SpaceX Starlink Phone Leak: Debunking Myths and Revealing the Real Satellite Connectivity Plan
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Key Takeaways
- The spacex starlink phone leak stems from misinterpretations and unsubstantiated rumors, not an official product announcement.
- SpaceX is not building a branded smartphone but embedding Starlink connectivity into existing phones via custom chipsets, as confirmed by President Gwynne Shotwell.
- Direct-to-Cell satellites are already operational, enabling standard smartphones to send texts via Starlink without cellular infrastructure.
- This technology turns phones into low orbit connectivity devices, leveraging low Earth orbit satellites for global coverage with lower latency.
- The vision is to create a global communication handset that works seamlessly worldwide, aided by SpaceX’s recent spectrum acquisition.
- Testing for mobile connectivity is set for 2026, with widespread availability expected in the coming years.
Table of contents
Introduction: The Buzz and the Reality
Rumors about a spacex starlink phone leak have set the tech world abuzz, suggesting that Elon Musk’s companies might launch a dedicated Starlink-branded smartphone. This speculation isn’t new—it echoes years of unsubstantiated “Tesla phone” rumors that have never been confirmed by official announcements or credible leaks.
But here’s the reality: SpaceX isn’t developing a branded smartphone to compete with Apple or Samsung. Instead, as confirmed by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell at a recent space conference, the company is pursuing a different strategy: embedding Starlink satellite connectivity directly into existing phones from all manufacturers through custom chipsets. This approach bypasses the need for a dedicated device and aims to revolutionize mobile connectivity from the inside out.

The purpose of this blog is to dissect the spacex starlink phone leak, separate fact from speculation, and explain SpaceX’s actual strategy for satellite-connected phones. We’ll address how this technology enables low orbit connectivity device features in everyday handsets, turning them into potential global communication handsets with ubiquitous coverage.
So, what does this mean for the future of mobile connectivity? Let’s dive in and explore the exciting details ahead.
Source of the SpaceX Starlink Phone Leak
The spacex starlink phone leak primarily stems from misinterpretations of SpaceX’s technical initiatives and confusion with unsubstantiated “Tesla phone” expectations that have circulated for years. Many assume that because Tesla innovates in electric vehicles, a SpaceX phone must be next—but that’s not the case.
SpaceX is actually partnering with microchip manufacturers to create custom silicon that enables direct satellite-to-cell communication in standard phones from any brand. This means your current smartphone could soon connect to Starlink satellites without any hardware modifications, aside from the embedded chipset. As Shotwell emphasized, this strategy avoids the need for a separate dedicated handset.
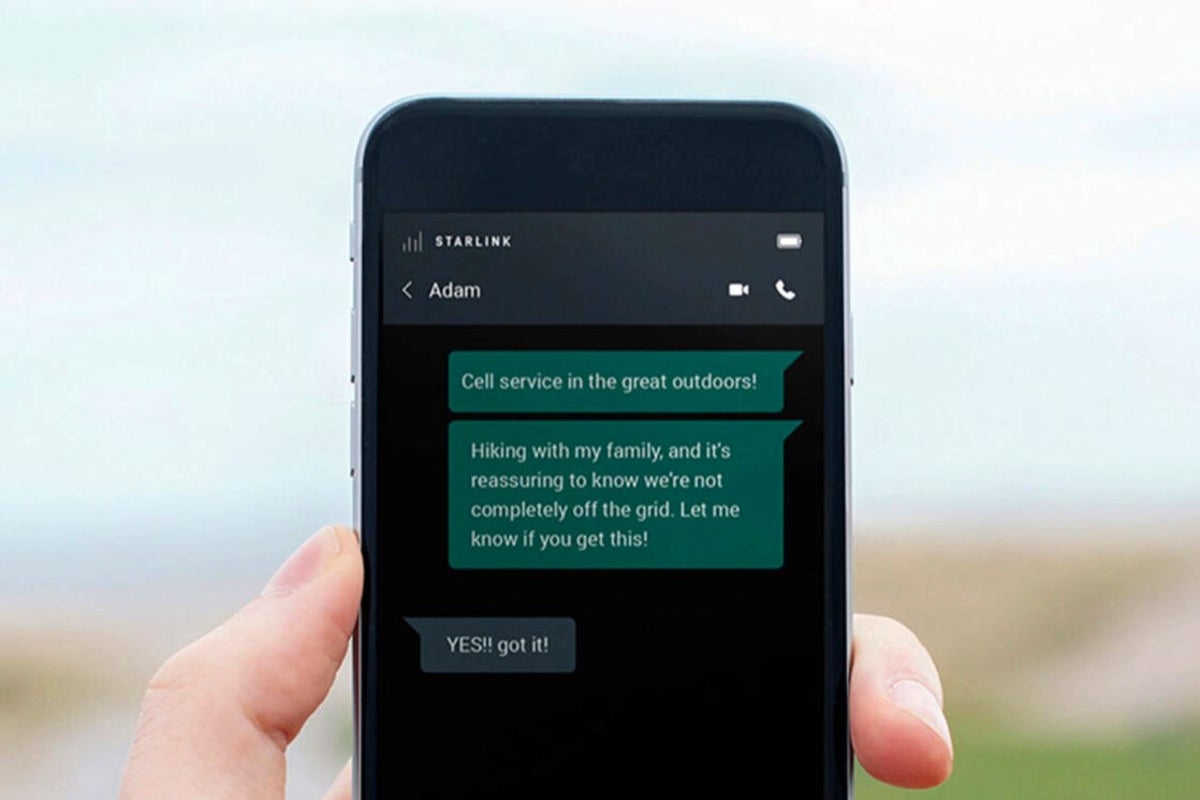
It’s crucial to differentiate confirmed projects from speculation. SpaceX has already launched Direct to Cell satellites in 2024, allowing unmodified standard smartphones to send text messages directly to Starlink satellites without relying on traditional cellular infrastructure. This is operational and proven, unlike any unannounced dedicated phone.
This chipset technology turns existing phones into low orbit connectivity devices by integrating with low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. When analyzing the credibility of the leak, it’s important to note its low reliability. SpaceX’s focus is on infrastructure-level integration, not consumer device launches, as reiterated by Shotwell’s statements.

This shifts our focus to the core technology making it all possible.
What is a Low Orbit Connectivity Device?
A low orbit connectivity device refers to a phone that leverages Starlink satellites orbiting at approximately 320 kilometers altitude, compared to traditional cell towers at 2-3 kilometers. This enables direct-to-satellite communication that bypasses terrestrial infrastructure entirely, as explained in technical overviews.
Here’s how it works technically: When your phone is out of cellular range, the custom chipset switches to connect with overhead LEO satellites for voice, text, and data. The satellite constellation provides redundancy, ensuring consistent coverage.
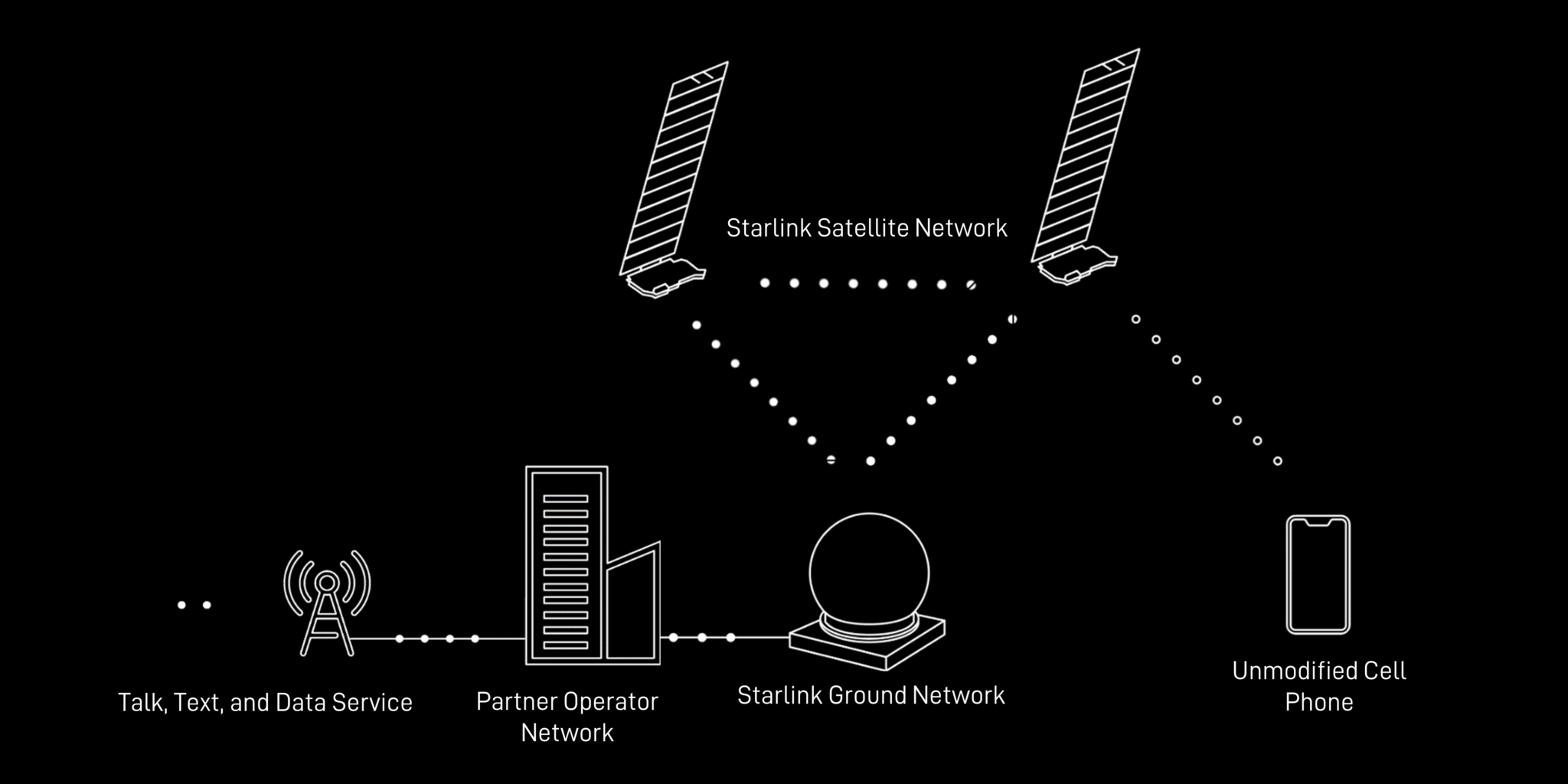
Contrast this with traditional cellular networks, which rely on ground-based towers, and existing satellite messengers like Iridium or Globalstar, which use higher orbits and suffer from higher latency. Starlink offers lower latency due to proximity and global coverage without dead zones.
Key advantages of low orbit connectivity devices include:
- Global coverage in remote areas: From deserts to oceans, stay connected wherever you are.
- Lower latency than geostationary satellites: Faster response times for real-time communication.
- Redundancy via thousands of satellites: The massive constellation ensures reliability.
- Elimination of dead zones: Say goodbye to spotty coverage in rural or rugged terrain.

However, there are challenges to address:
- Signal penetration issues: Buildings and obstacles can block satellite signals, affecting indoor performance.
- Higher power draw: Satellite links consume more battery, which is why optimizing power efficiency is crucial, as discussed in battery life analyses.
- Regulatory spectrum needs: Securing frequency bands for satellite communication is complex.
- Device size constraints: Antennas for satellite connectivity require space, which is why SpaceX opts for chipset embedding in standard phones rather than new hardware.
This foundation paves the way for rumored global communication handsets powered by low orbit connectivity. Think of LEO satellites as a “sky full of cell towers”—a network that makes global communication seamless and accessible.
The Vision of a Global Communication Handset
The vision of a global communication handset is a standard smartphone upgraded via Starlink chipsets to provide seamless worldwide connectivity without carrier-specific roaming limits. It’s not about a new device, but enhancing what we already have.
SpaceX’s business shift is significant. With a recent $17 billion acquisition of wireless spectrum from Ecostar Corp, SpaceX can operate independently as a mobile service provider, rather than just partnering with carriers like T-Mobile in the US or Rogers in Canada. This move, detailed in reports, opens new possibilities.
SpaceX’s strategy is to act as a “wholesale capacity provider” to telcos, eliminating dead zones rather than competing directly. Shotwell notes that spectrum ownership enables new discussions with partners, fostering collaboration instead of confrontation.
Practical use cases for global communication handsets include:
- Remote work in off-grid areas: Professionals can work from anywhere without connectivity worries.
- Emergency services and disaster response: Reliable communication during crises saves lives.
- Maritime and aviation links: Stay connected on ships and planes over oceans and remote regions.
- International travel without restrictions: No more hunting for local SIM cards or paying exorbitant roaming fees.
- Bridging digital divides in underserved regions: Bring internet access to communities lacking infrastructure, as highlighted in accessory guides that support connectivity.

Addressing key questions: This technology won’t fully replace smartphones but augment them. Plans will likely bundle satellite access into carrier subscriptions or as add-ons, with pricing and integration details pending telco deals. This vision naturally leads to the next step: starlink mobile test 2026.
Imagine hiking the Himalayas with uninterrupted video calls, or sailing across the Pacific while streaming data—this is the future SpaceX is building.
Roadmap to Connectivity: Starlink Mobile Test 2026
The roadmap includes starlink mobile test 2026, a pivotal milestone. SpaceX has outlined public plans: over the next two years, new direct-to-device satellites will be launched, with mobile phone testing starting in late 2026. Additionally, in 2026, operations will involve lowering approximately 4,400 satellites from 550km to 480km altitude for safety, as reported by Euronews.
What does the 2026 testing entail? It will involve a limited beta with Starlink-chip-equipped phones, focusing on:
- Signal reliability: Ensuring consistent connections in various environments.
- Data speeds: Testing bandwidth for voice, text, and data transmission.
- Battery use in satellite mode: Optimizing power consumption for practical daily use.
- Indoor performance: Addressing challenges with signal penetration in buildings.

Testing will be conducted in select regions with partners, paving the way for broader rollout.

Competitors in this space include Apple’s Emergency SOS, which allows limited emergency messaging on iPhone 14 and later models, and AST SpaceMobile, which has broader aims but an uncertain timeline. SpaceX leads with an operational constellation and spectrum ownership, giving it a significant advantage.
Projecting the timeline: Widespread availability is likely in 2027 and beyond, after testing, regulatory approvals, and partnership finalizations. Initially, it will focus on covering gaps in existing networks.

This roadmap debunks the spacex starlink phone leak once and for all—it’s all about chipset integration, not a new phone. Visualizing this with a timeline graphic would enhance engagement, showing key milestones from 2024 to 2027.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is SpaceX launching a Starlink-branded smartphone?
No, SpaceX is not developing a dedicated smartphone. Instead, they are focusing on embedding Starlink connectivity into existing phones via custom chipsets, as confirmed by President Gwynne Shotwell.

How does low orbit connectivity work on smartphones?
Low orbit connectivity uses chipsets to connect phones directly to Starlink satellites in low Earth orbit. When out of cellular range, the phone switches to satellite mode for voice, text, and data, leveraging the satellite constellation for global coverage.
What are the advantages of Starlink satellite phones over traditional cellular?
Advantages include global coverage without dead zones, lower latency compared to geostationary satellites, redundancy from thousands of satellites, and the ability to work in remote areas where cellular infrastructure is absent.
When will Starlink mobile connectivity be available to consumers?
Testing is set to begin in 2026, with widespread availability expected in 2027 or later. Initial rollout will likely focus on coverage gaps, with integration into carrier plans.
Will Starlink connectivity replace my current smartphone?
No, it will augment your existing phone. The goal is to add satellite capabilities to standard smartphones, not replace them. You’ll likely subscribe to satellite access through your carrier.
How much will Starlink satellite service cost?
Pricing details are not yet announced. It will likely be bundled into carrier subscriptions or offered as an add-on service, similar to current satellite messaging plans.





