Tech Regulation Trends 2026: Navigating AI Governance and Privacy in a Shifting Landscape
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Tech regulation trends 2026 AI governance privacy represent a pivotal shift from fragmented policies to coordinated frameworks balancing innovation with accountability.
- Global data policy shifts worldwide are evolving into a more interconnected quilt, demanding adaptive strategies from tech firms.
- Youth online safety laws are surging, requiring platforms to redesign algorithms and enhance protections for minors.
- Operational accountability in tech extends to algorithmic audits and transparency reporting, enforced through tools like federated data governance.
- AI governance is mission-critical for high-risk systems, mandating frameworks like acceptable use policies and human validation of outputs.
- The regulatory impact on big tech innovation is dual-edged, raising compliance costs but fostering stable environments for trustworthy tech.
Table of contents
- Tech Regulation Trends 2026: Navigating AI Governance and Privacy in a Shifting Landscape
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction
- Trend 1: The Global Patchwork Becomes a Quilt – Worldwide Data Policy Shifts
- Trend 2: Prioritizing the Digital Generation – Youth Online Safety Laws
- Trend 3: From Principle to Practice – Enforcing Operational Accountability in Tech
- Trend 4: Governing the Black Box – The Specific Challenge of AI Governance
- The Innovation Dilemma: Analyzing the Regulatory Impact on Big Tech Innovation
- Synthesis and Perspectives
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Tech regulation trends 2026 AI governance privacy represent a pivotal shift where fragmented policies evolve into coordinated frameworks balancing rapid innovation with accountability and public trust, as tech firms navigate AI, data protection, and safety demands. This post aims to provide a forward-looking overview of key global tech regulation trends 2026 AI governance privacy shaping technology governance, focusing on how they interplay with AI governance, privacy rules, and operational safety to influence tech operations, R&D, and product development [source].

How will these regulations reshape tech companies’ agility, R&D, and market strategies? This question is central for stakeholders seeking informational insights on tech governance. As we explore, we’ll tease the major trends ahead: worldwide data shifts, youth safety, operational accountability, AI specifics, and innovation impacts.
Trend 1: The Global Patchwork Becomes a Quilt – Worldwide Data Policy Shifts
This trend defines regulations shifting from isolated national rules to more interconnected global standards driven by cross-border data flows, economic rivalries, and demands for consistent consumer protections [source] [source].
Driving Forces in Detail:
- Cross-border data flows: These require harmonization to avoid conflicts, as data traverses borders seamlessly, pushing for aligned rules.
- Economic competition: Countries align standards for fair trade, reducing barriers and fostering global cooperation.
- Citizen demands: Amplified calls for uniform consumer protections turn a regulatory patchwork into a cohesive quilt.

Challenges for Tech Firms: They face diverse requirements for data policy shifts worldwide including data privacy (e.g., varying consent rules), cybersecurity (e.g., breach reporting timelines), and consumer safeguards (e.g., transparency mandates) across jurisdictions, necessitating adaptive strategies like detailed market analyses (mapping regulations per region) and localized compliance infrastructures (e.g., region-specific data centers) [source].
Opportunities: This complexity opens pathways for harmonized standards like emerging GDPR-like frameworks worldwide (e.g., EU’s global influence via adequacy decisions), creating strategic opportunities for scalable data governance that tech companies can leverage for efficiency [source].
Trend 2: Prioritizing the Digital Generation – Youth Online Safety Laws
Youth online safety laws surging as a core regulatory priority within broader child data protections and global privacy shifts, rather than purely standalone mandates [source].
Legislative Models:
- Age-appropriate design codes: Platforms must default to high-privacy settings for kids.
- Enhanced parental consents: Verifiable parental approval for data processing.
- Platform duties of care: Proactive harm prevention via risk assessments.
These influence content moderation (e.g., stricter algorithms for harmful content) and data practices for minors via stringent privacy rules like GDPR extensions (e.g., Article 8 on child consent) [source].

Impacts: These laws compel platforms to redesign algorithms (e.g., demote risky content for under-16s), limit data collection (e.g., no behavioral profiling without consent), and prioritize vulnerability protections amid rising global scrutiny on handling young users’ data [source].
Relatable examples: The U.S. Kids Online Safety Act or UK’s Online Safety Bill illustrate these trends in action, making digital spaces safer for youth.
Trend 3: From Principle to Practice – Enforcing Operational Accountability in Tech
Operational accountability in tech extends beyond financial audits to include algorithmic audits (independent reviews of AI decision-making), mandatory risk assessments (pre-deployment evaluations of biases and harms), and transparency reporting (public disclosures of data usage and model performance) [source] [source] [source].
Enforcement Tools: Regulators demand scrutiny of internal AI and data processes; frameworks like federated data governance decentralize ownership (e.g., data stays local while enabling shared analytics); “compliance as code” embeds policies into development pipelines (e.g., automated checks during CI/CD for regulatory alignment) for real-time risk monitoring [source] [source].

Risks and Balances: Overly rigid structures can stifle flexibility (e.g., slowing agile development), underscoring the need for human-in-the-loop oversight (e.g., executives approving AI outputs) to ensure ethical enforcement without hindering innovation [source].
Trend 4: Governing the Black Box – The Specific Challenge of AI Governance
AI governance is mission-critical for high-risk systems (e.g., those affecting health, finance, or hiring), mandating formal frameworks including acceptable use policies (rules on AI deployment), centers of excellence (dedicated teams for oversight), and human validation of outputs (manual checks on critical decisions) to build trust [source] [source].
Transparency and Intersections: Measures like AI labeling (disclosing AI-generated content) and liability rules (assigning responsibility for errors) intersect with privacy rules, addressing training data usage (e.g., anonymization requirements), inferential privacy risks (e.g., re-identifying users from models), and diverse regulatory environments (e.g., EU AI Act tiers) [source] [source].

Warnings: Embedded AI in software poses overlooked risks without governance, amplified by global variations in data security (e.g., encryption mandates) and cybersecurity (e.g., adversarial attack defenses) [source].
The Innovation Dilemma: Analyzing the Regulatory Impact on Big Tech Innovation
The regulatory impact on big tech innovation is a dual-edged sword where stringent rules on AI, privacy, and accountability raise compliance costs (e.g., hiring compliance officers) and demand local adaptations (e.g., region-specific AI models), potentially constraining agility [source] [source] [source].
Balanced Arguments: Regulations may stifle unchecked expansion but foster stable environments for trustworthy tech (e.g., certified safe AI gains consumer preference); examples include redirecting R&D toward auditable models (e.g., explainable AI), secure data practices (e.g., privacy-by-design), M&A scrutiny (e.g., antitrust blocks), and tax complexities (e.g., digital services taxes), leveling competition while enabling long-term market trust and global entry [source].
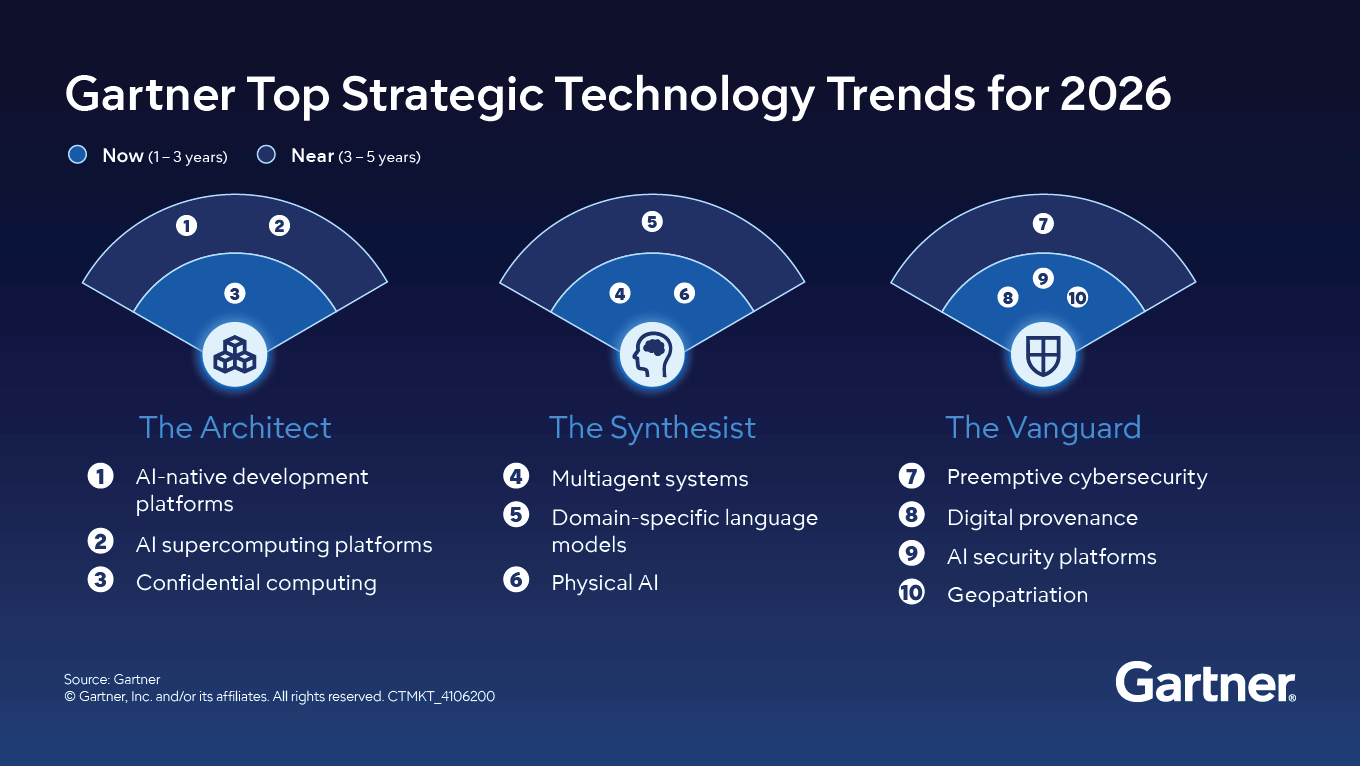
Proactive Benefits: Governance prevents breaches (e.g., data leaks costing millions), turning regulation into a competitive differentiator via sustainable innovation [source].
Synthesis and Perspectives
Tech regulation trends 2026 AI governance privacy show how AI governance, privacy rules enhancements, youth online safety laws, and operational accountability in tech will intertwine to demand resilient frameworks amid global complexities [source] [source].
Perspectives:
- Businesses: Should build scalable compliance like AI centers of excellence (cross-functional teams) and embedded code policies (automated regulatory checks).
- Consumers: Gain amplified rights (e.g., data deletion) and protections (e.g., age gates).
- Policymakers: Must refine implementation (e.g., flexible enforcement) without rigidity [source].

Final Thought: Stay informed on these evolving tech regulation trends 2026—subscribe for updates, share your thoughts in comments, or contact us to audit your compliance strategy—to navigate toward responsible innovation confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key tech regulation trends for 2026?
The key trends include worldwide data policy shifts, youth online safety laws, operational accountability in tech, and specific AI governance challenges, all intertwining with privacy rules to shape technology governance.
How will data policy shifts worldwide affect tech companies?
Tech companies will face diverse requirements across jurisdictions, necessitating adaptive strategies like market analyses and localized compliance infrastructures, but also opportunities for harmonized standards that streamline operations.
What are youth online safety laws, and why are they important?
Youth online safety laws are regulations that prioritize protections for minors, requiring platforms to implement age-appropriate designs, enhanced consents, and duties of care to prevent harm and ensure privacy, reflecting growing global scrutiny.
What does operational accountability in tech entail?
It involves extending accountability beyond finances to include algorithmic audits, risk assessments, and transparency reporting, enforced through tools like federated data governance and compliance as code for real-time monitoring.
Why is AI governance critical in 2026?
AI governance is critical for managing high-risk AI systems, ensuring transparency, liability, and privacy intersections, and preventing overlooked risks in embedded software, which is essential for public trust and safety.
How does regulation impact big tech innovation?
Regulation has a dual impact: it can raise compliance costs and constrain agility, but also fosters stable environments for trustworthy tech, redirects R&D toward secure practices, and levels competition, enabling sustainable growth.





