“`html
Mastering Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors and Beyond
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Encountering Gemini Pro function call tooling errors can halt AI integrations, but understanding common causes like incorrect signatures and data type mismatches is key.
- AI agents failing to call tools often point to broader issues such as insufficient permissions, flawed prompt engineering, or errors in tool definitions.
- Platform-specific errors like the ‘content not available’ Facebook error or the general ‘cannot fulfill request’ AI error require targeted troubleshooting.
- Network issues, exemplified by ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED chrome, can significantly impact AI tool performance and require systematic network and browser diagnostics.
- Proactive strategies including robust prompt engineering, accurate tool definitions, and comprehensive error handling are vital for a smooth AI experience.
Table of contents
- Mastering Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors and Beyond
- Key Takeaways
- Decoding Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
- What is Function Calling in Gemini Pro?
- Common Causes of Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
- Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
- When an AI Agent Isn’t Calling Tools
- Differentiating AI Agent Issues from Specific Function Calling Errors
- Reasons for an AI Agent Not Calling Tools
- Strategies to Diagnose and Fix AI Agent Tool Issues
- Tackling Specific Platform and AI Errors
- How to Fix ‘Content Not Available’ Facebook Error
- How to Solve ‘Cannot Fulfill Request’ AI Error
- Troubleshooting ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED in Chrome
- The Impact of Network Connectivity on AI Tools
- Detailed Guide to Troubleshoot ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED Chrome
- Proactive Strategies for Error Prevention
- Effective Prompt Engineering for AI
- Accurate Tool Definitions and Configurations
- Staying Updated with AI Models and Platform Changes
- Implementing Robust Error Handling in Applications
It’s a common scenario: you’ve integrated a powerful AI tool, perhaps even something as cutting-edge as Gemini Pro, expecting seamless automation. Yet, instead of the results you anticipated, you’re met with cryptic error messages. Frustration mounts as precious time and resources are seemingly wasted. You might be grappling with Gemini Pro function call tooling errors, or perhaps the issue is broader, with an AI agent not calling tools when it should. You might even be encountering platform-specific glitches like the notorious ‘content not available’ Facebook error, or the more general ‘cannot fulfill request’ AI error. Sometimes, the culprit is closer to home, like network problems causing ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED chrome. This post is designed to cut through the confusion, demystify these prevalent issues, and equip you with the knowledge and actionable steps to diagnose and resolve them, ensuring your AI integrations run as smoothly as intended.
Decoding Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
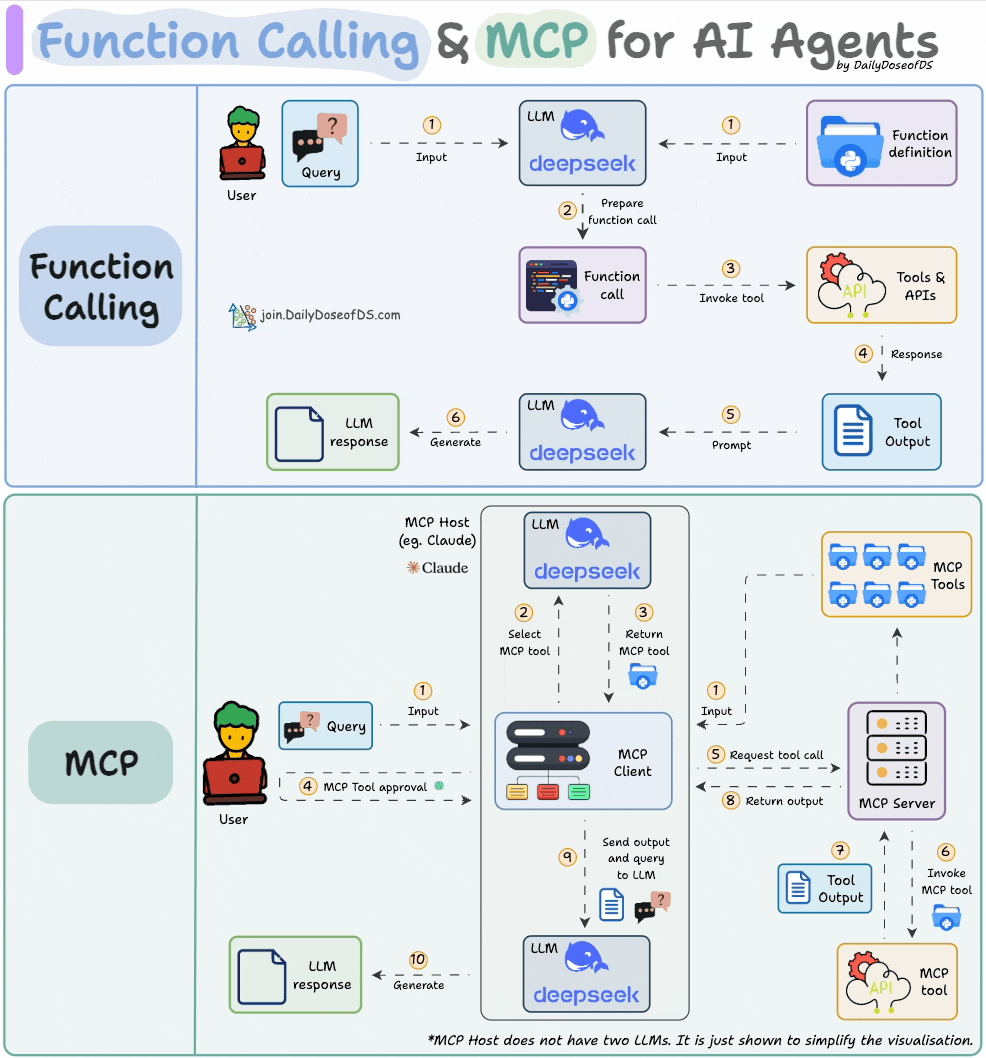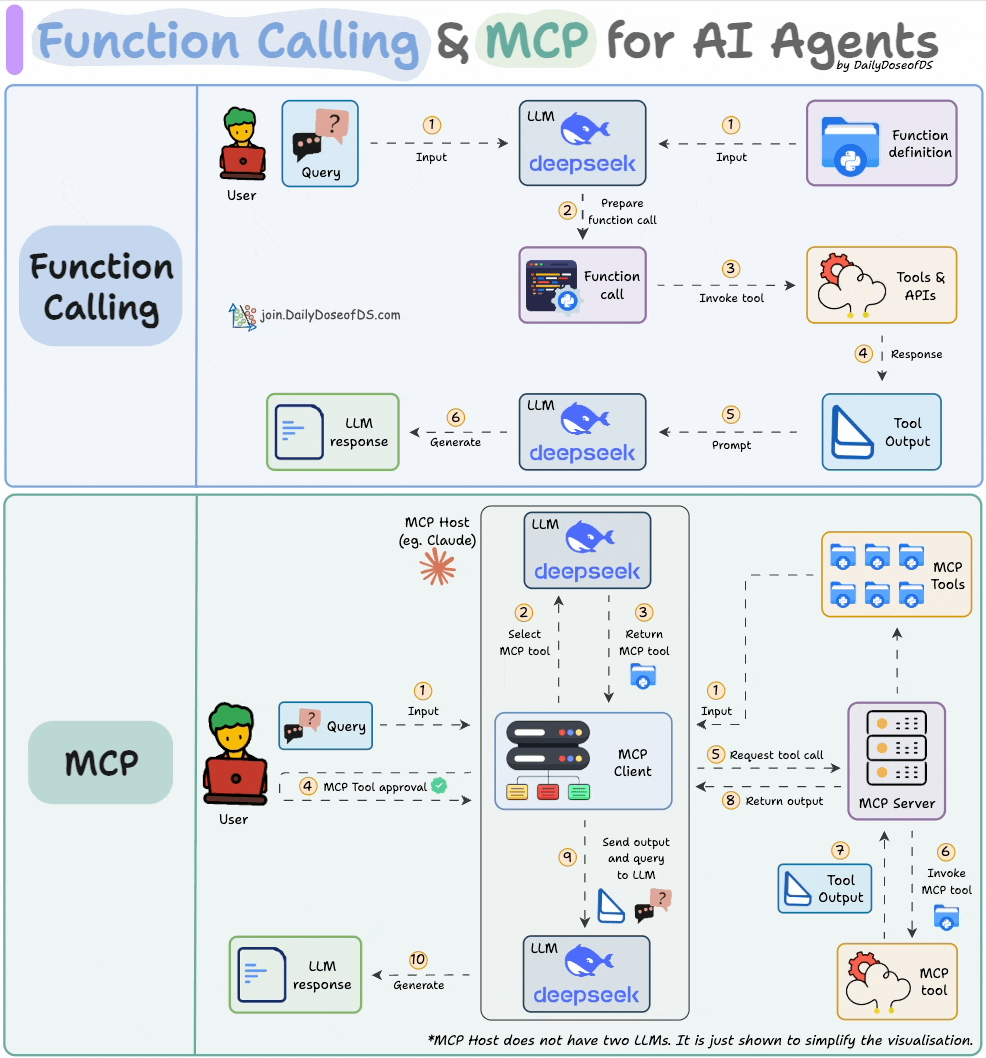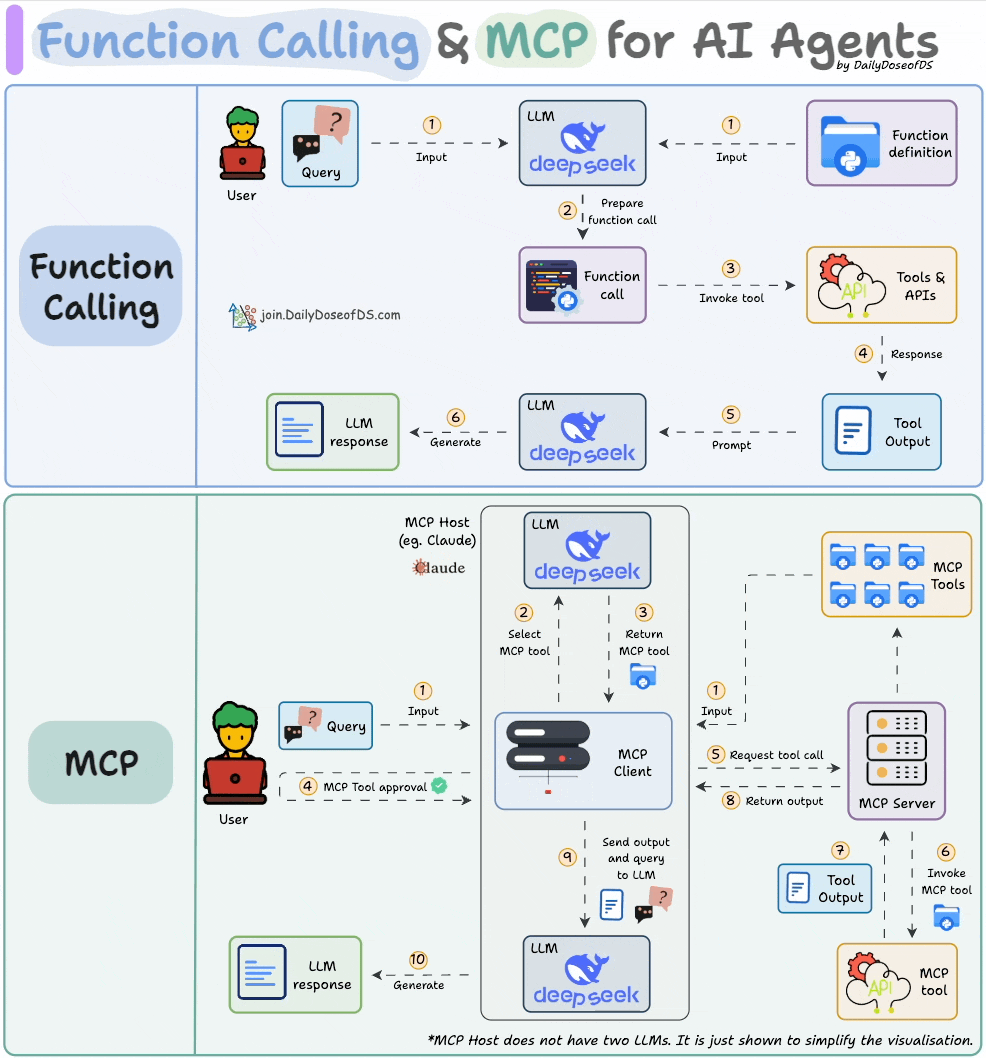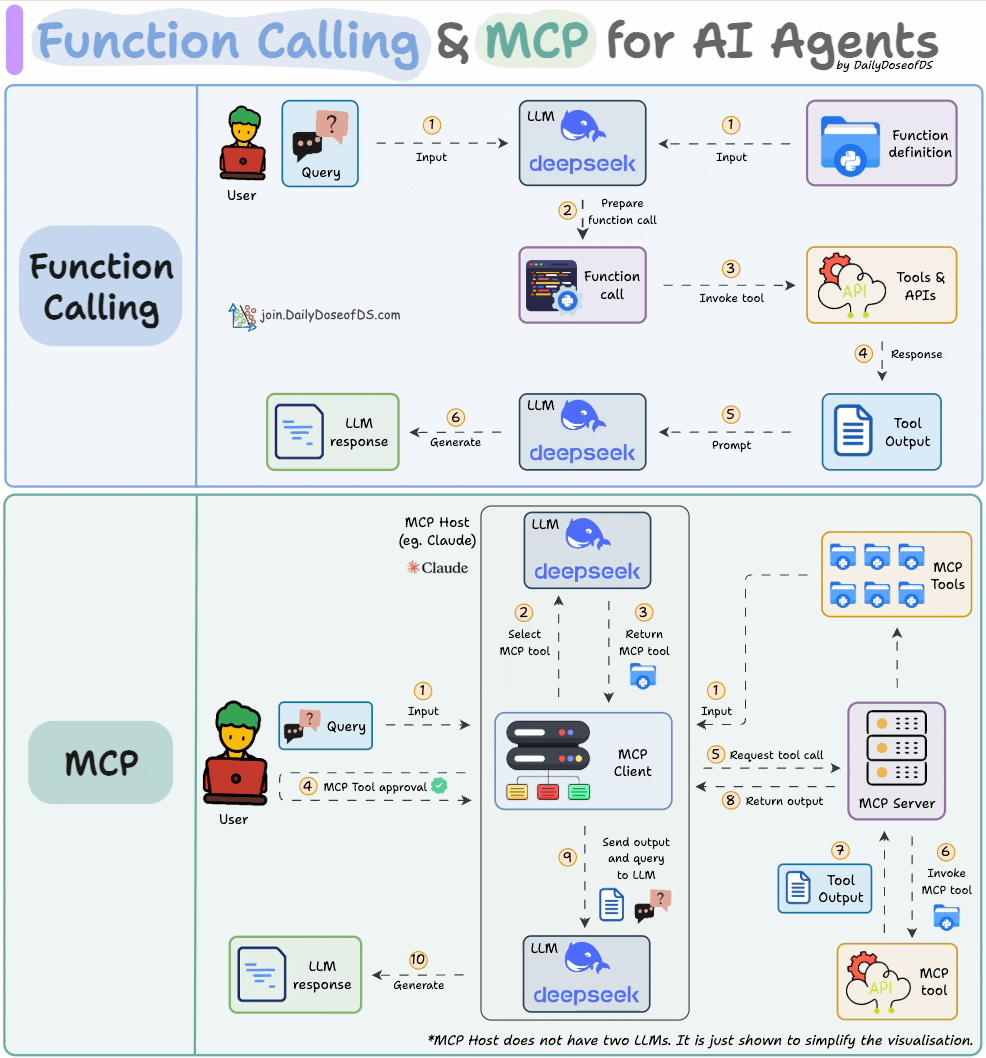
What is Function Calling in Gemini Pro?
Function calling in Gemini Pro is a sophisticated capability that allows the AI model to go beyond simple text generation. It enables Gemini Pro to interact with external systems by generating structured output that precisely defines a function to be called, along with its arguments. Essentially, it’s how Gemini Pro can be instructed to perform actions, retrieve specific data, or trigger processes outside of its own model. This opens up a universe of possibilities, allowing AI to act as an intelligent agent capable of fetching real-time information, performing complex calculations, or interfacing with your custom services.

Common Causes of Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
When function calling doesn’t work as expected, it often boils down to a few key areas:
- Incorrect Function Signature: This is perhaps the most frequent culprit. It happens when the way Gemini Pro formats the function call—the function name, the parameter names, or their expected types—does not precisely match the actual definition of the function you’ve provided. For instance, if your function expects a parameter named `userId` but Gemini Pro generates a call with `user_id`, or if it expects an integer and generates a string, the call will fail.
- Data Type Mismatches: Even if the function signature is correct, passing data of the wrong type will break the execution. This could involve sending a list when a string is required, providing a numerical value where text is expected, or inadvertently passing a `null` value for a parameter that the function cannot handle or considers mandatory.
- API Configuration Issues: The integration itself might be misconfigured. This includes using invalid or expired API keys, pointing to an incorrect API endpoint URL, or having issues with authentication or authorization. If the environment where the function is meant to be executed cannot properly reach or authenticate with the necessary services, function calls will inevitably fail.
- Rate Limits: Like many cloud-based services, AI models and their associated APIs often impose limits on how frequently they can be accessed within a given timeframe. Exceeding these limits, especially if you’re making a high volume of function calls, can result in temporary errors that prevent further invocations until the limit resets. This is a protective measure to ensure service stability and fair usage for all users. (Source: Google AI documentation on Gemini API quotas and limits)

Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for Gemini Pro Function Call Tooling Errors
When you encounter these errors, a methodical approach is your best ally:
- Verify Function Signature and Tool Definition: Scrutinize the function definition you’ve provided to Gemini Pro. Ensure that every parameter name, its data type (e.g., string, number, boolean, array), and the overall function name are exactly as they should be. Compare this meticulously against the structured output generated by Gemini Pro when it attempts a call. Look for even minor discrepancies.
- Validate Data Types in Payload: Before the function is invoked, inspect the actual data being passed as arguments. Use debugging tools or logging to check each value. If a mismatch is detected (e.g., a number is being sent as a string), implement necessary type conversions within your application logic before the function call is executed.
- Review API Configuration and Credentials: Double-check all configuration settings related to your API integration. Ensure your API keys are correct, active, and properly scoped. Verify that the API endpoint URL is accurate and that any necessary authentication headers or tokens are correctly implemented.
- Monitor API Usage and Rate Limits: Implement logging to track the frequency of your function calls. If you suspect you’re hitting rate limits, consult the provider’s documentation for specific limits and recommended strategies. This might involve implementing a queueing system, adding delays between calls, or using exponential backoff for retries. (Source: Google Cloud documentation on API rate limiting strategies)

When an AI Agent Isn’t Calling Tools
Differentiating AI Agent Issues from Specific Function Calling Errors
While function calling errors are quite specific, an AI agent not calling tools can be indicative of a broader set of problems. Function calling errors occur when the AI *tries* to call a tool but fails due to misconfiguration or incorrect parameters. An agent failing to call tools might mean it doesn’t even recognize the need to use a tool, or it’s unable to access or invoke it due to architectural or logical flaws within the agent’s design itself.
Reasons for an AI Agent Not Calling Tools
Several factors can lead to an AI agent neglecting its tool-using capabilities:
- Insufficient Permissions: The AI agent, running within a specific environment or framework, might not have been granted the necessary permissions or access rights to interact with the tools it needs. This is an authorization layer issue, where the agent’s identity or role lacks the privileges to execute certain actions.
- Tool Definition Errors: Beyond just the signature, the tool itself might be poorly defined or registered within the agent’s ecosystem. This could include missing or unclear descriptions, which are crucial for the AI to understand *when* and *why* to use a particular tool. If the tool isn’t properly discoverable or understandable by the agent, it won’t be invoked.
- Prompt Engineering Issues: The way you communicate with the AI agent is paramount. If the prompt is ambiguous, lacks context, or doesn’t clearly signal that an external action or tool usage is required, the agent might default to a purely generative response. The prompt needs to guide the AI towards recognizing the need for tool integration.
- Agent Logic Flaws: The core decision-making process of the AI agent might be flawed. It might fail to identify scenarios where tool usage is the most efficient or correct path, or its internal workflow might be designed in a way that prematurely dismisses the possibility of using a tool. This requires a deeper look into the agent’s architecture and reasoning process.

Strategies to Diagnose and Fix AI Agent Tool Issues
Addressing these agent-level problems requires a systematic approach:
- Verify Agent Permissions and Access Controls: Review the security and permission settings associated with your AI agent. Ensure that the agent has been explicitly granted access to the tools and APIs it’s intended to use. This might involve configuring roles, policies, or service accounts.
- Re-evaluate Tool Registration and Definitions: Go back to the source and check how each tool is registered with the AI agent framework. Confirm that all required metadata, especially comprehensive and clear descriptions, are present. Ensure the tool definitions are formatted correctly according to the agent’s specifications and that the agent can indeed “see” and understand these tools.
- Refine Prompt Engineering for Tool Usage: Experiment with different prompt structures. Clearly articulate the task and, where appropriate, explicitly guide the agent to use specific tools. For example, instead of “Find information about X,” try “Use the search tool to find information about X and then summarize it.” Provide clear examples within your prompts to demonstrate how tool usage should occur.
- Inspect Agent’s Internal Logic and State: For developers working with custom AI agents, debugging the agent’s execution flow is crucial. This involves logging intermediate states, the agent’s reasoning steps, and its internal representations of the problem. Understanding *why* the agent is or isn’t choosing to use a tool can reveal underlying logic flaws.

Tackling Specific Platform and AI Errors
How to Fix ‘Content Not Available’ Facebook Error
When interacting with AI features on platforms like Facebook, encountering a ‘content not available’ Facebook error can be perplexing. This usually means the AI cannot access the specific piece of content you’re referring to or trying to process.
Potential Causes:
- Content restrictions due to privacy settings (either yours, the creator’s, or Facebook’s policies).
- Temporary server issues or glitches on Facebook’s end.
- Outdated cached data in your browser or app that no longer reflects the content’s status.
- The content itself has been removed, deleted, or made inaccessible by its owner or Facebook.
- Geographical restrictions on the content.
- (Source: Facebook Help Center articles on content visibility and privacy)
Actionable Solutions:
- Check Privacy Settings: Review the privacy settings of your Facebook account and, if possible, the privacy settings of the specific post or content you’re trying to access. Ensure it’s visible to you or set to public.
- Verify Content Source and Availability: Try accessing the content directly through a standard browser or the Facebook app without involving the AI. Confirm that it is indeed available and visible to you.
- Clear Browser Cache and Cookies: Stale data can often cause display issues. In your browser settings, navigate to ‘Privacy and security’ and clear your browsing data, focusing on cache and cookies.
- Try a Different Browser or Incognito Mode: Test accessing the content on a different web browser or use an incognito/private browsing window. This helps isolate whether the issue is specific to your current browser’s configuration or extensions.
- Refresh the Page/App: Sometimes, a simple refresh of the Facebook page or a restart of the Facebook app can resolve temporary glitches.
How to Solve ‘Cannot Fulfill Request’ AI Error
The ‘cannot fulfill request’ AI error is a broad indicator that the AI system is unable to process your query. This can happen for a variety of reasons related to the input itself or the AI’s limitations.
Potential Causes:
- The request lacks sufficient information, context, or clarity.
- The request is too complex, multi-faceted, or ambiguous for the AI to parse effectively.
- The request falls outside the AI’s knowledge base or current capabilities.
- Internal processing errors or limitations within the AI model or the platform it’s running on.
Common Workarounds and Debugging Steps:
- Provide More Context and Specificity: Elaborate on your request. Add background details, clarify any terms, and be as precise as possible about what you need. Instead of “Tell me about AI,” try “Explain the concept of generative AI, focusing on its applications in image creation.”
- Simplify the Request: If your request involves multiple steps or complex logic, try breaking it down into smaller, sequential queries. Address one aspect at a time.
- Rephrase the Prompt: Try asking the same question or making the same request using different words or sentence structures. Sometimes, a slight change in phrasing can help the AI interpret your intent more accurately.
- Specify Desired Output Format: If you have a particular format in mind for the response (e.g., a bulleted list, a table, a concise summary, a detailed explanation), clearly state this in your prompt.
- Try a Different AI Model or Tool: If you have access to multiple AI tools or models, try posing your request to a different one. Different models have varying strengths, weaknesses, and training data, so one might be able to fulfill a request that another cannot.
Troubleshooting ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED in Chrome
The Impact of Network Connectivity on AI Tools
AI tools, particularly those that are cloud-based and rely on constant communication with servers for processing, are highly sensitive to network stability. An intermittent or changing network connection can disrupt the flow of data, leading to API call failures, incomplete requests, and a host of errors. The ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED error in Chrome is a prime example, signaling that the browser detected a change in your network configuration while it was trying to establish or maintain a connection. This directly impacts AI tools that need a reliable internet connection to function.

Detailed Guide to Troubleshoot ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED Chrome
When Chrome throws this error, especially while using AI tools, it’s time for some focused troubleshooting:
-
Perform Basic Network Checks:
- Check Router/Modem: The first step is often the simplest: restart your modem and router. Unplug them, wait about 30 seconds, and plug them back in. This can resolve many common connectivity issues.
- Verify Wi-Fi/Ethernet Connection: Ensure your device is securely connected to your network. If you’re on Wi-Fi, try moving closer to the router or switching to a wired Ethernet connection if possible.
- Test Internet Speed and Stability: Use an online speed test service to check your download and upload speeds and, importantly, look for packet loss. High latency or packet loss can cause connection instability. (Source: Speedtest.net)
-
Chrome-Specific Solutions:
- Clear Cache and Cookies: Corrupted or outdated cache data can interfere with network requests. Go to Chrome Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data. Select “Cached images and files” and “Cookies and other site data,” and choose a time range (e.g., “All time”).
- Reset Chrome Settings: Sometimes, extensions or custom settings can cause network problems. Resetting Chrome to its default state can fix this. Go to Chrome Settings > Advanced > Reset and clean up > Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Disable/Remove Problematic Extensions: Browser extensions, especially those that modify network behavior (like ad blockers or VPNs), can sometimes cause conflicts. Temporarily disable all extensions, then re-enable them one by one to identify the culprit.
- Flush DNS Cache: Your computer stores DNS records to speed up website lookups. If these records become outdated or corrupted, it can lead to connection issues.
- Windows: Open Command Prompt as administrator and type
ipconfig /flushdns, then press Enter. (Source: Microsoft documentation) - macOS: Open Terminal and type
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder, then press Enter and enter your password. (Source: Apple support) - Linux: The command varies by distribution, but often involves
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-cachesor similar commands for network managers.
- Windows: Open Command Prompt as administrator and type
- Check Proxy Settings: Ensure that your proxy settings in Chrome are correctly configured or disabled if you are not using a proxy server. Go to Chrome Settings > System > Open your computer’s proxy settings.
-
Consider Broader Network Problems: If the
ERR_NETWORK_CHANGEDerror persists across multiple browsers and devices on your network, the issue might lie with your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or your local network hardware beyond your router. Contact your ISP if you suspect this might be the case.
Proactive Strategies for Error Prevention
Effective Prompt Engineering for AI
The foundation of successful AI interaction lies in clear and effective prompts. Spend time crafting prompts that are unambiguous, provide sufficient context, and clearly state the desired outcome. Think from the AI’s perspective: what information does it absolutely need to perform the task accurately and decide when to leverage tools? Experimentation is key, and iterating on your prompts based on the AI’s responses is a crucial part of the process.
Accurate Tool Definitions and Configurations
For function calling and AI agents to operate reliably, the definitions of the tools they can use must be precise. This includes not just function signatures but also descriptive documentation that helps the AI understand the tool’s purpose and use cases. Regularly review and update these definitions as your tools or their functionalities evolve. Ensure that the parameters, data types, and expected return values are accurately represented.
Staying Updated with AI Models and Platform Changes
The AI landscape is rapidly evolving. Providers like Google frequently update their models (e.g., Gemini) and APIs. Changes can introduce new features, deprecate old ones, or alter error behaviors. It’s vital to stay informed about these updates by following official documentation, release notes, and blogs. Being aware of platform changes can help you anticipate and adapt to potential issues before they arise. (Source: General AI trends and updates)

Implementing Robust Error Handling in Applications
For developers integrating AI capabilities into their applications, building in comprehensive error handling is non-negotiable. This means not just catching generic errors but anticipating specific API errors, implementing intelligent retry mechanisms (like exponential backoff), providing clear and user-friendly error messages, and robust logging for debugging. A well-handled error can turn a frustrating user experience into a manageable one.
Navigating the complexities of AI tools, from specific Gemini Pro function call tooling errors to broader challenges like AI agents not calling tools, requires a systematic and informed approach. Whether you’re wrestling with platform quirks such as the ‘content not available’ Facebook error, the general ‘cannot fulfill request’ AI error, or even browser-level network disruptions like ERR_NETWORK_CHANGED chrome, the solutions often lie in meticulous verification, clear communication, and proactive maintenance. By applying the diagnostic steps and preventative strategies outlined in this guide, you can significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of your AI integrations, unlocking their true potential. Remember that the journey with AI is one of continuous learning and adaptation. Share your experiences and troubleshooting tips in the comments below to help build a stronger community of AI problem-solvers. Subscribe for more insights into the ever-evolving world of artificial intelligence!

For further reading on Gemini Pro and AI integration, explore these resources:
“`





