objectives.
Conclusion
The journey of **overcoming AI integration challenges** is not a singular project with a definitive end date. Instead, it is an ongoing process of strategic implementation, continuous adaptation, and incremental improvement. Organizations that approach AI integration with a clear vision, robust planning, and a commitment to addressing the inherent complexities are significantly more likely to succeed.

This article has outlined an **effective AI adoption roadmap** that encompasses several critical elements. It begins with establishing a strong **AI strategy for businesses** that aligns AI initiatives with tangible business objectives. It stresses the paramount importance of ensuring high **data quality issues in AI**, which form the bedrock of any reliable AI system. Furthermore, it underscores the necessity of actively **mitigating AI bias in business** to ensure ethical and equitable outcomes. The roadmap also covers meticulous integration planning, strategies for developing talent and fostering the right organizational culture, and the vital implementation of security-by-design principles from the outset.

Organizations that diligently invest in these foundational elements and strategic principles are far better positioned to transition successfully from experimental AI pilots to scalable, ROI-positive AI implementations. By embracing a systematic and thoughtful approach, businesses can unlock the transformative power of AI and secure a significant competitive advantage in the evolving technological landscape. This requires a proactive stance, a willingness to learn, and a steadfast commitment to integrating AI in a manner that is both strategically sound and ethically responsible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the most common reason AI projects fail?
A1: The most common reasons include poor data quality, lack of clear business objectives, inadequate stakeholder buy-in, integration challenges with existing systems, and an underestimation of the change management required.
Q2: How can businesses measure the ROI of AI initiatives?
A2: ROI can be measured by tracking specific KPIs tied to business objectives, such as cost reduction (e.g., reduced operational expenses, lower error rates), revenue growth (e.g., increased sales, improved customer lifetime value), enhanced efficiency (e.g., faster processing times, reduced cycle times), or improved customer satisfaction (e.g., higher NPS scores).
Q3: Is it necessary to have a dedicated AI team?
A3: While a dedicated AI team can be beneficial for complex initiatives, it’s not always necessary for all businesses. A successful AI strategy can also be achieved through cross-functional teams, upskilling existing employees, or strategic partnerships with external AI experts and vendors.
Q4: How can small businesses implement AI without significant resources?
A4: Small businesses can start by leveraging readily available AI-powered tools and platforms (e.g., cloud-based AI services, AI-enhanced CRM systems). Focusing on specific, high-impact use cases with clear ROI and gradually scaling up can be an effective strategy.
Q5: What are the biggest ethical considerations when deploying AI?
A5: Key ethical considerations include AI bias and fairness, data privacy and security, transparency and explainability of AI decisions, accountability for AI outcomes, and the potential impact on employment. Ensuring human oversight and establishing clear governance frameworks are crucial.
“`