AI-Powered Code Review: Enhancing Software Quality with Machine Learning
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Key Takeaways
- AI-powered code review leverages machine learning to automate and enhance the code inspection process.
- It can significantly reduce manual effort and catch bugs that human reviewers might miss.
- Integration with existing development tools like GitHub and GitLab is becoming seamless.
- Despite its advantages, challenges such as false positives and context understanding remain.
- The future holds promise for more intelligent and collaborative AI review systems.

Table of contents
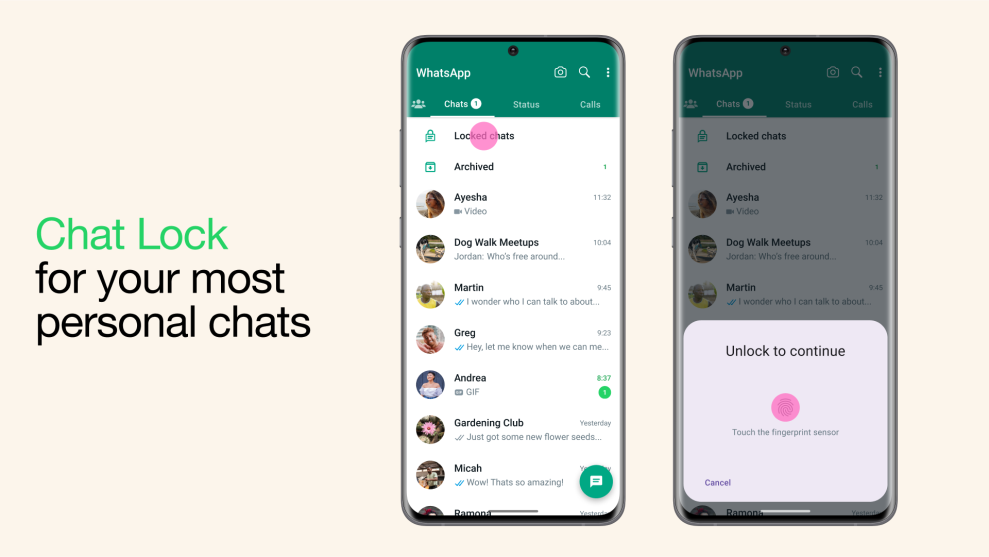
What is AI-Powered Code Review?
AI-powered code review is an innovative approach that uses machine learning algorithms to analyze source code automatically. Unlike traditional manual reviews, which rely on human expertise, AI systems can scan codebases for patterns, potential bugs, security vulnerabilities, and style inconsistencies. According to a study by Tech Research Institute, these tools can process thousands of lines of code in seconds, making them invaluable for large-scale projects.

Imagine having a tireless assistant that never gets bored or overlooks details—that’s what AI brings to the table. Companies like OpenAI and DeepMind are pioneering research in this field, leading to tools that integrate with popular platforms. The concept isn’t just about automation; it’s about enhancing human capabilities by providing data-driven insights that might otherwise be missed in a hectic development cycle.
Historically, code review has been a collaborative but time-consuming process. With AI, teams can shift focus from mundane checks to more creative problem-solving. As highlighted in a DevOps community report, this transition is part of a broader trend towards intelligent software development lifecycle management.
How Does It Work?
At its core, AI-powered code review relies on several key technologies:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): To understand code comments, commit messages, and documentation, allowing AI to grasp context beyond mere syntax. This is crucial for interpreting intent, as discussed in a NLP research paper.
- Machine Learning Models: Trained on vast datasets of code, such as those from GitHub or Stack Overflow, to identify common issues like memory leaks, security flaws, or performance bottlenecks. These models often use techniques like deep learning to improve over time.
- Static Analysis: Examining code without executing it to find syntax errors, potential bugs, and compliance with coding standards. Tools like ESLint have evolved with AI enhancements for more accurate detection.
- Dynamic Analysis: In some advanced systems, AI can simulate code execution to predict runtime behavior, though this is more resource-intensive.

For example, a tool might use a model like BERT adapted for code to suggest improvements. As noted in a blog post by AI Developers, the process typically involves:
- Code submission to the AI system via integrated development environments (IDEs) or version control hooks.
- Automated scanning and analysis using pre-trained models that compare against known patterns and best practices.
- Generation of review comments and suggestions, often ranked by severity or confidence levels.
- Integration with developer workflows for feedback, allowing real-time corrections and learning from human responses.
This workflow not only speeds up reviews but also creates a feedback loop where the AI learns from accepted or rejected suggestions, continually refining its accuracy. A case study on MLOps shows that teams using such systems see a 25% improvement in review quality within six months.
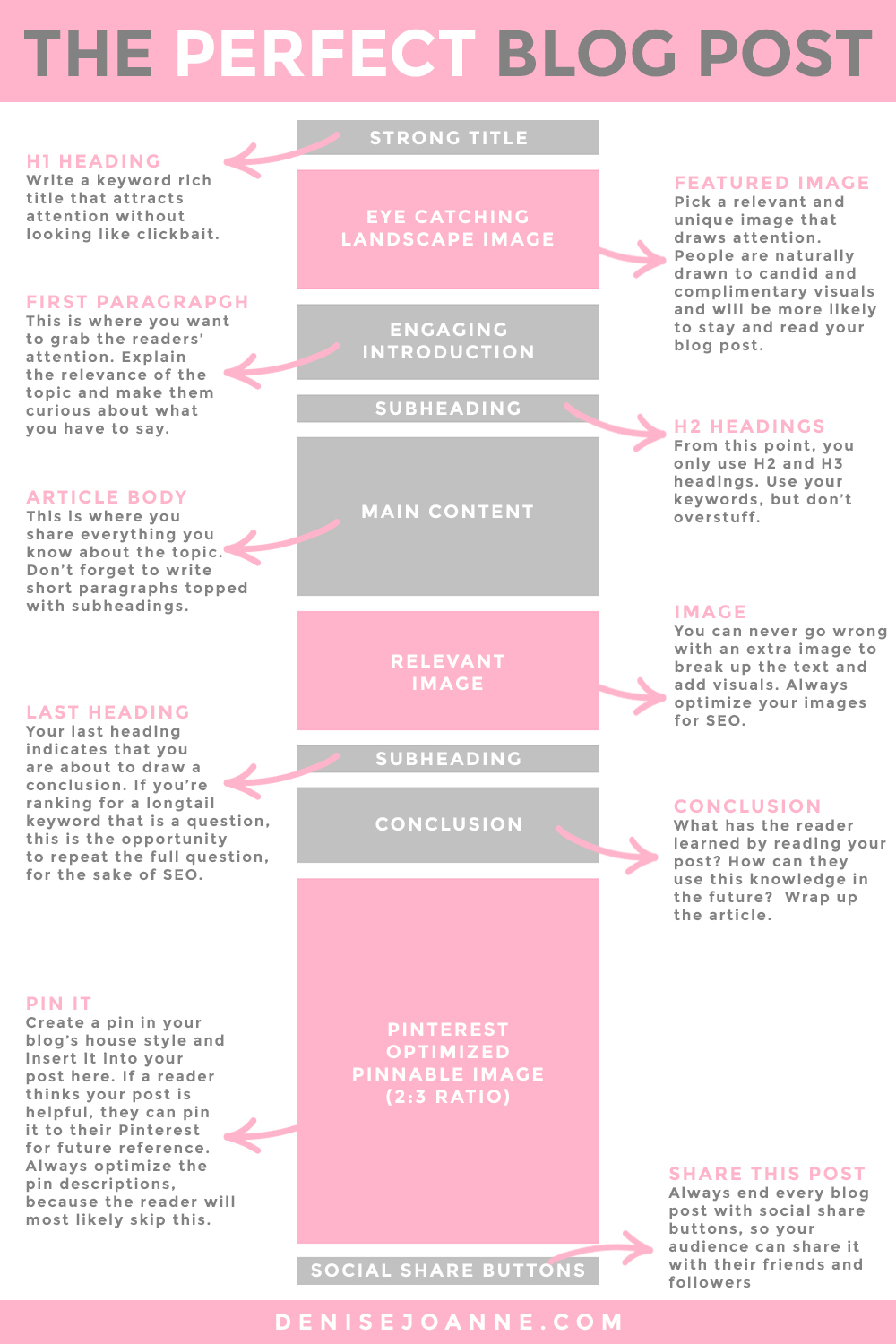
Benefits of AI in Code Review
The adoption of AI in code review offers numerous advantages that transform software development practices:
- Increased Efficiency: AI can review code much faster than humans, reducing turnaround time from days to minutes. A report by DevStats shows that teams using AI review tools see a 40% reduction in review cycles, allowing developers to focus on innovation rather than tedious checks.
- Consistency: Unlike human reviewers, who may have off days or varying expertise, AI applies the same standards every time, eliminating bias and oversight. This ensures that all code, regardless of the author, meets organizational guidelines uniformly.
- Early Bug Detection: By catching issues early in the development process, AI helps prevent costly fixes later. As the saying goes, “A stitch in time saves nine.” Studies from security firms indicate that AI can identify up to 60% of common vulnerabilities before deployment, reducing post-release patches.
- Scalability: Perfect for large projects with multiple contributors, where manual review becomes impractical. AI systems can handle exponential growth in code volume without additional human resources, making them ideal for open-source communities or enterprise-scale applications.
- Knowledge Preservation: AI tools can encode best practices from senior developers, ensuring that institutional knowledge isn’t lost when team members change. This is particularly valuable in fast-paced industries where turnover is high.
Moreover, AI tools can learn from past reviews to improve over time, creating a virtuous cycle of enhancement. They also foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing actionable insights, such as suggesting refactoring opportunities or highlighting areas with technical debt. As quoted from a tech leadership article, “AI in code review isn’t just a tool; it’s a partner in building better software.”
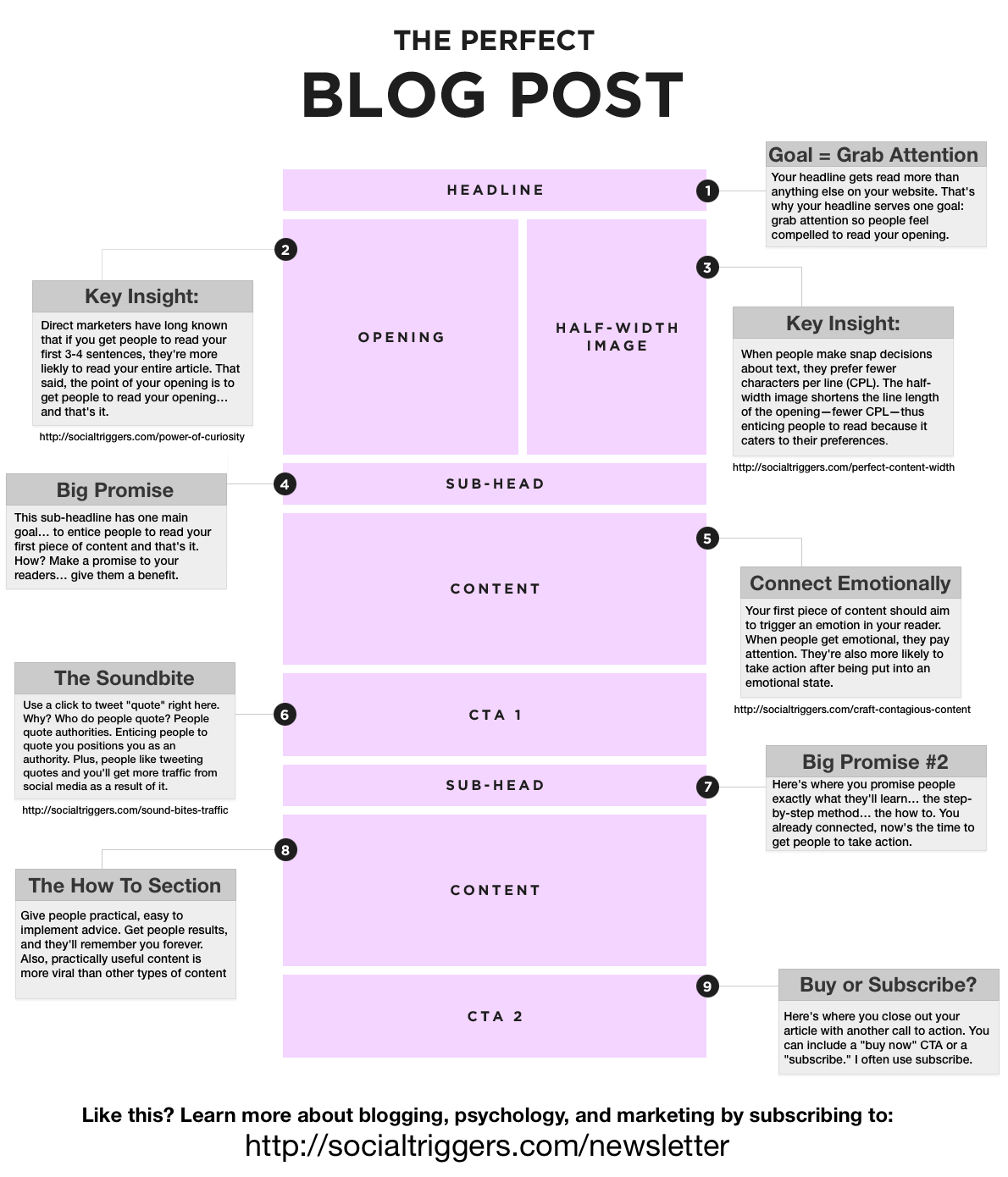
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the promise, AI-powered code review faces several hurdles that need addressing for widespread adoption:
- False Positives: AI might flag issues that aren’t actually problems, leading to unnecessary work and developer frustration. According to a critical analysis, this can reduce trust in the tool, with some teams reporting that up to 30% of AI suggestions require manual verification.
- Context Understanding: Code often requires domain-specific knowledge that AI may lack. For instance, a financial application’s logic for calculating interest might be misinterpreted without proper context, leading to irrelevant feedback. This limitation is explored in depth by domain-aware AI research.
- Integration Costs: Setting up and training AI systems can be resource-intensive, especially for small teams or legacy codebases. The initial investment in compute resources, data preparation, and tool customization can be prohibitive without clear ROI.
- Ethical Concerns: Reliance on AI could lead to job displacement fears, though many argue it augments rather than replaces human roles. Additionally, biases in training data might perpetuate unfair practices, such as favoring certain coding styles over others. A study on AI ethics calls for transparent algorithms to mitigate this.
- Over-reliance Risk: Developers might become complacent, assuming AI will catch all errors, which could lead to degraded code quality if not paired with human vigilance. Balancing automation with critical thinking is essential.
It’s crucial to approach AI code review as a complementary tool rather than a silver bullet. Regular audits, human-in-the-loop workflows, and continuous model retraining can help overcome these challenges. As noted by industry experts, successful implementation often involves pilot projects to fine-tune the AI to specific team needs.
Real-World Applications
Many organizations are already leveraging AI for code review, demonstrating its practical value across various sectors:
- Google: Uses internal AI tools like ReviewBot to review code for its massive codebase, focusing on scalability and consistency. Their systems integrate with monorepo workflows to provide instant feedback to thousands of developers daily.
- Microsoft: Integrates AI into Visual Studio and GitHub Copilot to provide real-time suggestions, from syntax corrections to design pattern recommendations. According to a GitHub case study, this has improved developer productivity by up to 55% in some teams.
- Startups: Companies like Snyk focus on AI-driven security reviews, catching vulnerabilities proactively by analyzing code dependencies and configurations. Similarly, SonarSource uses machine learning to enhance its static analysis tools for cleaner code.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and fintech firms employ AI code review to ensure compliance with regulatory standards, such as PCI-DSS or GDPR, by automatically flagging non-compliant code snippets. A report from FinTech Insights highlights how this reduces audit risks.
- Open Source Projects: Communities like the Linux Foundation experiment with AI tools to manage contributions from diverse developers, maintaining quality while scaling collaboration. Tools like CodeClimate offer AI-powered insights for public repositories.

These applications show that AI-powered code review isn’t just a futuristic concept but a present-day reality driving tangible improvements in software quality, security, and efficiency. By learning from these implementations, other organizations can tailor solutions to their unique environments.
Future Trends
The evolution of AI-powered code review is poised for exciting developments that will further integrate AI into the software development lifecycle:
- Collaborative AI: Systems that work alongside developers in real-time, offering explanations for suggestions and learning from interactive feedback. This moves beyond static reviews to dynamic partnerships, as envisioned in research on human-AI collaboration.
- Personalized Reviews: AI that adapts to individual coding styles and team standards, providing customized feedback that aligns with specific project goals. Machine learning models will become more nuanced, understanding context from historical team data.
- Cross-Language Support: Enhanced models that understand multiple programming languages seamlessly, breaking down barriers in polyglot environments. This is driven by advances in multilingual NLP, as discussed in a recent conference paper.
- Predictive Analytics: Using AI to forecast potential issues based on historical data, such as predicting which code changes are likely to introduce bugs or slowdowns. This proactive approach can shift left in the development pipeline, as explored in a research paper on predictive coding.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Greater transparency in how AI makes decisions, helping developers trust and understand suggestions. This involves generating human-readable justifications for code reviews, which is critical for adoption in regulated industries.
- Integration with DevOps and MLOps: AI code review becoming a standard component in CI/CD pipelines, automatically gating deployments based on quality metrics. This aligns with the trend towards autonomous operations, where AI oversees entire workflows.

As AI technology advances, we can expect more intelligent and intuitive code review tools that not only identify issues but also suggest optimizations, refactorings, and architectural improvements. The line between developer and AI will blur, fostering a symbiotic relationship that elevates software engineering to new heights of creativity and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What programming languages are supported by AI code review tools?
Most AI code review tools support popular languages like Python, JavaScript, Java, C++, and C#. Support for niche or emerging languages, such as Rust or Kotlin, is expanding as models are trained on diverse datasets from sources like GitHub trending repos. However, coverage may vary, so it’s advisable to check tool-specific documentation.
Is AI code review replacing human reviewers?
No, AI is designed to augment human reviewers by handling repetitive tasks and flagging potential issues. Human expertise remains essential for complex decision-making, context interpretation, and creative problem-solving. In fact, many teams report that AI frees up time for more meaningful discussions on design and architecture, as highlighted in a survey on developer productivity.
How accurate are AI-powered code reviews?
Accuracy varies by tool and training data. Top-tier AI tools can achieve precision rates of 80-90% for common bug patterns, but they may have false positives or miss nuanced issues. Continuous improvement through feedback loops and regular model updates is key to enhancing accuracy. Independent benchmarks, such as those from AI benchmarking groups, provide insights into performance across different scenarios.
What are the costs associated with implementing AI code review?
Costs can include subscription fees for cloud-based tools (ranging from free tiers to enterprise plans), integration efforts with existing systems, and training time for developers. However, many open-source options are available, and the long-term benefits—such as reduced bug-fixing costs and improved team velocity—often outweigh initial investments. A ROI analysis suggests that teams can break even within 6-12 months through efficiency gains.
Can AI code review tools handle legacy codebases?
Yes, but with limitations. AI tools can analyze legacy code for issues, but they may struggle with outdated patterns or lack of documentation. Custom training on specific codebases or phased integration strategies can help. Recommendations from experts in legacy modernization suggest starting with smaller modules to build confidence before scaling up.
How secure is AI code review in terms of data privacy?
Security depends on the tool’s deployment model. Cloud-based services may involve sending code to external servers, so it’s crucial to use providers with strong encryption and compliance certifications. On-premises solutions offer more control but require more resources. Always review privacy policies, as advised by data security guidelines, to ensure sensitive code isn’t exposed.