Smart Bike Sensors & AI Integration: The Future of Connected Commuting
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Smart bike sensors with AI integration are transforming bicycles from passive vehicles into intelligent transportation devices that analyze surroundings in real time.
- Key hardware includes GPS, 3D accelerometers, LiDAR, and cameras, which collect data for cycling performance tech enhancements.
- AI and machine learning algorithms process sensor data to enable real-time pattern detection, adaptive motor output, and autonomous learning.
- Connected commuting devices like smart helmets and phones work in harmony with bikes via Bluetooth, ANT+, and cloud networks for seamless communication.
- Practical benefits span improved safety through collision avoidance, efficiency via optimized routing, and security with GPS tracking and predictive maintenance.
Table of contents
- Smart Bike Sensors & AI Integration: The Future of Connected Commuting
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction: The Dawn of Intelligent Bicycles
- What Sensors Power Smart Bikes?
- How AI Makes Sense of Sensor Data
- How Smart Bikes Talk to Other Devices
- Why Safety Matters for Daily Commuting
- Optimizing Your Commute Route and Energy Use
- Protecting Your Bike and Extending Its Life
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction: The Dawn of Intelligent Bicycles
Imagine a world where your bicycle isn’t just a passive vehicle, but an intelligent companion that analyzes its surroundings in real time and adapts to riding conditions. This is the reality brought by AI-powered sensors, transforming bicycles into smart transportation devices. Smart bike sensors AI integration is making commutes safer, more efficient, and data-driven, directly addressing the informational search intent of modern cyclists seeking advanced cycling performance tech.

Rather than mere machines, modern smart bikes function as intelligent transportation devices that learn from rider behavior and environmental data to optimize every aspect of the commute. As referenced in research on AI smart bicycles, these bikes are evolving rapidly, leveraging connected commuting devices to create a seamless ecosystem. This post serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding this emerging technology landscape, where innovation meets daily transportation needs.
What Sensors Power Smart Bikes?
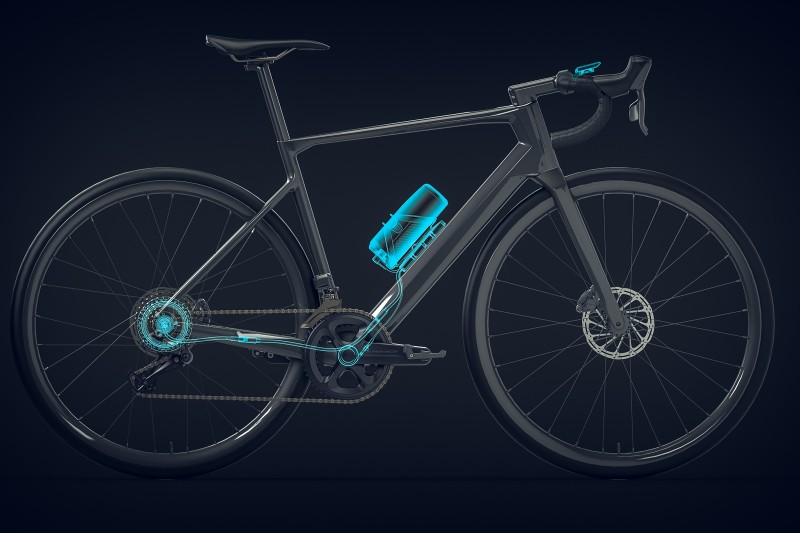
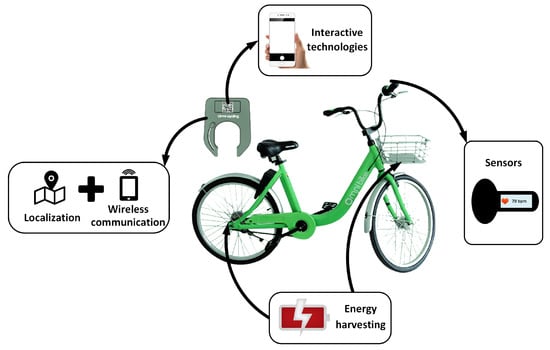
The hardware layer of smart bikes is equipped with a suite of sensors that collect vast amounts of data, forming the backbone of smart bike sensors technology. Here’s a breakdown of the key sensors:
- GPS modules: Track location and route information for commuters, enabling navigation and journey logging.
- 3D accelerometers: Measure vibration and surface irregularities—critical for detecting road hazards. As noted in research on smart bike systems, these sensors help improve cycling infrastructure by identifying rough terrain.
- Power and torque sensors: Monitor pedaling force to provide detailed cycling performance feedback. According to insights on smart features in bicycles, these sensors are shaping the future of biking by optimizing energy output.
- Cadence sensors: Track rotation speed to optimize pedaling efficiency, ensuring riders maintain an ideal pace for endurance and speed.
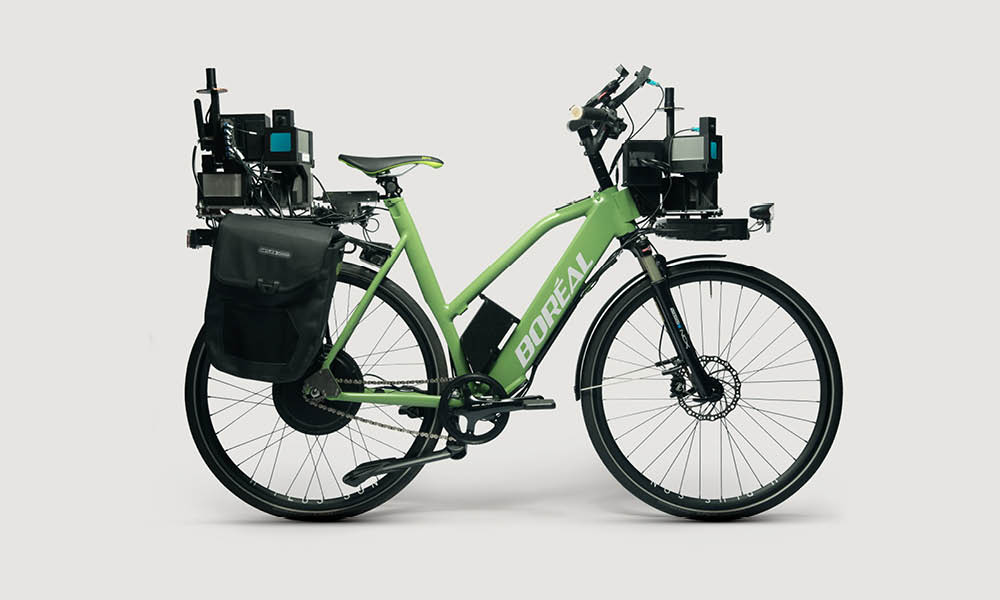
- LiDAR sensors: Advanced research bikes use up to five LiDAR sensors mounted in different directions, capturing 360-degree point cloud data at high frequency. As explained in tech research, these sensors record surroundings ten times per second with 240,000 data points per scan, enabling the bike to “see” its environment in unprecedented detail for obstacle detection.
- Video cameras: Provide environmental awareness and aid in collision detection, acting as the eyes of the bike for real-time hazard assessment.
- Brake pressure sensors: Monitor braking force and performance, ensuring responsive and safe stopping in various conditions.
- Tire grip and weather sensors: Offer real-time safety monitoring for traction and weather conditions. As highlighted in the smart future of electric bikes, these sensors are crucial for adaptive control, automatically adjusting bike behavior on wet or slippery surfaces.
However, raw sensor data alone is not valuable. As emphasized in discussions on wearable tech, data must be processed to become useful—this is where AI integration transforms information into intelligence.
How AI Makes Sense of Sensor Data
AI integration is the brain behind smart bikes, turning raw data into actionable insights. Through machine learning algorithms, sensor information is processed to assign meaning to environmental data. For instance, AI can classify points in a LiDAR scan as “street,” “vegetation,” or “building,” as detailed in AI smart bicycles research and cutting-edge AI technologies.

Key AI functionalities that enhance cycling performance include:
- Real-time pattern detection: AI systems detect patterns in rider behavior, analyze riding posture, and predict maintenance needs before components fail, as noted in smart bike technology insights. This proactive approach reduces downtime and improves reliability.
- Adaptive motor output: Algorithms adapt motor output based on terrain, rider weight, and pedaling cadence, optimizing power delivery for efficiency. This is explored in smart bike technology trends, showing how AI personalizes the riding experience.
- Autonomous learning features: AI learns individual rider patterns to automatically activate eco modes or conserve energy during idle states, making commutes more sustainable and cost-effective.
Quote: “AI transforms bicycles from data collectors to intelligent decision-makers, paving the way for safer and smarter commuting.” This intelligence needs to be shared across connected commuting devices, bridging toward an integrated ecosystem.
How Smart Bikes Talk to Other Devices
The true power of connected commuting devices emerges when they work in harmony. Smart bikes communicate via a network of technologies, creating a seamless ecosystem for cyclists.

- Connectivity protocols: Bluetooth and ANT+ connectivity enable bicycles to pair with smartphones, wearable fitness trackers, and smart helmets. As discussed in connectivity in bicycles, this integration is key to expanding functionality beyond the bike itself.
- Data flow architecture: Data flows between the bike’s onboard sensors, mobile applications, and cloud servers, creating a unified information network. This mirrors AI-powered smart homes trends, where devices interconnect to enhance user experience through centralized control.
- Smart helmets integration: Helmets with rear lights and turn signals integrate into the ecosystem to make riders more visible to motorists, reducing accident risk. AI in cycling details how these devices sync with bike sensors for coordinated safety alerts.
- AI-powered bike lights: Adjust brightness based on lighting conditions and can integrate turn signals for improved visibility, reacting dynamically to environmental changes.
- GPS tracking and geofencing: Alert riders if their bike moves outside a designated zone—critical for theft prevention on commuter bikes. Smart bike features highlight this capability, especially as e-bikes become premium targets.
- Collision avoidance technology: Uses sensors and cameras to forecast potential accidents and alert riders in time to take action, leveraging real-time data analysis.
- Real-time route optimization: Considers elevation, surface quality, and traffic conditions to allow commuters to plan faster and more pleasant journeys. Research shows how AI processes this data for optimal pathfinding.
- Automated incident detection: Identifies hazards such as potholes, bumps, cracks, and uneven surfaces, which are georeferenced and displayed in real time on users’ smartphones or computers. As defined in smart bike system research, this feature enhances infrastructure feedback and rider awareness.
This ecosystem delivers practical benefits to commuters, starting with the most critical aspect: safety.
Why Safety Matters for Daily Commuting
For urban commuters, daily traffic hazards are a reality. Smart bike sensors address these risks proactively through advanced safety features built on AI integration and connected commuting devices.

- Sensor-based brake systems: Monitor brake pressure and tire grip, automatically adjusting torque and slowing the bike when sensors detect rain or slippery surfaces. Smart bike technology describes how this system prevents skidding and improves control in adverse conditions.
- Collision detection and warning systems: Alert riders to potential hazards before they become critical, using data from cameras and LiDAR. As seen in AI smart bicycles, these systems reduce accident risk by providing early warnings.
- Automatic brake light activation: Increases visibility to motorists by activating based on deceleration patterns, ensuring that following vehicles are aware of slowing or stopping, even in low-light scenarios.
- Blind spot detection systems: Cameras and sensors provide warnings of nearby vehicles, enhancing situational awareness. AI in cycling insights cover this feature, which is particularly valuable in dense urban traffic.
Safety establishes trust; with these features, commuters can ride with confidence, knowing their bike is actively protecting them. This foundation allows for a transition into efficiency benefits that optimize daily rides.
Optimizing Your Commute Route and Energy Use
Smart bike sensors AI integration excels in making commutes more efficient by leveraging data for intelligent decision-making. Key features that enhance cycling performance tech include:
- AI-optimized route planning: Considers terrain elevation, road surface quality, traffic conditions, and personal fitness levels to suggest faster, more pleasant commuting paths. Research shows how this leads to time savings and reduced physical fatigue for daily riders.
- Real-time analytics for decision-making: Enables commuters to make superior choices during rides—such as deciding when to conserve energy on long distances or adapting to steep hills. As per smart bike controls, this analytics-driven approach personalizes the commute for maximum efficiency.
- Cycle path quality assessment: Evaluates cycle path quality, measuring surface conditions that traditional road-monitoring equipment cannot assess due to size and weight constraints. This technology, detailed in tech explorations, helps riders avoid rough patches and contributes to infrastructure improvements.
Because the system knows elevation changes, it can recommend routes that minimize effort, making commuting less strenuous and more enjoyable. Efficiency benefits demonstrate practical value, leading to maintenance and security advantages that protect your investment.
Protecting Your Bike and Extending Its Life
Connected commuting devices offer robust security and maintenance features, ensuring that your bike remains safe and operational for years. Through smart bike sensors and AI integration, these benefits include:

- GPS tracking and geofencing systems: Provide immediate alerts when bikes leave designated zones, protecting against theft—especially critical as e-bikes achieve premium product status. The smart future of electric bikes emphasizes this feature, giving riders peace of mind during parking or storage.
- Predictive maintenance methodology: AI algorithms compare usage patterns and sensor data to identify wear and tear before failures occur. For example, by monitoring brake pad thickness or battery health, the system can alert riders to schedule servicing, thus extending the bike’s lifespan and preventing costly repairs.
- Maintenance alerts: Integrated with mobile apps, these alerts provide timely notifications based on real-time data, ensuring that components like chains, tires, and motors are maintained optimally for sustained cycling performance.
With these benefits, smart bikes are revolutionizing the commuting experience, blending innovation with practicality to meet the demands of modern urban life.
Frequently Asked Questions

Q: What exactly are smart bike sensors, and how do they differ from traditional bike components?
A: Smart bike sensors are advanced hardware like GPS, LiDAR, and accelerometers that collect real-time data on environment, performance, and rider behavior. Unlike traditional parts, they integrate with AI to provide actionable insights, making bikes intelligent and responsive rather than passive.
Q: How does AI integration improve cycling safety in daily commutes?
A: AI processes sensor data to detect hazards, predict collisions, and adapt systems like braking automatically. For instance, it can classify road surfaces and adjust torque, or warn riders of nearby vehicles, significantly reducing accident risks through proactive measures.
Q: Can smart bikes connect to other devices I already use, like smartphones or smartwatches?
A: Yes, through connectivity protocols like Bluetooth and ANT+, smart bikes pair seamlessly with smartphones, smartwatches, and other connected commuting devices. This allows for data synchronization, app-controlled features, and enhanced ecosystem integration for a unified experience.
Q: Are smart bikes only suitable for electric bicycles, or can they be added to regular bikes?
A: While commonly featured in e-bikes, smart sensor technology can be retrofitted to traditional bicycles via add-on kits. This brings cycling performance tech like GPS tracking and performance analytics to any bike, making advanced features accessible to all riders.
Q: How does predictive maintenance work, and is it reliable for preventing breakdowns?
A: Predictive maintenance uses AI to analyze data from sensors—such as vibration from components or battery usage patterns—to forecast wear before failures occur. It’s highly reliable when calibrated correctly, offering timely alerts that extend bike life and reduce unexpected repairs.
Q: What are the key benefits of a connected commuting ecosystem for urban cyclists?
A: The ecosystem enhances safety through device synergy (e.g., smart helmets with bike lights), improves efficiency via real-time route optimization, and boosts security with theft prevention tools. It creates a cohesive network that makes commuting smarter, safer, and more enjoyable.