Exploring Zoox Robotaxi Production Facility Capacity: Location, Scale, and the Competitive Landscape
Estimated reading time: 18 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Zoox, an Amazon subsidiary, is developing a unique, purpose-built fully electric robotaxi, distinguishing itself from competitors who often retrofit existing vehicles.
- Central to Zoox’s strategy is a dedicated manufacturing plant in California’s Bay Area, specifically designed for mass-producing its robotaxi.
- The planned Zoox robotaxi production facility capacity at full scale is *over 10,000 vehicles annually*, a significant number aimed at supporting large-scale urban fleet deployments.
- Factors like high automation, a robust custom supply chain, and a skilled workforce are critical for Zoox to achieve its production goals.
- In the zoox vs waymo vs tesla robotaxi market, Zoox’s dedicated facility and vehicle design contrast with Waymo’s OEM partnerships and Tesla’s vertical integration, potentially offering advantages in optimization but requiring higher initial investment.
- The zoox robotaxi commercial launch date is tied closely to the manufacturing ramp-up, with initial public rides planned for Las Vegas in 2025, followed by San Francisco.
- Achieving high-volume production at the amazon zoox manufacturing plant california is *essential* for Zoox to move beyond pilots and compete effectively for market share in the burgeoning robotaxi industry.
Table of contents
- Exploring Zoox Robotaxi Production Facility Capacity: Location, Scale, and the Competitive Landscape
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction
- Zoox’s Dedicated Manufacturing Plant in California
- Understanding Zoox’s Production Capacity
- Zoox in the Competitive Robotaxi Market: Zoox vs. Waymo vs. Tesla
- Timeline and Commercial Deployment
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
The rise of autonomous robotaxis is poised to How AI is Changing the World: Transforming Your Everyday Life and revolutionize urban transportation, marking a significant shift in how people move within cities. This burgeoning market is attracting massive investment and intense competition among key players like Waymo, Tesla, and Zoox. These companies are not just developing advanced AI and sensor technology; they are in a heated race to *deploy* driverless vehicles at a scale sufficient to disrupt traditional ride-hailing and personal car ownership. Each competitor has adopted a distinctly different strategy for bringing their vision to life (Source – Source).

Waymo, the self-driving unit of Alphabet (Google’s parent company), has largely focused on retrofitting existing vehicle platforms with its proprietary autonomous driving stack. Tesla, known for its electric vehicles, is pursuing a vertically integrated approach, aiming to upgrade its standard production cars with increasingly sophisticated AI capabilities to eventually enable robotaxi services using its existing fleet and manufacturing capacity. Zoox, acquired by Amazon in 2020, has taken an entirely different path. Instead of modifying existing cars, Zoox is developing a purpose-built, fully electric robotaxi from the ground up. This distinctive vehicle lacks traditional driver controls like a steering wheel and pedals, being designed purely for autonomous urban mobility (Source – Source). This fundamental strategic difference has profound implications, especially when considering the critical factor of production scale.

The ability to manufacture these complex autonomous vehicles reliably and at volume is paramount to success in the robotaxi market. This brings us to the core topic of this blog post: the zoox robotaxi production facility capacity. While the technology grabs headlines, the *industrial muscle* required to produce thousands of safe, reliable robotaxis is the quiet engine driving deployment. This post will delve into Zoox’s dedicated manufacturing plant in California, its ambitious production capacity goals, how this capacity compares to competitors in the broader zoox vs waymo vs tesla robotaxi market, and the crucial link between achieving scaled production and determining the precise zoox robotaxi commercial launch date and subsequent expansion plans. Understanding Zoox’s manufacturing capability provides vital insight into its potential trajectory and its competitive position in the race for autonomous mobility.
Zoox’s Dedicated Manufacturing Plant in California
Zoox’s strategic decision to design a novel, purpose-built autonomous vehicle necessitated an equally innovative approach to manufacturing. Their production efforts are primarily centered in California’s bustling Bay Area, a hub known for both tech innovation and manufacturing prowess. Initially, Zoox operated a smaller facility in Fremont, California, which served as a crucial site for developing and producing early prototypes and conducting rigorous testing. This allowed engineers and manufacturing experts to refine the complex assembly process for their unique vehicle design. However, scaling a robotaxi service across cities requires a much larger throughput than a prototype facility can provide.
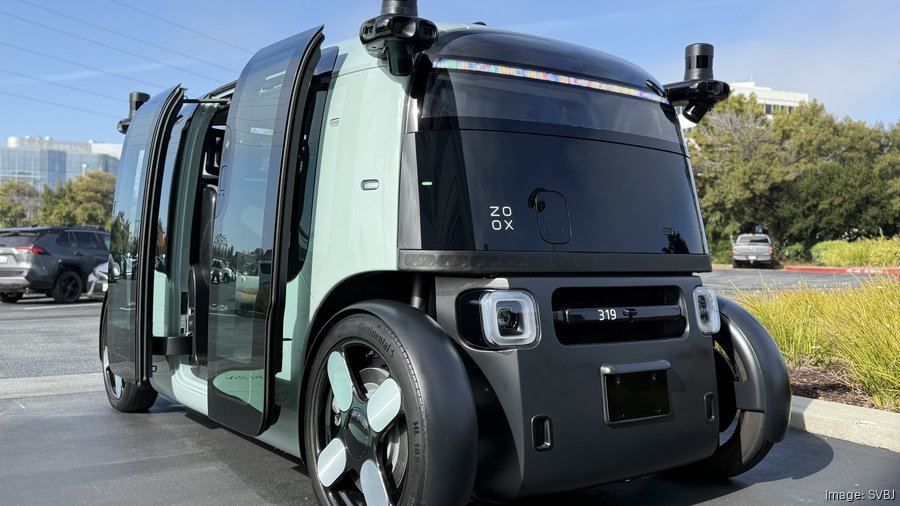

Recognizing this need, Zoox significantly expanded its manufacturing footprint by establishing a new, much larger dedicated manufacturing site. This new facility is also located in California, specifically designed and engineered to dramatically scale up robotaxi output (Source). This move is a clear indicator of Zoox’s commitment not just to developing the technology, but to becoming a *mass producer* of autonomous vehicles. It signals a transition from the R&D phase to serious, high-volume manufacturing preparatory to commercial deployment.
The significance of building a dedicated facility for the amazon zoox manufacturing plant california cannot be overstated. This approach starkly contrasts with competitors like Waymo, which primarily collaborate with traditional automakers to integrate their self-driving technology into existing vehicle models, or even Tesla, which, while vertically integrated, initially focused on adapting its standard EV production lines for autonomy (Source – Source). By controlling the entire manufacturing process in its own facility, Zoox can fully optimize its vehicles for their intended purpose: autonomous urban ride-hailing.

This purpose-built production capability means that every aspect of the vehicle – from the chassis designed without a steering column or pedals, to the unique bidirectional driving system, to the seamless integration of the sensor array and battery pack – can be optimized for autonomy, passenger safety, comfort, and the demanding duty cycle of urban ride-hailing (Source – Source). It allows for a level of integration and design synergy that is challenging to achieve when retrofitting technology onto a vehicle platform originally designed for human driving. The The Rise of Unbeatable AI-Powered Smart Vehicles: Exploring the Cutting Edge of AI in Cars hinges on such integrated design.
The new Bay Area plant is engineered for serial production, meaning it’s built to produce vehicles on an assembly line in significant numbers. Its current status involves setting up the production lines, calibrating complex machinery, and training the specialized workforce needed to assemble these advanced vehicles. The initial focus is on carefully ramping up output as Zoox transitions from its test fleets to providing commercial service. This involves moving from producing a small number of hand-built or low-volume vehicles to a more streamlined, higher-volume process capable of supporting city-wide operations. This facility is specifically tasked with supporting Zoox’s planned expansion across U.S. cities, with Las Vegas and San Francisco publicly named as among the first commercial markets targeted for offering public robotaxi rides (Source – Source). The success of this plant in achieving its production targets is directly linked to Zoox’s ability to meet its deployment timelines and establish a significant presence in the robotaxi market.
Understanding Zoox’s Production Capacity
Getting into the nuts and bolts of Zoox’s operational capabilities means focusing directly on the zoox robotaxi production facility capacity. This number is arguably as important as the technological readiness of the autonomous driving system itself. Without the ability to build vehicles at scale, even the most advanced robotaxi technology remains confined to test tracks and limited pilot programs.
The question on many minds is: how many robotaxis can zoox produce per year once their new California facility is fully operational? The planned annual production capacity for Zoox’s new manufacturing facility is substantial: at full scale, it can assemble *over 10,000 robotaxis annually* (Source). This figure is transformative. It represents the capability to move beyond small test fleets to fielding large, citywide autonomous fleets that can truly begin to serve the transportation needs of residents and visitors. A fleet of 10,000 vehicles is large enough to cover significant areas of a major city or launch simultaneously in multiple smaller markets.

It’s important to contrast this planned capacity with Zoox’s current operational scale. As of recent reports, Zoox is still largely in the testing and pilot phase, operating a low-volume production line that has supported the deployment of around two dozen test vehicles across six cities (Source, Source). The transition from “dozens” to “hundreds” and eventually to “thousands” per year is a massive undertaking, involving scaling personnel, optimizing supply chains, and perfecting assembly processes under serial production conditions. The new plant is designed precisely to enable this leap, allowing Zoox to move from producing hundreds of vehicles in the initial ramp-up phases to thousands as operations mature and demand from commercial deployment grows (Source, Source).
Several factors determine the true, achievable production capacity of such a sophisticated manufacturing facility:
- Automation Level: The degree to which the assembly line is automated directly impacts speed, consistency, and potentially quality. Advanced robotics and automated systems streamline repetitive tasks, increasing throughput and allowing the specialized human workforce to focus on complex assembly and quality control points unique to an autonomous vehicle.
- Supply Chain Robustness: Manufacturing 10,000 vehicles annually requires a highly reliable and high-volume supply chain. For Zoox’s purpose-built vehicle, this means sourcing a multitude of custom components – from specialized chassis parts to integrated sensor arrays, lidar units, radar systems, and large, high-density battery packs. Ensuring consistent, high-quality delivery of these unique parts is essential for maintaining a steady production flow and reaching the desired zoox robotaxi production facility capacity. Disruptions in sourcing, particularly for cutting-edge components like advanced sensors or batteries, can severely constrain output.
- Workforce: While automation is key, assembling and testing complex, first-of-their-kind vehicles like the Zoox robotaxi requires a highly skilled human workforce. Engineers, technicians, and assembly line personnel need specialized training to handle the unique components and rigorous quality control processes. Zoox’s decision to custom-build its hardware means it needs expertise not just in traditional vehicle assembly but also in integrating sophisticated electronics, software, and sensor systems. Building and retaining this skilled base is vital for production ramp-up and long-term capacity.
- Facility Design and Efficiency: The layout and engineering of the factory itself play a crucial role. A purpose-built facility, like Zoox’s new California plant, can be designed from the ground up to optimize the flow of materials and assembly steps specifically for the robotaxi. This supports more efficient processes compared to trying to adapt traditional auto manufacturing plants, which are designed for vehicles with internal combustion engines, steering wheels, and pedals, to accommodate a completely different form factor and component set (Source). Lean manufacturing principles and continuous process improvement are critical for maximizing throughput within the physical constraints of the plant.
Achieving the target of over 10,000 vehicles per year is not just a manufacturing goal; it is a prerequisite for Zoox to become a meaningful player in the robotaxi market. This capacity allows them to envision and execute large-scale fleet deployments needed to serve the populations of major urban centers.
Zoox in the Competitive Robotaxi Market: Zoox vs. Waymo vs. Tesla
Understanding Zoox’s production capacity gains context when viewed within the broader zoox vs waymo vs tesla robotaxi market. These three companies represent distinct strategic approaches to conquering the autonomous ride-hailing frontier, and their manufacturing strategies are a key differentiator. Comparing their core features highlights where Zoox’s approach, heavily reliant on its zoox robotaxi production facility capacity, fits into the competitive landscape.

Let’s compare the key aspects:
- Vehicle Type:
-
- Zoox: Purpose-built robotaxi, designed from scratch for autonomy without traditional driver controls.
-
- Waymo: Primarily modifies production vehicles from partners (e.g., Jaguar I-PACE electric SUVs, Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid minivans) by integrating their autonomous driving system.
- Tesla: Adapting its own production vehicles (Model 3/Y/S/X) with advanced driver-assistance hardware/software, with rumors of potentially dedicated robotaxi designs in the future.
-
- Manufacturing Model:
-
- Zoox: Operates a dedicated facility specifically for assembling its unique robotaxi design.
-
- Waymo: Partners with traditional Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) like Jaguar Land Rover and Stellantis (formerly Fiat Chrysler) to build the base vehicles, which Waymo then integrates with its autonomous technology.
- Tesla: Vertically integrated; uses its own Gigafactories to produce its vehicles, aiming to leverage this capacity for future robotaxi deployment.
-
- Fleet Size & Scale:
-
- Zoox: Currently operating dozens of vehicles in test/pilot phases across several cities, with the new plant aiming to scale to thousands.
-
- Waymo: Operates a fleet of several hundred vehicles providing public or employee rides in operational markets like Phoenix, San Francisco, and Los Angeles.
- Tesla: Has tens of vehicles in pilot programs, with aggressive plans for large-scale deployment announced.
-
- Vehicle Control Model:
-
- Zoox: Vehicle is *fully* autonomous with no steering wheel, pedals, or manual driver controls, designed solely for AI operation.
-
- Waymo: Vehicles are autonomous but retain manual controls (steering wheel, pedals) for human safety drivers or specific operational needs.
- Tesla: Working toward Level 4/Level 5 autonomy, but current production cars are designed with full manual driver controls and require human supervision for L2/L3 functions.
-
- Deployment Status:
-
- Zoox: In early pilots and testing, with commercial launches planned soon in Las Vegas and San Francisco.
-
- Waymo: Commercially operational with public ride services in several U.S. cities, including fully driverless options in some areas.
- Tesla: Has announced robotaxi plans and timelines but does not yet operate a public commercial robotaxi fleet.
-
This comparison highlights how Zoox’s purpose-built vehicle, enabled by its dedicated manufacturing facility, represents a significant divergence from its main competitors. Waymo relies on the established mass-production capabilities of traditional OEMs, retrofitting standard passenger vehicles (Source). Tesla leverages its existing massive EV production lines and aims to activate autonomy capabilities in its standard vehicles (Source). Zoox, however, is building a unique factory to produce a unique vehicle (Source).

The potential advantages of Zoox’s approach are clear: complete control over the vehicle design and build process allows for maximum optimization for autonomous operation, passenger experience (e.g., seating layout, ride comfort in a bidirectional vehicle), safety features specifically for an autonomous context, and the demanding operational profile of a constantly running urban robotaxi (Source – Source – Source). This could potentially lead to a more robust, efficient, and safer robotaxi in the long run.
However, this strategy also comes with potential disadvantages: the initial investment in designing a new vehicle and building a dedicated factory is substantially higher than retrofitting existing platforms. Furthermore, the ramp-up time to achieve high-volume production in a new, specialized facility might be longer and face different challenges compared to leveraging established automotive production lines or OEM partnerships. The Critical AI Challenges Tech Industry 2025: Future Trends and Upcoming Regulations for all players include navigating the complex intersection of advanced AI, hardware design, manufacturing scalability, and regulatory landscapes.
Crucially, production capacity, specifically the zoox robotaxi production facility capacity and its competitors’ abilities to scale, is a key battleground in this market. The operational scale of a robotaxi service is directly proportional to the number of vehicles that can be reliably deployed. The first player to successfully produce and deploy large, reliable fleets capable of serving significant demand in multiple cities is likely to capture significant early market share and establish network effects (Unbeatable AI-Powered Transportation: Revolutionary Self-Driving Cars Dominating 2025 and Beyond). Zoox’s ambitious production goal of over 10,000 vehicles per year indicates their understanding that winning the robotaxi race requires not just superior technology but also superior manufacturing and deployment capability.
Timeline and Commercial Deployment
The path to the zoox robotaxi commercial launch date is intricately linked to the readiness of its technology and, perhaps even more critically, the scaling of its manufacturing operations. Zoox has publicly stated its plans, providing a concrete timeline for its initial public rollout. The company is actively preparing to launch its first public robotaxi rides in Las Vegas in 2025 (Source). This marks a significant milestone, moving beyond employee-only pilots and limited public demonstrations to offering rides to the general public in a major U.S. city.
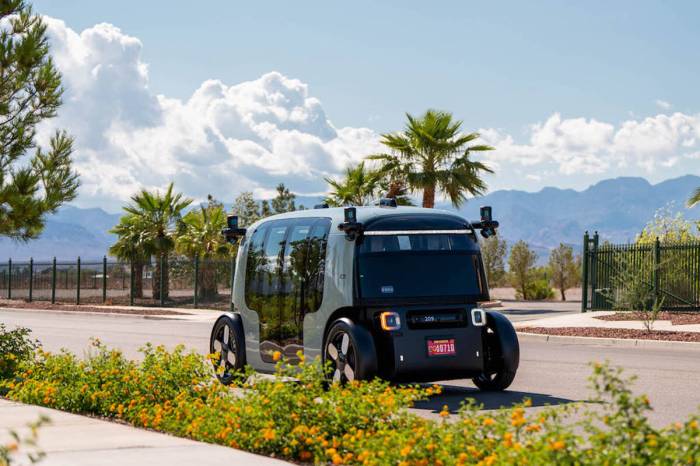

Following the initial launch in Las Vegas, San Francisco is planned to be the next city where Zoox will offer public rides (Source). These initial markets represent strategic choices – environments where Zoox has significant testing experience (San Francisco) or areas with specific characteristics conducive to early autonomous deployment (Las Vegas). The speed at which Zoox can expand its service to additional areas within these cities, and then to entirely new markets, depends heavily on the scaling of manufacturing at the amazon zoox manufacturing plant california (Source, Source – Source).

The initial operational focus for Zoox will involve phased rollouts. This typically begins with carefully defined operational domains – specific neighborhoods or routes – often starting with employee or limited public pilot programs in controlled environments. As the technology proves itself and the manufacturing ramps up, these operational domains can be expanded, and services opened to a wider public. This measured approach allows Zoox to gather real-world data, refine its AI and operations, and ensure safety before attempting widespread deployment.
Scaling the zoox robotaxi production facility capacity is not just about building vehicles; it’s critical for Zoox’s broader commercial ambitions (Source, Source – Source). A small fleet can only serve a limited number of rides. To compete effectively with established ride-hailing services and other robotaxi providers, Zoox needs a large, reliable fleet capable of meeting significant demand in busy urban centers.
As the new California facility ramps up towards its target of over 10,000 vehicles assembled annually, the company’s ability to move from testing and limited pilots to fully operational, high-capacity robotaxi fleets in multiple U.S. cities will accelerate (Source, Source – Source). This increased production capacity directly enables broader commercial deployment and geographic expansion, which in turn directly impacts Zoox’s potential market share and operational scale in the burgeoning autonomous mobility sector. The 2025 launch is just the beginning, heavily dependent on the successful execution of their manufacturing strategy in California.
Conclusion
Zoox has embarked on a bold and unique strategy in the race to deploy autonomous robotaxis: building a purpose-designed vehicle specifically for this application, rather than adapting existing car models.
Central to this strategy is the establishment of its dedicated amazon zoox manufacturing plant california. This facility is not merely an assembly line; it is the physical embodiment of Zoox’s commitment to controlling the entire vehicle development and production process.
The significance of the zoox robotaxi production facility capacity cannot be overstated. With a target of assembling over 10,000 vehicles annually at full scale, Zoox aims to achieve the volume necessary for meaningful, city-wide service deployments (Source, Source). This planned capacity directly answers the question of how many robotaxis can zoox produce per year once operations are fully ramped up.

Looking at the zoox vs waymo vs tesla robotaxi market, Zoox’s dedicated plant and custom vehicle design offer potential advantages in optimization compared to Waymo’s reliance on OEM partnerships or Tesla’s adaptation of existing vehicle platforms (Source – Source). However, this path also demands higher initial investment and faces the complexities inherent in establishing a novel manufacturing pipeline.
The progress at the California facility is the key enabler for Zoox’s zoox robotaxi commercial launch date, with the planned 2025 debut in Las Vegas marking the critical first step towards public service (Source).
The coming years will be telling, revealing whether Zoox’s vertically integrated, custom manufacturing approach will successfully translate into large-scale, reliable deployments.
The success of its California plant and its ability to consistently reach and maintain the planned production capacity will ultimately be critical in determining Zoox’s market share and solidifying its position as a leader among the pioneers of autonomous mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Zoox’s approach to robotaxi production?
Zoox builds a purpose-designed, fully electric robotaxi from scratch in its own dedicated manufacturing facility in California, rather than retrofitting existing vehicles.
- Where is the main Zoox robotaxi production facility located?
Zoox’s primary, dedicated manufacturing plant is located in California’s Bay Area, designed for serial production.
- What is the planned annual production capacity of the Zoox factory?
At full scale, Zoox’s new manufacturing facility is designed to assemble over 10,000 robotaxis annually.
- How does Zoox’s manufacturing compare to Waymo and Tesla?
Zoox uses a dedicated plant for its unique purpose-built vehicle. Waymo partners with traditional OEMs to retrofit vehicles. Tesla is vertically integrated, adapting its own standard EV production lines for potential robotaxi use.
- When is the Zoox robotaxi commercial launch date?
Zoox is planning to launch its first public robotaxi rides in Las Vegas in 2025, with San Francisco planned to follow.
- Why is a dedicated manufacturing facility important for Zoox?
A dedicated facility allows Zoox to optimize every aspect of its unique purpose-built vehicle for autonomy, safety, and urban ride-hailing, controlling the entire design and build process for better integration and efficiency at scale.
- What factors affect Zoox’s production capacity?
Key factors include the level of automation in the plant, the robustness of the supply chain for custom components, the size and skill of the workforce, and the efficiency of the facility’s design and processes.