Feeling the Virtual: How Haptic VR Controllers Innovation is Redefining Immersion
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Haptic VR controllers innovation is transforming virtual reality tech from a purely visual experience into a tactile one, allowing users to feel textures, resistance, and impacts.
- Force feedback VR gaming goes beyond simple vibrations to simulate weight, tension, and recoil, dramatically enhancing realism and emotional engagement.
- Immersive input devices form an interconnected ecosystem, including haptic controllers, gloves, vests, and suits, working together to deliver full-body feedback.
- The applications of advanced haptics extend far beyond gaming into critical fields like surgical simulation, physical therapy, and industrial prototyping.
- Future trends point towards neuro-haptics, full-hand temperature fidelity, and wireless full-body rigs, promising even deeper immersion.
Table of contents
- Feeling the Virtual: How Haptic VR Controllers Innovation is Redefining Immersion
- Key Takeaways
- From Pixels to Physical: The Rise of Haptic VR Controllers
- The Science of Sensation: How Haptic Feedback Works
- Beyond Vibrations: The Force Feedback Gaming Revolution
- The Immersive Input Device Ecosystem: Controllers, Gloves, and Beyond
- Integrating Haptics into the Fabric of Virtual Reality Tech
- The Future of Feeling: What’s Next for Haptic VR
- Frequently Asked Questions
From Pixels to Physical: The Rise of Haptic VR Controllers
Imagine reaching into a virtual reality tech environment and not just seeing a virtual object, but feeling its rough texture, its weight, and the resistance as you pull it toward you. This is the promise of haptic VR controllers innovation, a field that is fundamentally transforming virtual interaction from a purely visual spectacle into a rich, physical experience. By enabling users to feel textures, resistance, and impacts, this technology is closing the sensory gap that has long separated us from digital worlds (source), (source), (source).

Today’s immersive gaming gear extends far beyond the headset. It encompasses a suite of hand-held devices and wearables designed to simulate real-world touch, with immersive input devices like advanced controllers at the forefront (source), (source).
The purpose of this exploration is to delve into how rapid advancements in haptics and force feedback VR gaming are redefining our sense of presence and control within virtual reality tech, satisfying the growing curiosity about the true potential of immersive gaming gear. To understand this revolution, we must first journey through the evolution of haptic technology itself.
The Science of Sensation: How Haptic Feedback Works
At its core, haptic feedback in VR controllers is about delivering tactile sensations through precise mechanical forces. Using actuators—small motors or mechanisms—these devices generate vibrations, simulate textures, and create resistance to mimic physical sensations like grasping an object or feeling the friction of a surface (source), (source), (source).

The key innovations driving this field forward are multifaceted:
- Advanced Actuators: Moving beyond simple rumble, new actuators provide multimodal feedback including precise force, nuanced texture, and even thermal cues.
- Finger Tracking Integration: Haptic gloves incorporate sensors to track individual finger movements, allowing for interactions as delicate as picking up a virtual egg.
- Adaptive Triggers: These components can dynamically adjust their tension in real-time, simulating the pull of a bowstring or the gradual squeeze of a trigger (source), (source), (source).
Showcasing the cutting edge of haptic VR controllers innovation are devices like the WEART TouchDIVER Pro haptic gloves, which feature six actuation points across the fingers and palm for incredibly lifelike simulations of touch and grasp (source). On the controller front, Haply Robotics has developed high-fidelity force feedback controllers, recognized as CES 2026 Innovation Honorees, which excel in applications from teleoperation to virtual design (source). These examples represent the vanguard of immersive input devices, directly enabling the next leap: true force feedback VR gaming.

Beyond Vibrations: The Force Feedback Gaming Revolution
Force feedback VR gaming represents a significant evolution from basic haptic vibrations. It is specifically engineered to simulate physical properties like weight, tension, recoil, and the complex interactions between virtual objects. This means feeling the strain of pulling a bowstring, the jarring impact of a shield block, or the kick of a virtual firearm (source), (source), (source).
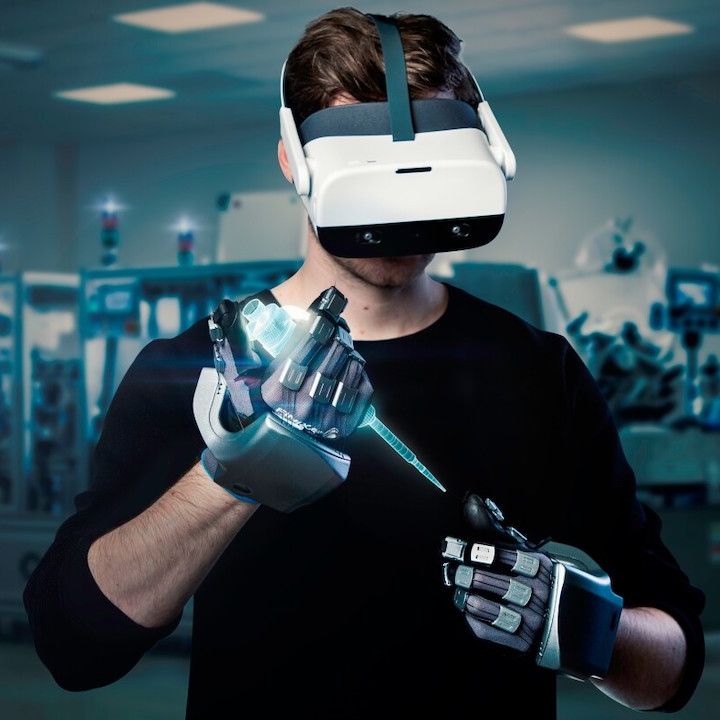

The impact on the gaming experience is profound:
- Heightened Realism: Force feedback provides natural physical responses, making virtual worlds feel tangible and believable.
- Accelerated Skill Development: The tactile feedback loop allows players to learn and adjust their motor skills more quickly, as in a racing sim where you feel the loss of tire traction.
- Boosted Emotional Engagement: By engaging the sense of touch, these devices create a stronger physiological sense of presence, amplifying fear, excitement, and triumph (source), (source).
Concrete examples are already in players’ hands. The PS5’s DualSense controller uses adaptive triggers to let drivers feel the granular difference between gravel and asphalt or to simulate the unique recoil of various in-game weapons (source). In dedicated VR spaces, shooters are utilizing haptic vests or gloves to replicate the thud of a bullet impact on a shield or the unsettling, organic texture of an alien creature (source), (source). This level of detail is part of a larger ecosystem of immersive input devices working in concert for full immersion.
The Immersive Input Device Ecosystem: Controllers, Gloves, and Beyond
Immersive input devices are best understood as an interconnected system. Haptic VR controllers don’t operate in isolation; they integrate with vests like bHaptics for millisecond-level torso impacts, omnidirectional treadmills, motion platforms, and haptic gloves to create a symphony of full-body feedback (source), (source), (source).
The following table compares the key device types in this ecosystem:
| Device Type | Strengths | Examples | Complements Controllers By |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controllers | High-fidelity force feedback, portability | Haply Robotics, PS5 DualSense | Providing core hand interaction and reliable force simulation (source), (source), (source) |
| Gloves | Finger-specific textures, thermal cues | WEART TouchDIVER Pro | Enabling detailed grasping and fine motor tactile feedback (source) |
| Vests/Suits | Full-body impacts, wind simulation | bHaptics | Delivering torso and limb feedback for environmental effects (source), (source) |

Controllers like those from Haply Robotics excel in precision tasks such as virtual assembly or surgical simulation, where reliable force feedback is paramount. They compete with and complement gloves like the TouchDIVER Pro, which offer superior finger-level immersion for tasks like virtual pottery or piano playing but may sacrifice some portability and simplicity. Ultimately, they serve different needs: controllers often prioritize robustness and reliability for enterprise use, while vests and gloves enhance emotional presence in gaming or specialized training (source), (source), (source). This synergy is a driving force in advancing the broader field of virtual reality tech.

Integrating Haptics into the Fabric of Virtual Reality Tech
Haptic VR controllers innovation does not exist in a vacuum. It is both a driver and a beneficiary of progress across the entire spectrum of virtual reality tech. Advances in high-resolution headset displays, low-latency inside-out tracking, and sophisticated software APIs are essential for synchronizing tactile cues with visual and auditory stimuli (source), (source). For a deeper look at the headsets that pair with these controllers, explore our guide to the Best VR Headsets for Gaming in 2024. Also, see how platforms like the Meta Quest 3 are pioneering this integrated space.
The applications stretch far beyond the gaming sphere:
- Surgical Simulation: Devices like HaptX gloves provide surgeons-in-training with realistic force feedback when practicing delicate procedures, improving skill transfer and patient safety.
- Physical Therapy: For stroke recovery, haptic systems offer real-time motor feedback, helping patients relearn movements by “feeling” correct motion paths.
- Industrial Prototyping: Designers can “feel” virtual parts and assemblies, testing ergonomics and fit before a physical prototype is ever built.
- Automotive Ergonomics: Car manufacturers use haptic feedback to simulate button presses and control feel in virtual cockpit models (source), (source), (source).

Of course, challenges remain. Latency—the delay between action and tactile response—can break immersion, while high costs have limited widespread adoption. However, these are being mitigated through more scalable actuator designs and predictive software algorithms that anticipate user movements (source). These solutions are paving the way for an even more immersive future.

The Future of Feeling: What’s Next for Haptic VR
The synergy of haptic VR controllers innovation and force feedback VR gaming is achieving what was once science fiction: true sensory immersion by bridging the gap between sight and touch. This is demonstrated by the coordinated dance of gloves, vests, and controllers—a suite of immersive input devices that is revolutionizing virtual reality tech (source), (source), (source). This evolution is part of broader Mind-Blowing VR Gaming Innovations and is transforming entertainment as explored in How VR is Changing Gaming and Entertainment in 2025.

Looking ahead, the horizon is buzzing with potential:
- Neuro-Haptics: Research into direct neural stimulation could bypass physical actuators entirely, creating tactile sensations perceived directly by the brain.
- Full-Hand Fidelity: Next-gen gloves aim to simulate not just pressure and texture, but precise temperature gradients, from the warmth of a virtual sunbeam to the chill of ice.
- Wireless Full-Body Rigs: The pursuit of untethered, lightweight systems will make high-fidelity full-body haptics more accessible for home use (source), (source).

The path forward is clear: we encourage you to explore current haptic VR controllers innovation in your own setups and stay tuned for the next wave of virtual reality tech. Whether for gaming, professional training, or healthcare, haptic VR controllers stand as the cornerstone for building truly immersive experiences that we can not only see but profoundly feel (source), (source). To complete your immersive setup, check out our roundup of Top Gaming Accessories.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between haptic feedback and force feedback in VR?
Haptic feedback is a broad term for any tactile feedback technology, including simple vibrations. Force feedback is a specific, advanced subset of haptics that simulates physical forces like weight, tension, and resistance. While all force feedback is haptic, not all haptic feedback provides true force simulation.
Are haptic VR controllers compatible with all VR headsets?
Compatibility varies. Many high-end haptic controllers and gloves are designed for PC-powered VR systems (like SteamVR) and require specific software integration. Some, like the PS5’s DualSense, are designed for their specific console ecosystem. Always check manufacturer specifications for compatible headsets and platforms.
What are the main challenges holding back widespread adoption of advanced haptics?
The primary challenges are cost and complexity. High-fidelity haptic devices can be expensive, and creating compelling, well-integrated haptic content requires additional development work. Latency is also a critical technical hurdle, as any delay between action and feeling can disrupt immersion.
Can haptic technology be used for purposes other than entertainment?
Absolutely. As discussed, haptic technology has serious applications in medicine (surgical training, rehabilitation), industry (virtual prototyping, remote operation of machinery), education (interactive learning models), and more. The ability to provide realistic touch feedback is valuable in any field where physical interaction is important.
What should I look for when choosing a haptic VR controller or glove?
Consider your primary use case. For gaming, look at supported titles and the type of feedback (rumble vs. adaptive triggers vs. finger tracking). For professional simulation, prioritize fidelity, reliability, and software support. Key specs include degrees of freedom (DOF), feedback type (vibration, force, thermal), latency, and, of course, compatibility with your existing VR system.