How to Do Keyword Research: A Beginner’s Guide for SEO Success
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Keyword research is the non-negotiable foundation of any successful SEO strategy, driving targeted organic traffic to your site (source).
- Understanding search intent—the “why” behind a search—is more critical than the keyword itself for creating relevant content.
- Long-tail keywords (specific, longer phrases) are your best bet as a beginner, offering lower competition and higher conversion potential.
- A sustainable strategy involves building topic clusters—a pillar page supported by in-depth cluster content—to boost topical authority.
- Place your primary keyword strategically in key areas like the title, H1, and meta description, but always prioritize a natural, user-friendly reading experience.

Table of contents
- How to Do Keyword Research: A Beginner’s Guide for SEO Success
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction: The SEO Foundation You Can’t Ignore
- Why Search Intent and Keyword Types Matter for Your SEO Strategy
- The Complete Keyword Research Process: From Brainstorming to Analysis
- Creating a Sustainable Keyword Strategy with Topic Clusters
- Where and How to Place Keywords for Maximum SEO Impact
- Keyword Research Tools and Measuring Your Success
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction: The SEO Foundation You Can’t Ignore
Imagine building a house on sand. No matter how beautiful the design, it won’t stand. The same is true for your website’s content without proper keyword research. It is the essential bedrock of SEO, determining whether your pages attract a steady stream of interested visitors or get lost in the digital void (source).

This guide is your blueprint. If you’re a beginner wondering how to start keyword research to grow your site, you’re in the right place. We’ll walk through five core areas: understanding search intent and keyword types, a practical step-by-step process, building a long-term strategy, nailing keyword placement, and using the right tools to measure your wins.
Why Search Intent and Keyword Types Matter for Your SEO Strategy
Before you type a single word into a tool, you need to understand the “why”. Search intent is the fundamental goal a user has when they type a query into Google. Are they looking to learn, to buy, or to find a specific site? Matching your content to this intent is the golden rule of modern SEO (source). Get it wrong, and even perfect keyword research won’t help you rank. For a deeper dive, see our guide on understanding search intent.
The Main Types of Search Intent:
- Informational: Seeking knowledge or an answer. (e.g., “what is SEO”, “how to bake sourdough”).
- Commercial: Researching before a potential purchase. (e.g., “best running shoes 2024”, “HubSpot vs. Salesforce reviews”).
- Navigational: Looking for a specific website or page. (e.g., “Facebook login”, “Penbrief blog”).

Next, let’s talk about the keywords themselves. They generally fall into two camps:
- Head Terms (Short-Tail): Broad, high-volume, and fiercely competitive. Think “marketing” or “shoes.” Ranking for these as a new site is like trying to win the lottery.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Longer, more specific phrases with lower search volume but far less competition and higher conversion intent. For example, “how to do keyword research for a local bakery” (source).
These long-tail phrases are your low-hanging fruit. They directly connect to a user’s specific problem and signal clear intent. Targeting them builds early momentum and qualified traffic. Choosing the right mix of keyword types based on intent directly determines if you attract curious browsers or ready-to-buy customers. Learn more about different keyword types and their uses.
The Complete Keyword Research Process: From Brainstorming to Analysis
Now, let’s roll up our sleeves. Effective keyword research isn’t a one-time event; it’s a repeatable cycle. Follow these five steps to build a powerful list of SEO keywords.

Step 1: Brainstorming & Topic Generation
Start by thinking like your audience. What questions do they have? What problems are they trying to solve? Jot down every topic related to your business, product, or niche. Use your own expertise, customer support queries, and forums like Reddit to seed your initial list.
Step 2: Using Tools for Volume & Competition Analysis
Take your brainstormed topics and feed them into tools to get data. Monthly Search Volume (MSV) tells you how often a keyword is searched. Competition level indicates how hard it will be to rank.
- Free Tools: Google Keyword Planner, Google Trends, and your own Google Search Console data are excellent starting points.
- Paid Tools: SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz offer deeper insights like keyword difficulty scores and precise competitor data.

Check out our curated list of the best keyword research tools for a full breakdown.
Step 3: Identifying “Striking Distance” Keywords
Be realistic. A keyword with 10,000 monthly searches might be impossible for your new site. A “striking distance” keyword is one where your domain authority gives you a realistic shot at ranking on the first page. Look for phrases with decent volume but lower competition—often those long-tail gems (source).
Step 4: Competitive Keyword Gap Analysis
Why guess what works when you can see what’s working for your competitors? A keyword gap analysis reveals the specific keywords your competitors rank for that you don’t. This is a goldmine for uncovering missed opportunities in your niche (source).

Step 5: Incorporating Search Listening & Trend Identification
SEO isn’t static. Use tools like Google Trends and social listening to catch rising queries and shifts in how your audience talks about topics. This helps you create timely, relevant content that captures emerging traffic.
For a detailed walkthrough of this entire process, visit our comprehensive guide on how to do keyword research.
Creating a Sustainable Keyword Strategy with Topic Clusters
A list of keywords is just a list. A keyword strategy is a plan to dominate your corner of the internet. The most effective method today is the topic cluster model.
What Are Topic Clusters?
Imagine a solar system. At the center is a pillar page—a comprehensive, ultimate guide on a core topic (e.g., “The Complete Guide to Content Marketing”). Orbiting it are cluster pages—detailed articles on specific subtopics (e.g., “How to Write a Blog Post,” “Social Media Content Calendar Template”). All these pages are interlinked, signaling to Google that your site is a definitive authority on that subject (source).
The One Keyword Per Page Principle
Each piece of content should have one primary keyword or focus keyword. This prevents your own pages from competing against each other (keyword cannibalization) and makes it crystal clear to search engines what each page is about.
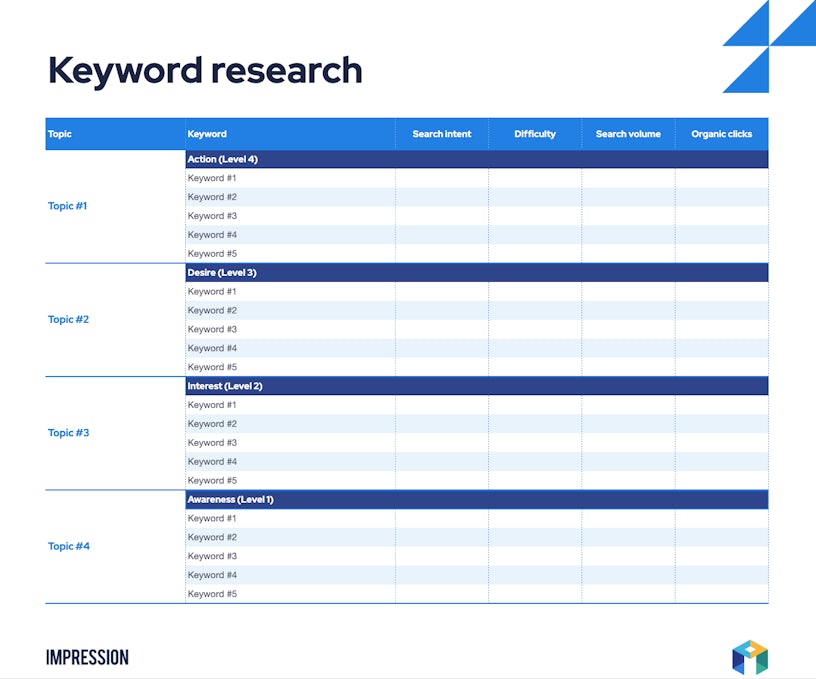
Grouping Keywords & Mapping to the Buyer Journey
Organize your keyword list by theme and intent. Then, map them to where a customer is in their journey:
- Awareness: Informational keywords. (User problem: “What is email marketing?”)
- Consideration: Commercial/investigative keywords. (User problem: “Best email marketing software for small business”)
- Decision: Transactional keywords. (User problem: “Mailchimp free trial”)
By structuring content this way, you guide visitors from initial curiosity to confident conversion. For more on structuring your approach, see our SEO keyword research best practices.
Where and How to Place Keywords for Maximum SEO Impact
You’ve done the research and built your strategy. Now, let’s optimize. Smart keyword placement helps search engines understand your content, but never at the expense of readability.
1. Page Title & H1 Tag
Your primary keyword must be in your page title (the clickable headline in search results, ideally under 60 characters) and your H1 (the main headline on the page). These are the strongest signals of your page’s topic (source).
2. Meta Description
This 155-160 character snippet is your ad copy. Lead with your keyword, use active language, and clearly state the page’s value to improve click-through rates from search results (source).
3. H2 & H3 Subheadings
Use your supporting keywords and related phrases in 2-3 subheadings. This structures your content for easy scanning and reinforces topical relevance (source).
4. Introduction & Body Content
Naturally include your focus keyword in the first 100 words. Sprinkle related terms throughout the body where they fit contextually. The key is a natural flow.
5. Keyword Density & The “Stuffing” Pitfall
Forget old-school percentage rules. Keyword density should be minimal and natural. “Keyword stuffing”—forcing keywords unnaturally—creates a terrible user experience and can trigger search engine penalties. As emphasized in multiple SEO checklists, always write for humans first, and optimization second (source).
Keyword Research Tools and Measuring Your Success
You need the right gear for the job. Here’s a quick overview of essential tools and how to track your progress.
Essential Tools Overview
- Free Suite: Google Search Console (your actual ranking data), Google Keyword Planner (search volume estimates), and Google Trends (interest over time).
- Professional Tools: SEMrush and Ahrefs offer powerful competitive analysis, keyword difficulty scores, and gap analysis features (source).

Tracking Performance
Your dashboard is Google Search Console. Monitor key metrics for your target SEO keywords:
- Impressions: How often your page appeared in search results.
- Clicks: The traffic you earned.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Clicks ÷ Impressions. A low CTR might mean your title/meta description needs work.
- Average Position: Your average ranking for a query.
Modern SEO & AI-Era Considerations
Search is getting smarter. Google now understands synonyms, related concepts (semantic search), and entities (people, places, things). Your keyword strategy should evolve beyond exact-match phrases. Research and include semantically related terms to cover a topic fully and future-proof your content (source).
Continuous Refinement
Keyword research is not a “set it and forget it” task.
Schedule quarterly reviews to analyze what’s working, identify new keyword opportunities, and adapt your strategy based on data. This cycle of research, creation, and analysis is what leads to lasting SEO success.
Frequently Asked Questions

What’s the difference between a primary keyword and a focus keyword?
None—they are the same thing. It’s the main keyword or keyphrase that a specific page is optimized to rank for. It defines the core topic of the content.
How many keywords should I target per blog post?
Stick to one primary keyword per post to maintain clear focus. However, you should naturally include 5-10 semantically related terms and long-tail variations within the content to support the main topic.
Is keyword research still important with voice search and AI?
Absolutely, but the approach evolves. Voice search tends to use longer, conversational phrases (perfect for long-tail keywords). AI-powered search still relies on understanding user intent and topical authority, both of which are built through diligent keyword and topic research.
Can I do effective keyword research for free?
Yes. The free trio of Google Keyword Planner, Google Trends, and Google Search Console provides a powerful foundation for beginners. You can uncover search volume, trends, and see what keywords are already bringing you traffic.
How long does it take to see results from keyword-optimized content?
SEO is a long-term game. For new content targeting low-competition keywords, you might see traction in 1-3 months. For more competitive terms, it can take 6 months to a year or more to achieve top rankings. Consistency is key.



