Intel Gaudi 3 AI Accelerator Specs: The Enterprise Inference Powerhouse
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- The Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator delivers a 4x AI compute performance leap over its predecessor, specifically for BF16 operations critical to LLMs.
- With 128 GB of HBM2e memory and 3.7 TB/s of bandwidth, it supports larger, more complex AI models for both training and enterprise inference.
- Its open, Ethernet-based networking (800 GbE) eliminates proprietary lock-in, enabling scalable, cost-effective clusters using standard data center infrastructure.
- Dual form factors (OAM and PCIe) and deep software support provide unmatched deployment flexibility for virtualized, containerized, and bare-metal AI cloud deployment strategies.
- For organizations planning their AI cloud deployment 2026 roadmap, Gaudi 3 represents a future-proof platform that balances raw power with operational pragmatism.
Table of contents
- What is Intel Gaudi 3? Purpose-Built AI Hardware for Modern Workloads
- Core Technical Specifications: Deep Dive into Gaudi 3 Architecture
- Compute Architecture
- Memory Configuration
- Networking and Host Interface
- Power and Media Processing
- Real-World Performance Advantages: From Specs to Impact
- Compute Performance in Practice
- Memory Efficiency & Model Support
- Network Scalability & Deployment Efficiency
- Deployment Flexibility
- Enterprise Inference Chips: How Gaudi 3 Fits the Competitive Landscape
- Gaudi 3’s Competitive Positioning
- Primary Use Cases for Enterprise Inference
- Deployment Model Flexibility
- AI Cloud Deployment 2026: Strategic Roadmap and Enterprise Access
- Open Ecosystem Strategy
- Virtualization and Containerization Support
- Scalability and Growth Pathways
- Software Maturity and Day-Zero Readiness
- What Gaudi 3 Means for Your AI Compute Infrastructure Planning
- Performance-Per-Dollar Value Proposition
- Operational Integration and Minimal Disruption
- Future-Proofing for 2026 and Beyond
- Competitive Assessment Framework
- Frequently Asked Questions
In the race to operationalize artificial intelligence, enterprise infrastructure decisions are becoming critical competitive differentiators. The choice of AI acceleration hardware will define an organization’s capabilities, costs, and agility for years to come. At the heart of this decision is understanding the raw potential and practical implications of specifications like those of the Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator. This deep dive goes beyond the marketing sheets to analyze what these specs mean for your server performance boost, your strategy for enterprise inference chips, and your roadmap for AI cloud deployment 2026.

What is Intel Gaudi 3? Purpose-Built AI Hardware for Modern Workloads
Intel Gaudi 3 is not a general-purpose processor; it is a purpose-built AI accelerator architected from the ground up for the crushing computational demands of generative AI and large language models (LLMs). It represents Intel’s strategic commitment to providing an open, scalable alternative in a market hungry for choice. Built on a 5nm process, Gaudi 3 combines dense compute, massive high-bandwidth memory, and a standards-based networking approach to deliver a platform that supports both training and inference across virtualized, containerized, and bare-metal environments. This flexibility is key for enterprises looking to consolidate AI workloads without creating new infrastructure silos. Partners like Dell are already integrating Gaudi 3 into enterprise solutions, signaling its readiness for mainstream deployment.

Core Technical Specifications: Deep Dive into Gaudi 3 Architecture
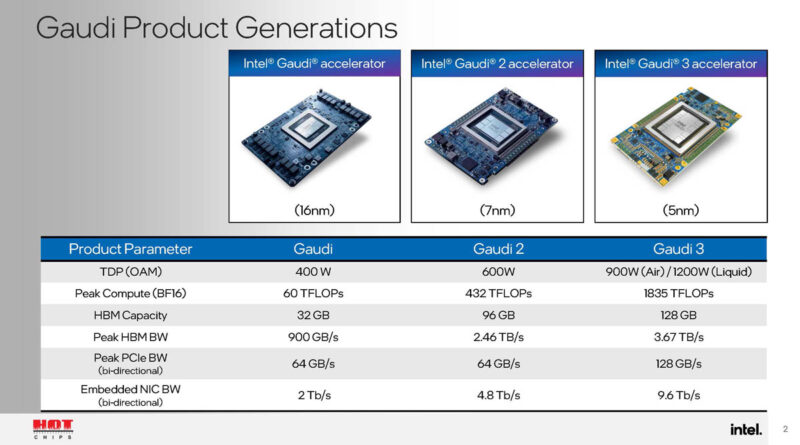
The Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator specs tell a story of generational leap. It is offered in two primary form factors: an OCP OAM 2.0 mezzanine card for high-density deployments and a PCIe Gen5 add-in card for integration into existing server architectures, providing immediate deployment flexibility.

Compute Architecture
At its core, Gaudi 3 houses 64 Tensor Processor Cores (TPCs), each equipped with 8 Matrix Multiplication Engines (MMEs). This configuration delivers a staggering 1.8 PFlops of FP8 and BF16 compute performance. To put that in perspective, PFlops (Peta-Floating Point Operations Per Second) measure raw computational speed; a higher number means the accelerator can process the complex math of AI models faster. Compared to Gaudi 2, this represents a 2.7x increase in TPCs and a 4x increase in MMEs. The practical translation? A 4x AI compute performance for BF16 operations, which is Intel’s optimized precision format for LLM inference and training, directly enabling a significant server performance boost for AI workloads.
Memory Configuration
AI model size and complexity are exploding. Gaudi 3 answers with a formidable memory subsystem:
- HBM Capacity: 128 GB HBM2e (vs. 96 GB in Gaudi 2)
- HBM Bandwidth: 3.7 TB/s (vs. 2.46 TB/s)
- On-die SRAM: 96 MB (vs. 48 MB)
- SRAM Bandwidth: 12.8 TB/s read/write (vs. 6.4 TB/s)
This 33% capacity increase, coupled with 1.5x higher memory bandwidth, is not just about bigger numbers. It allows for larger batch sizes, supports more expansive model parameters, and reduces the latency caused by fetching data from slower memory. For LLMs and computer vision models, this means the entire model can reside in ultra-fast HBM, drastically speeding up processing. This memory headroom is critical for future-proofing against increasingly large AI models.
Networking and Host Interface
Scale is where Gaudi 3 truly differentiates itself. It features a massive 1200 GB/s of bidirectional networking bandwidth. Crucially, it integrates 24x 800 GbE MACs (supporting 6x OSFP ports). This commitment to standard Ethernet eliminates the need for expensive, proprietary interconnects, enabling Ethernet-based scaling across nodes using existing data center networking gear. The host interface is PCIe Gen5 x16, offering 128 GB/s of peak bandwidth—double that of Gaudi 2’s PCIe Gen4. This open approach reduces total cost of ownership and avoids vendor lock-in, a major consideration for enterprises building large-scale AI clusters.

Power and Media Processing
Gaudi 3 is built for real-world data centers. It incorporates 14 media decoders for multimedia processing tasks. Its Thermal Design Power (TDP) is rated at 900W for the OAM card and 600W for the PCIe variant. These ratings are designed to fit within standard air-cooled server infrastructure, avoiding the need for exotic and costly liquid cooling solutions that can derail deployment plans. This balance of power and thermal efficiency is a key part of its practical enterprise appeal.
Real-World Performance Advantages: From Specs to Impact
Raw specifications are meaningless without context. Here’s how the Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator specs translate into tangible benefits, shaping how AI is changing the world of enterprise IT.

Compute Performance in Practice
The 4x compute improvement for BF16 workloads means enterprises can achieve faster time-to-insight for training runs and lower latency for real-time inference. This translates to the ability to serve more concurrent users from a generative AI application or to run more simultaneous experiments on the same hardware footprint, directly delivering that promised server performance boost.
Memory Efficiency & Model Support
The expanded 128 GB HBM capacity is a game-changer for model support. It allows entire large models—or significant chunks of massive models—to be loaded into the accelerator’s ultra-fast memory. This avoids the performance-killing bottleneck of swapping data to slower system RAM, slashing inference latency and training times for state-of-the-art models. This capability is essential for cutting-edge AI research and deployment.
Network Scalability & Deployment Efficiency
The 2x networking bandwidth and standard Ethernet focus mean enterprises can build cost-effective, massive AI clusters. You can start with a single Gaudi 3 accelerator for proof-of-concept and scale linearly to hundreds of nodes using the same Ethernet switches that power the rest of your data center. This eliminates a major financial and operational barrier to hyperscale AI.
Deployment Flexibility
Gaudi 3 is designed for the modern hybrid cloud. It delivers near-bare-metal performance within virtualized environments like VMware Cloud Foundation and is fully manageable in containerized Kubernetes clusters. This allows IT teams to consolidate expensive AI workloads onto shared, efficiently managed infrastructure rather than managing isolated, underutilized hardware silos.
Enterprise Inference Chips: How Gaudi 3 Fits the Competitive Landscape
As businesses move from AI experimentation to production, the demand for efficient, scalable enterprise inference chips skyrockets. Gaudi 3 is positioned squarely to meet this demand, offering a compelling blend of performance, openness, and integration that directly supports business transformation.
Gaudi 3’s Competitive Positioning
Unlike some proprietary alternatives, Gaudi 3 champions an open ecosystem. It integrates via standard PCIe Gen5 and uses Ethernet for scaling, preventing lock-in to a single vendor’s stack. Its support for mainstream AI frameworks and precision formats (FP8, BF16) means development teams can use familiar tools. This makes it a strategic choice for enterprises valuing flexibility and long-term optionality.

Primary Use Cases for Enterprise Inference
- Large-Scale AI Training: Fine-tuning massive foundation models (like LLMs for specific industries) benefits immensely from the 128 GB HBM capacity and high compute throughput, enabling faster iteration and innovation. This is where the raw specs turn into competitive advantage.
- Generative AI Inference at Scale: Deploying real-time chatbots, content creation tools, or image generation services requires consistent, low-latency performance. Gaudi 3’s architecture is built to handle these demanding, variable workloads efficiently.
- Cost-Effective Scaling: Organizations can scale AI capabilities from a single server to a full cluster while maintaining a favorable price-performance ratio, protecting investments as needs grow. This scalability is a core tenant of modern AI infrastructure.
Deployment Model Flexibility
The dual form factor strategy serves distinct needs. The OAM mezzanine card enables ultra-high-density deployments (up to 8 accelerators per baseboard), ideal for new, hyperscale-optimized infrastructure. The PCIe add-in card allows enterprises to drop Gaudi 3 into existing dual-slot servers, modernizing current infrastructure for AI with minimal disruption and providing an immediate server performance boost.
AI Cloud Deployment 2026: Strategic Roadmap and Enterprise Access
Planning your AI cloud deployment 2026 strategy requires a platform that is both powerful today and adaptable tomorrow. Gaudi 3’s architecture is built for this horizon.
Open Ecosystem Strategy
Intel’s bet on Ethernet (RoCE) over proprietary interconnects is a long-term play. It reduces deployment friction, ensures multi-vendor compatibility, and future-proofs clusters against single-supplier roadmaps. For 2026 planning, this openness is insurance against technological dead-ends.

Virtualization and Containerization Support
Native integration with VMware and Kubernetes means AI workloads can be managed within an enterprise’s existing operational framework. As AI becomes embedded in every application, this ability to manage AI infrastructure with the same tools as the rest of the IT estate drastically reduces operational complexity and cost.

Scalability and Growth Pathways
With support for clusters from 1 to 100+ nodes linked by its 800GbE ports, Gaudi 3 accommodates every stage of an AI journey. Enterprises can start with a focused pilot and expand seamlessly to enterprise-wide deployment without rearchitecting their core AI infrastructure.
Software Maturity and Day-Zero Readiness
Gaudi 3 launches with optimized software support for leading AI models and frameworks. Support for FP8/BF16 precision means development teams spend less time on low-level performance tuning and more time building applications, accelerating the path from infrastructure investment to business value. This software readiness is a critical differentiator.
What Gaudi 3 Means for Your AI Compute Infrastructure Planning
Performance-Per-Dollar Value Proposition
The synthesis of 4x compute gains, flexible form factors, and open networking creates a compelling value argument. Better price-performance means running more AI workloads within a fixed budget or achieving results faster, directly impacting the bottom line. This is especially true in virtualized environments where consolidation amplifies savings.

Operational Integration and Minimal Disruption
Gaudi 3 is designed for integration, not disruption. Standard interfaces and deep software support mean IT teams can manage it with existing skills and tools. This reduces training overhead, accelerates deployment timelines, and lowers the overall risk of adopting new AI acceleration technology.
Future-Proofing for 2026 and Beyond
The 128 GB HBM and massive bandwidth provide headroom for the ever-growing size of AI models. The commitment to open Ethernet networking protects against interconnect lock-in as clusters scale. Gaudi 3 is a platform built not just for today’s models, but for the more demanding models of 2026 and 2027.
Competitive Assessment Framework
For organizations evaluating their AI infrastructure today, Gaudi 3 demands a seat at the table. It is particularly relevant for enterprises with existing Intel or VMware relationships, those invested in Ethernet-based data centers, or any organization strategically seeking to avoid single-vendor dependency in their AI stack. As with any major decision, a thorough competitive assessment is crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary advantage of Intel Gaudi 3 over Gaudi 2?
The primary advantage is a 4x increase in AI compute performance for BF16 workloads, coupled with a 33% increase in HBM memory (128 GB) and a shift to standard 800 Gb Ethernet for scaling. This combination delivers significantly faster training and inference for large models while enabling more cost-effective, open cluster designs.
Is Intel Gaudi 3 only for AI training, or is it good for inference too?
Intel Gaudi 3 is architected as a unified platform for both training and inference. Its high memory bandwidth, large HBM capacity, and support for efficient precision formats like FP8 and BF16 make it exceptionally capable for demanding enterprise inference scenarios, such as serving large language models in production.
Why is Gaudi 3’s use of standard Ethernet important?
Using standard Ethernet (800 GbE) instead of a proprietary interconnect is crucial for reducing cost and avoiding vendor lock-in. It allows enterprises to build and scale AI clusters using their existing data center networking switches and expertise, rather than investing in expensive, single-vendor networking hardware.
Can I deploy Intel Gaudi 3 in a virtualized environment?
Yes. Gaudi 3 has deep integration with VMware Cloud Foundation, allowing it to deliver near-bare-metal performance in virtual machines. This enables consolidation of AI and traditional workloads on shared infrastructure, improving utilization and simplifying management.
What should an enterprise consider when choosing between the OAM and PCIe form factors of Gaudi 3?
Choose the OAM mezzanine card for new, green-field deployments where maximum accelerator density per server is the goal. Choose the PCIe add-in card to modernize existing server fleets with minimal disruption, leveraging standard dual-slot server designs. The PCIe variant also has a lower TDP (600W vs. 900W), which can be a factor in power-constrained data centers.






