GPT-6 Development Timeline and Capabilities: Forecasting the Next Frontier of OpenAI
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
Key Takeaways
- OpenAI is expected to shorten the release gap compared to previous models, driven by maturing infrastructure.
- The gpt-6 official release date 2026 is highly projected, with closed previews starting mid-2026 and a public rollout late 2026/early 2027.
- GPT-6’s core innovation will be *Agentic Reasoning*, allowing the model to act as an autonomous operating system for complex tasks.
- It will feature **persistent memory** and true multimodality, including native video and 3D environment understanding.
- The rise of efficient **on-device LLMs** will necessitate hybrid architectures, where the cloud-based GPT-6 handles frontier tasks while local models manage privacy and latency.
Table of contents
Setting the Stage: The Acceleration of AI
We are currently witnessing an unprecedented acceleration in the field of artificial intelligence. What started as complex predictive modeling has swiftly transitioned into autonomous, generative creation. This shift defines the current state of AI acceleration, setting the stage for the massive anticipation surrounding OpenAI’s next flagship model.

The ecosystem is buzzing, not just with speculation, but with concrete developmental milestones. OpenAI is currently expanding the GPT-5 ecosystem and infrastructure, rigorously optimizing its performance, and gathering the vast data sets necessary for the leap to the next frontier-class model launch. This phase of refinement, as documented by various internal sources, is the critical foundation being laid before any formal announcement of the successor. (Source: OpenAI’s Infrastructure Expansion)
The purpose of this post is clear: to provide an informational, evidence-based analysis of the projected openai gpt-6 development timeline and its anticipated capabilities. We move beyond wishful thinking and anchor our predictions in historical precedent, infrastructure demands, and the explicit, albeit limited, statements made by OpenAI leadership.
The Evidence-Based OpenAI GPT-6 Development Timeline
Historical Cadence and Future Predictions
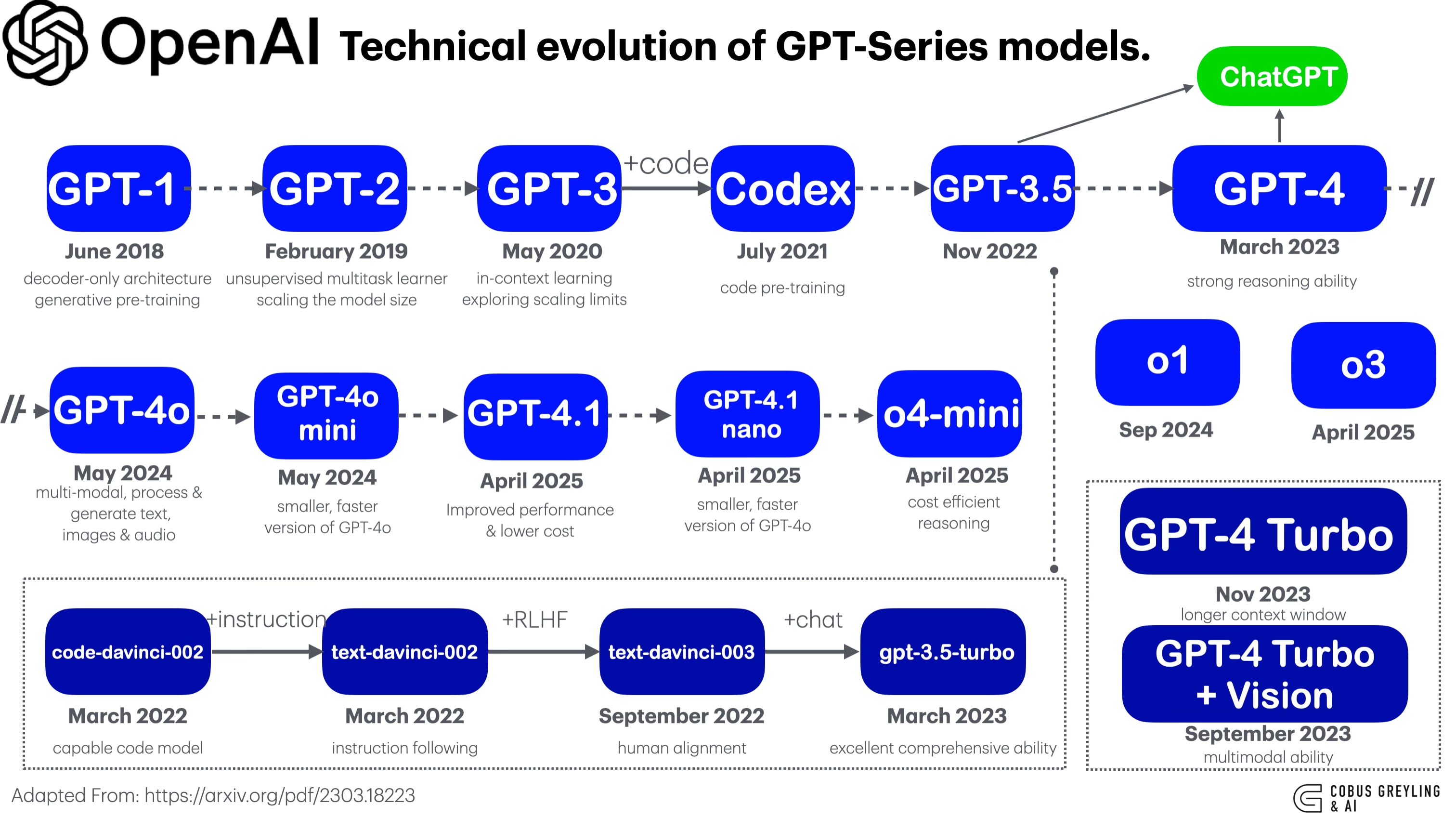
To predict the future, we must first analyze the past. OpenAI’s historical release cadence offers vital clues. There was an approximate 28-month gap between the release of GPT-4 (March 2023) and the projected full rollout of GPT-5 (August 2025). (Source: Historical Release Data)

However, the critical factor is acceleration. Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, has explicitly noted that the gap between GPT-5 and GPT-6 is anticipated to be *shorter* than previous intervals. This statement implies that the foundational training methodologies and, more importantly, the advanced infrastructure required for scaling these models are reaching a critical level of maturity, allowing for faster development cycles.
“The cadence is quickening, not slowing down. While the jumps in capability remain massive, the time between those jumps is shrinking.”
(Source: Sam Altman Interview and Analysis of Release Cadence)
The Confirmed Non-Release of 2025
While speculation often runs wild, we have one essential, confirmed fact regarding the openai gpt-6 development timeline: OpenAI definitively stated in mid-October 2025 that GPT-6 will not be released in 2025. This is crucial. It confirms that the earliest possible soft launch or limited availability would occur in 2026.
This brings us directly to the keyword: gpt-6 official release date 2026.

It must be framed as a highly supported projection, not an official, publicly announced date. Multiple independent analyses and AI roadmap projections converge on a definitive release window of 2026–2027.
Mid-2026 is cited by industry watchers as the most likely starting point for closed, private previews. These early access phases are critical for enterprise partners and, most importantly, for **Red Teaming**—the rigorous safety testing required for models that possess true frontier capabilities.
(Sources: Datastudios Projection, Exploding Topics Analysis, Blacksmith Agency Forecast)
Projected Roadmap Milestones (2026-2027)
The path to public release is rarely instantaneous. It is a calculated, three-stage rollout designed to manage compute strain, gather feedback, and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Ongoing 2025 – H1 2026: Consolidation and Optimization. The current focus remains heavily on maximizing the power and stability of the GPT-5.x reasoning model updates. This phase is less about scaling parameters and more about infrastructure optimization, ensuring the training pipeline for GPT-6 is flawless and hyper-efficient. (Source: Infrastructure Focus)
- Mid-2026: Internal Deployment and Safety Testing. This is the crucial moment of “first light” for GPT-6. It will involve internal deployment to select employees and external safety professionals. Extensive safety testing, known as Red Teaming, must be completed before any broader public access is considered. (Source: Safety and Internal Testing)
- Late 2026 / Early 2027: Staged Public Rollout. The model will likely debut in the API for developers first, potentially followed by high-value enterprise tenants who can manage the initial scale and complexity. A full public rollout into the consumer ChatGPT user base would follow this initial staging, cementing the 2026–2027 window as the operational timeline.

Critical Analysis of GPT-6 Expected Features
The true excitement surrounding GPT-6 isn’t just *when* it arrives, but *what* it will fundamentally change. Based on OpenAI’s current research vectors and public statements, the capabilities of GPT-6 will move far beyond simple text generation or enhanced context windows.
Personalization, Persistent Memory, and Context
GPT-6 is projected to evolve from a powerful, stateless assistant into a true “personal AI.” This involves the critical introduction of **Persistent Memory**.
Currently, LLMs forget context between sessions, requiring users to constantly re-establish identity, history, and preferences. GPT-6 is designed to learn and adapt to user preferences *across sessions* and even *across different applications*. This long-term memory will not rely solely on impossibly large context windows, but on a combination of massive token capacity and sophisticated, learned user profile models that prioritize and compress relevant biographical, professional, and stylistic information.

Imagine an AI that remembers your specific project nomenclature from six months ago, or your strict preference for APA citation style, without being prompted. This level of intimacy transforms the interaction from transactional to symbiotic. (Sources: Dawn of Truly Personal AI, Expected Features Analysis)
Advanced Agentic Reasoning: AI as an Operating System
Perhaps the most impactful feature will be the maturation of Agentic Reasoning. We define “agentic behavior” as the ability to perform complex, multi-step tasks autonomously. This involves not just writing code or generating text, but:
- **Planning:** Devising a strategy across multiple internal tools and external APIs.
- **Execution:** Carrying out steps sequentially.
- **Revision:** Self-correcting based on failed execution steps or real-time feedback.
- **Reporting:** Delivering the final, validated outcome.
For GPT-6, this structured, deliberate reasoning is expected to become the *default* operational mode, significantly minimizing user intervention. It moves the model from being a clever tool to becoming an operating system process for complex knowledge work—like autonomously managing project timelines or handling sophisticated data analysis requests that require calling multiple external services. This is a massive conceptual leap, positioning GPT-6 squarely in the race to develop next-generation AI agents. (Source: Microsoft AI Agent News, Agentic Behavior Expectation, OpenAI DevDay Roadmap Clues)
The True Multimodal Leap (Video and 3D)
While GPT-4o established seamless text, image, and audio interaction, GPT-6 is anticipated to push into true *frontier multimodality*. This means native understanding and manipulation of time-series data, specifically video and 3D environments.
Anticipated features include:
- Analyzing complex video content (e.g., medical scans, security footage) and generating summaries and predictions based on temporal relationships.
- Enhanced 3D environment modeling, critical for robotics, advanced virtual reality (VR), and digital twin applications.
- Improved audio integration, potentially allowing the model to generate synchronized, contextual soundtracks from text prompts or video inputs.
This move towards comprehensive understanding of dynamic, real-world data is foundational to creating the autonomous agents described above. (Source: Multimodality Expectations)
Efficiency and Architectural Superiority
The era of simply making models larger is fading. While parameter counts for GPT-6 will undoubtedly grow, the architectural focus will be on efficiency over raw size. We expect to see further refinement of techniques like sparse activation and **Mixture-of-Experts (MoE)** architecture.
This approach allows the model to leverage massive numbers of parameters without requiring all of them to be active for every single inference. The benefit is twofold:
- It provides the necessary depth for complex reasoning (superior performance).
- It dramatically increases throughput and drives down the per-token inference costs, making the powerful model economically viable for widespread commercial use.
(Source: Architectural Focus Analysis)
The Competitive Landscape: Cloud vs. Edge AI
As OpenAI races toward AGI with its massive, centralized models, a parallel revolution is taking place: the rapid growth of localized LLMs running efficiently on consumer hardware. This **edge AI** presents a necessary counterpoint to the massive scale of GPT-6.
On-Device LLMs vs. GPT-6 Capabilities: A Trade-Off Analysis
The market of 2026 will not be a winner-take-all environment. It will be defined by the necessary trade-offs between centralized power and localized efficiency. Here is a direct comparison addressing on-device llms vs gpt-6 capabilities:
Trade-Off 1: Latency and Accessibility
GPT-6 (Cloud): Cloud-dependent, requiring network connectivity, and subject to marginal network latency.
On-Device LLMs: Near-instantaneous response times, accessible offline, and fully integrated into the operating system environment.
Trade-Off 2: Performance vs. Size
GPT-6 (Cloud): Frontier scale, offering superior complex reasoning, creative generation, and deep analytical depth. Necessary for tasks requiring multimodal or highly abstract thinking.
On-Device LLMs: Constrained by hardware limits (typically models < 10B parameters), sufficient for routine tasks like text generation, basic summarization, drafting emails, and local search.
Trade-Off 3: Privacy and Data Security
GPT-6 (Cloud): Data must be transmitted to OpenAI’s servers for processing, raising compliance and privacy concerns, particularly in regulated industries.
On-Device LLMs: They offer a crucial privacy advantage as data remains local, never leaving the user’s device. This dramatically reduces regulatory and data security risks for both users and enterprises seeking secure drafting capabilities. (Source: Enterprise AI Report on Privacy)

The Hybrid Routing Solution
The inevitable solution to these trade-offs is the rise of Hybrid Routing Architectures.
A small, efficient on-device model will act as a “smart router.” This router will intercept all user requests:
- If the task is simple (e.g., summarize this text, draft a quick reply) or requires strict privacy (accessing local contacts/photos), the on-device model handles it locally and instantly.
- If the request is highly complex, requires massive knowledge retrieval, or demands frontier-level agency (e.g., “Develop a five-year marketing strategy based on global market trends”), the router compresses the prompt and escalates the request to the powerful, cloud-based GPT-6 API.
This integration ensures optimal performance, leveraging the best of both worlds—speed and privacy on the edge, unparalleled intelligence in the cloud. (Source: Hybrid Architecture Roadmap)
Market Impact and the Hardware Race
The impending launch of GPT-6 is not just a software event; it is the ultimate catalyst for the next generation of consumer hardware. The demand for seamless local AI is driving major chip manufacturers and smartphone OEMs (Apple, Google, Samsung) to heavily invest in dedicated, high-TOPS (Trillions of Operations Per Second) Neural Processing Units (NPUs).

This investment is necessary to facilitate the **future of on-device ai in smartphones 2026** and beyond. (Source: Apple Intelligence Preview and AI Chips and Smartphone Future)
Generative AI is transforming smartphones from mere communication devices into personalized, secure AI hubs. (Source: Hardware Investment Report)
The Future of On-Device AI in Smartphones 2026
The market is heading toward a clear dual-path outcome:
- GPT-6 (Cloud): Will be the dominant force for highly complex, creative, academic, enterprise, and high-stakes tasks where absolute fidelity, logical consistency, and profound reasoning depth are non-negotiable. This is the AI used for research and large-scale problem-solving.
- On-Device AI: Will handle nearly all everyday, personalized utility: local photo search, secure, real-time drafting, proactive notification triage, context-aware device control, and all offline functions. This is the invisible, trusted layer of personalization.
The ultimate winner in the 2026 market will not be the company that makes the fastest chip or the largest model, but the platform that successfully builds the *most seamless integration* between the localized, private AI layer and the powerful, global frontier model.
Summary of Findings
The evidence strongly suggests that the **openai gpt-6 development timeline** points toward a late-2026 or early-2027 public release, following extensive internal testing throughout mid-2026. This model will not merely be “better”; it will be architecturally superior, focusing on **personalized agency**, true multimodality (including native video), and reasoning superiority that allows it to operate autonomously.
GPT-6 will define the pinnacle of centralized, large-scale AI power, but it will simultaneously catalyze a fundamental shift toward the privacy and speed offered by local models. The next frontier is hybrid—a world where every device contains a secure, smart router, seamlessly connecting personal needs to global intelligence.

Frequently Asked Questions
Will GPT-6 be released in 2025?
No. OpenAI has definitively stated that GPT-6 will not be released in 2025. The focus throughout this period is on the expansion and optimization of the GPT-5 ecosystem and preparing the vast infrastructure required for the subsequent model generation. Public or even closed beta access is not anticipated until mid-to-late 2026.
What is the most anticipated new capability of GPT-6?
The most transformative capability expected is **Advanced Agentic Reasoning**. This allows GPT-6 to go beyond answering questions or generating text, enabling it to function as an autonomous agent—planning, executing, and self-correcting multi-step tasks (like software development or complex research) with minimal user supervision. This fundamentally changes how users interact with AI.
How will GPT-6 handle data privacy compared to on-device LLMs?
GPT-6 will remain a centralized, cloud-dependent model, meaning sensitive data must be sent off-device for processing. Conversely, on-device LLMs (Edge AI) process data locally, offering superior privacy, low latency, and guaranteed offline access. The market consensus is that a **hybrid architecture** will emerge, where the local device determines if a request can be handled securely on-device before escalating only the most complex, non-private requests to the GPT-6 cloud API.
What is the significance of the hardware race in relation to GPT-6?
The launch of GPT-6 is fueling the demand for highly optimized hardware, specifically dedicated Neural Processing Units (NPUs) in consumer devices. These specialized chips are crucial for running the small, efficient LLMs required for the privacy and speed offered by local AI. Without this advanced hardware, users cannot fully benefit from the seamless hybrid AI experience, making the NPU race as important as the model development race.